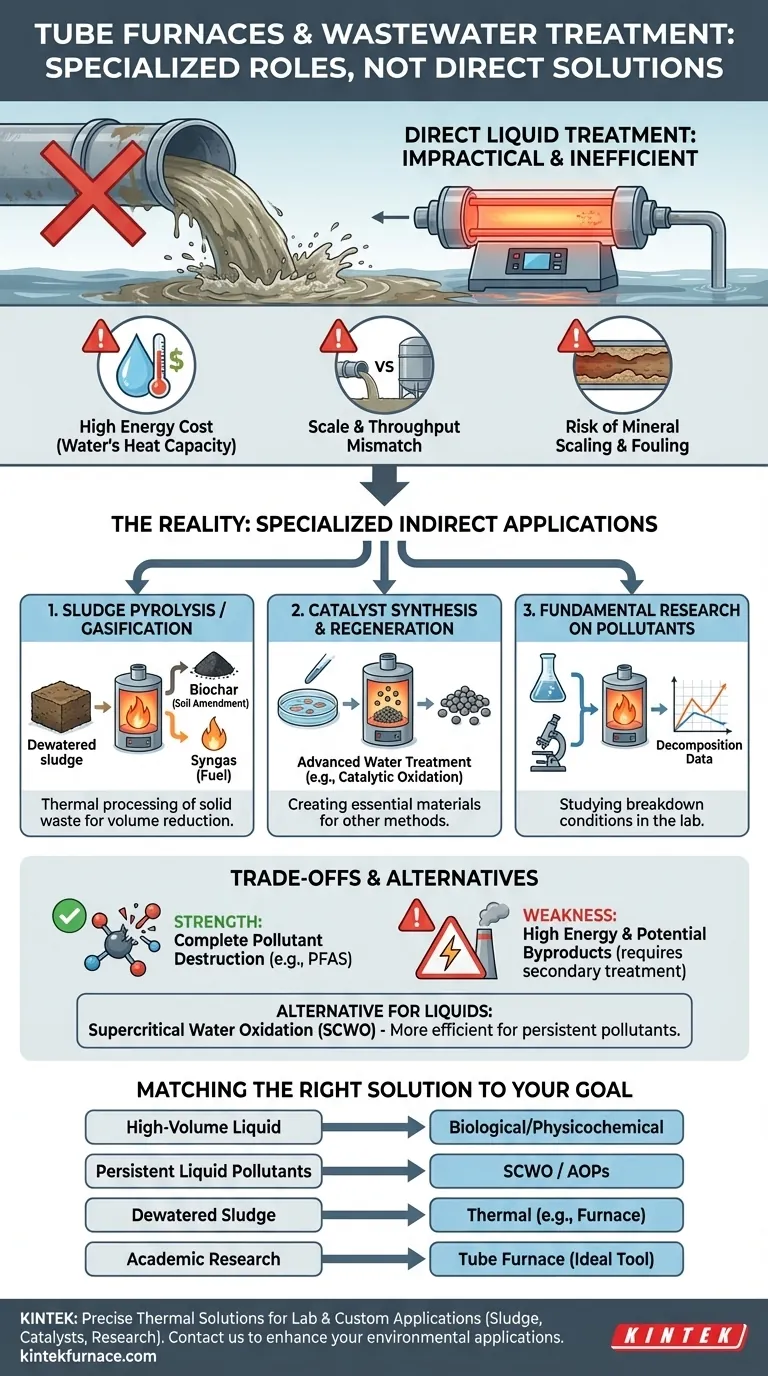
While a direct application is rare, a tube furnace is not a conventional method for treating liquid wastewater. Its role in environmental treatment is highly specialized, primarily focusing on the thermal processing of solid materials like dried sludge, the synthesis of catalysts used in other water treatment methods, or for fundamental laboratory research on pollutant decomposition. Treating large volumes of water directly with a tube furnace is generally impractical due to prohibitive energy costs and engineering challenges.
A tube furnace is a high-temperature materials processing tool, not a practical solution for bulk liquid wastewater treatment. The core issue is the immense energy required to heat water. However, the principle of thermal decomposition it represents is applied in more suitable technologies designed for challenging waste streams, such as incineration for dewatered sludge or Supercritical Water Oxidation for persistent liquid pollutants.

Why Tube Furnaces Are Not a Standard Wastewater Solution
The core challenge lies in applying a tool designed for controlled, high-temperature reactions on solids or gases to the problem of treating large volumes of liquid. The fundamental physics and economics work against this application.
The Problem of Water's High Heat Capacity
Water has a very high specific heat capacity. This means it requires a tremendous amount of energy to raise its temperature.
