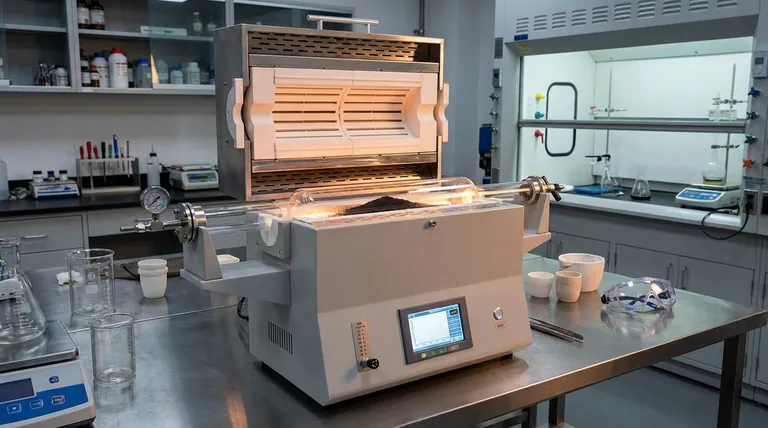
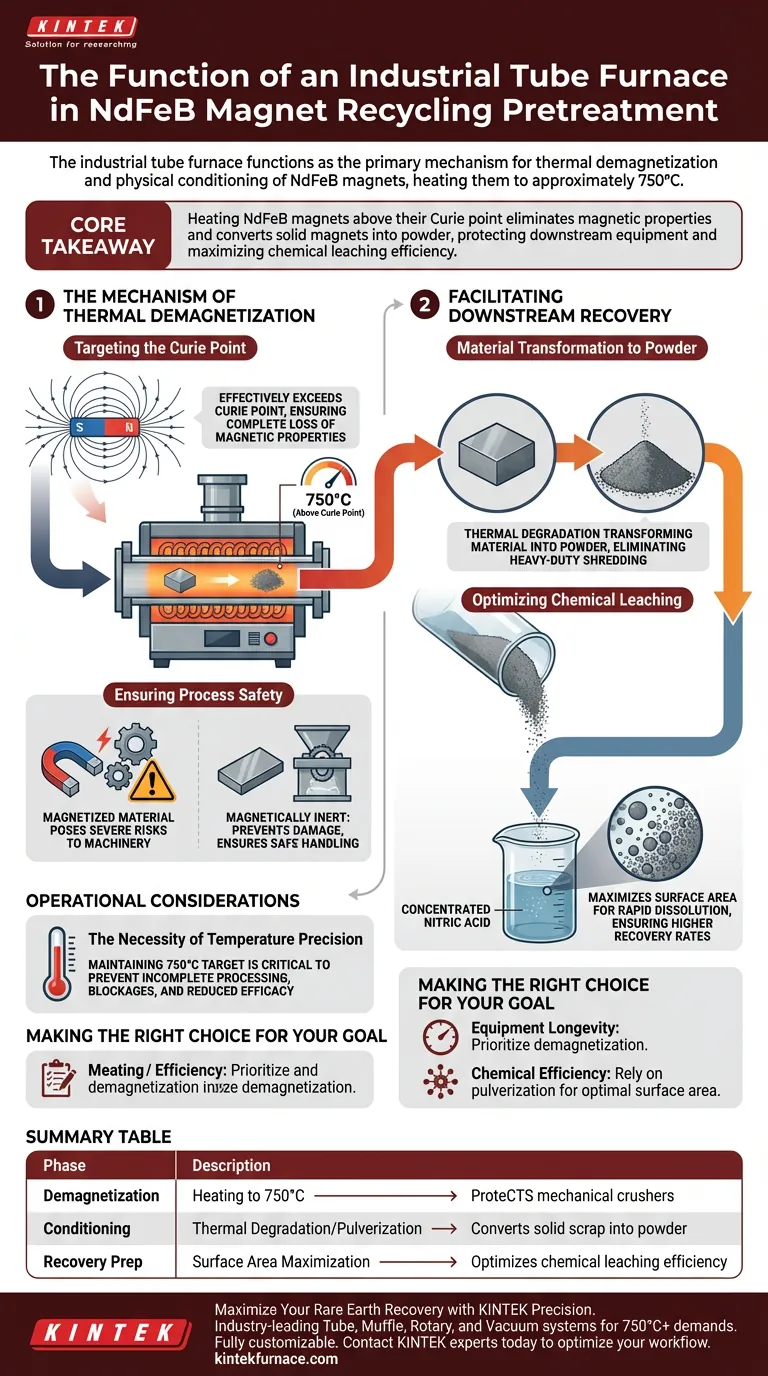
The industrial tube furnace functions as the primary mechanism for thermal demagnetization and physical conditioning in the recycling of NdFeB (Neodymium-Iron-Boron) magnets. By subjecting the magnets to temperatures of approximately 750°C, the furnace neutralizes their magnetic field and structurally degrades the material into a manageable state.
Core Takeaway By heating NdFeB magnets above their Curie point, the tube furnace eliminates magnetic properties and converts solid magnets into powder. This thermal pretreatment is essential for protecting downstream mechanical equipment and maximizing the efficiency of chemical leaching.

The Mechanism of Thermal Demagnetization
Targeting the Curie Point
To strip a permanent magnet of its magnetic field, it must be heated beyond a specific thermal threshold known as the Curie point.
The industrial tube furnace is calibrated to operate at approximately 750°C. This temperature effectively exceeds the Curie point of NdFeB magnets, ensuring the complete loss of magnetic properties.
Ensuring Process Safety
Attempting to crush or process fully magnetized materials poses severe risks to industrial machinery due to magnetic attraction and resistance.
By utilizing the tube furnace for pretreatment, you render the material magnetically inert. This prevents damage to mechanical crushers and ensures safe handling during subsequent stages.
Facilitating Downstream Recovery
Material Transformation to Powder
The function of the tube furnace extends beyond simple demagnetization; it induces a physical transformation of the feedstock.
The high-temperature exposure causes the solid magnets to break down, effectively transforming the material into a powder form. This eliminates the need for heavy-duty shredding of solid blocks.
Optimizing Chemical Leaching
The efficiency of the recycling process relies heavily on how well the material dissolves in chemical reagents.
By converting the magnet into powder, the furnace maximizes the surface area available for reaction. This significantly facilitates the dissolution process in concentrated nitric acid, ensuring higher recovery rates of rare earth elements.
Operational Considerations
The Necessity of Temperature Precision
The effectiveness of this pretreatment phase relies entirely on maintaining the thermal profile.
If the furnace fails to sustain the 750°C target, the material may retain residual magnetism. This incomplete processing can cause blockages in the mechanical crushing line and reduce the efficacy of the acid leaching stage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is Equipment Longevity: Prioritize the demagnetization capability to prevent magnetic forces from damaging your mechanical crushers.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Efficiency: Rely on the furnace's ability to pulverize the material, creating the optimal surface area for rapid nitric acid dissolution.
The industrial tube furnace is the prerequisite step that converts hazardous, solid scrap into a safe, reactive feedstock for rare earth recovery.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Furnace Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Demagnetization | Heating to 750°C (Above Curie Point) | Protects mechanical crushers from magnetic damage |
| Conditioning | Thermal Degradation/Pulverization | Converts solid scrap into high-surface-area powder |
| Recovery Prep | Surface Area Maximization | Optimizes chemical leaching efficiency in nitric acid |
Maximize Your Rare Earth Recovery with KINTEK Precision
Efficiency in NdFeB recycling starts with precise thermal control. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Muffle, Rotary, and Vacuum systems designed to meet the rigorous 750°C+ demands of magnet pretreatment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to your specific lab or industrial volume requirements.
Ready to optimize your recycling workflow?
Contact KINTEK experts today to discover how our advanced thermal solutions can enhance your material processing and protect your downstream equipment.
Visual Guide
References
- Sandeep Bose, Parisa A. Ariya. Neodymium recovery from NdFeB magnets: a sustainable, instantaneous, and cost-effective method. DOI: 10.1039/d3gc03756h
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the methods for treating wastewater using a tube furnace? Explore Specialized Thermal Applications
- How does the use of a tube furnace enhance cellulose-amine materials? Unlock Superior Porosity & Surface Area
- Why is high-purity argon gas essential during the pyrolysis of Cu@Zn-NC in a high-temperature tube furnace?
- What are the key features of a quartz tube furnace? Discover High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- Why use sealed vacuum tubes for perovskite supports? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Thin-Film Synthesis
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in polyimide pyrolysis? Precision Control for Carbon Molecular Sieves
- What are the functions of a quartz tube fixed-bed reactor? Ensure Precision in Catalyst Evaluation
- What is the function of a Quartz Tube Furnace in the dry thermal oxidation of silicon wafers? Enhance Your Oxide Quality



