Treating wastewater in a furnace would mean spending the vast majority of your energy just to heat the water itself, rather than treating the tiny fraction of contaminants within it. This makes the process incredibly inefficient and economically unviable for any significant scale.
Issues with Scale and Throughput
Tube furnaces are typically laboratory or small-scale production devices with limited internal volume and flow-rate capacity.
Wastewater treatment plants, by contrast, must process thousands or millions of gallons of water per day. The physical size and design of a tube furnace are fundamentally mismatched for this high-throughput requirement.
The Risk of Mineral Scaling and Fouling
Wastewater contains dissolved minerals, salts, and organic matter. When heated to high temperatures, these substances would precipitate out of the solution.
This process, known as scaling or fouling, would quickly clog the narrow process tube of the furnace, leading to blockages, reduced efficiency, and potential equipment failure.
Where Tube Furnaces Are Used in Environmental Applications
While not used for direct liquid treatment, tube furnaces are valuable tools in related environmental fields. This is likely the context where the idea originated.
Pyrolysis and Gasification of Sludge
Wastewater treatment generates a semi-solid byproduct called sludge. After dewatering, this sludge can be treated thermally.
A furnace is used to heat the sludge in an oxygen-free (pyrolysis) or oxygen-limited (gasification) environment. This process can convert the waste into valuable products like biochar (a soil amendment) or syngas (a fuel gas), effectively destroying pollutants and reducing waste volume.
Catalyst Synthesis and Regeneration
Many advanced wastewater treatments, such as catalytic wet air oxidation, rely on specialized catalysts to break down pollutants.
Tube furnaces are essential laboratory and production tools for creating these catalysts. They provide the precise, high-temperature, and atmospherically controlled conditions needed to synthesize complex catalytic materials on a support structure.
Fundamental Research on Pollutants
In a research setting, a tube furnace is an excellent tool for studying the thermal decomposition of specific pollutants.
Scientists can use it to determine the exact temperatures and conditions required to break down a new or persistent contaminant, like those found in pharmaceuticals or pesticides. This data then informs the design of larger, purpose-built treatment reactors.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Thermal Treatment
Using heat to destroy waste is a powerful concept, but it comes with significant challenges. Understanding these trade-offs is key to selecting the right technology.
The Strength: Complete Pollutant Destruction
The primary advantage of high-temperature thermal treatment is its ability to break down even the most stubborn organic compounds, such as PFAS ("forever chemicals"), into simpler, harmless molecules like carbon dioxide and water.
The Weakness: Energy Cost and Byproducts
As discussed, the energy consumption can be enormous, making it the most expensive component of operation.
Furthermore, incomplete combustion or the presence of certain elements (like chlorine or nitrogen) can create harmful byproducts, such as dioxins or NOx gases, which require their own secondary gas treatment systems.
The Alternative: Specialized Thermal Technologies
For difficult liquid waste, engineers have developed more appropriate technologies that apply thermal principles efficiently.
Supercritical Water Oxidation (SCWO), for example, heats and pressurizes water until it enters a "supercritical" state where it acts like a solvent that rapidly dissolves and oxidizes organic pollutants. This is far more efficient than boiling water at atmospheric pressure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To effectively treat wastewater, you must match the technology to the specific waste stream, volume, and treatment objective.
- If your primary focus is treating high-volume municipal or industrial wastewater: Rely on proven biological and physicochemical treatment methods, augmented by filtration.
- If your primary focus is destroying highly persistent "forever chemicals" in a concentrated liquid stream: Investigate specialized technologies like Supercritical Water Oxidation (SCWO) or advanced oxidation processes (AOPs).
- If your primary focus is managing and reducing the volume of dewatered waste sludge: Explore thermal processes like pyrolysis, gasification, or incineration, where a furnace-like reactor is a central component.
- If your primary focus is academic research on pollutant breakdown: A tube furnace is an ideal and indispensable tool for controlled laboratory experiments.
Choosing the right treatment method begins with correctly matching the technology to the specific waste stream and operational scale.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Use | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Direct Wastewater Treatment | Not practical due to high energy costs and scaling issues | Inefficient for liquids, high energy use |
| Sludge Pyrolysis/Gasification | Thermal processing of dewatered sludge to produce biochar or syngas | Requires solid waste, not liquid |
| Catalyst Synthesis | Creating catalysts for advanced water treatment methods | Limited to lab or small-scale production |
| Pollutant Research | Studying thermal decomposition of contaminants in controlled settings | Not suitable for large-scale treatment |
Need precise thermal solutions for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we tailor our products to meet your unique experimental requirements, whether for sludge processing, catalyst development, or pollutant research. Contact us today to enhance your environmental applications with reliable, efficient equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab



















