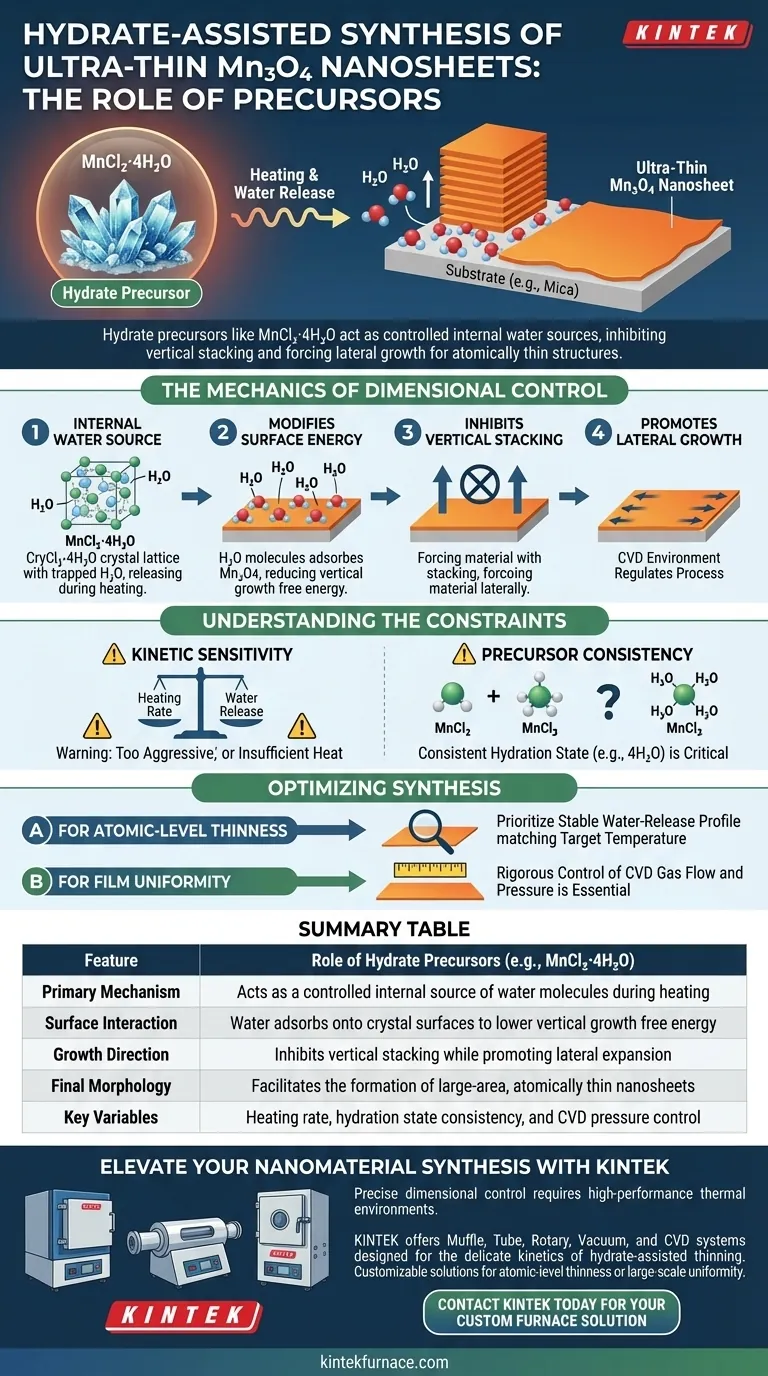
The primary function of hydrate precursors, such as MnCl2·4H2O, is to act as a controlled release agent for water molecules during the synthesis process. When heated, these precursors liberate water that adsorbs onto the crystal surface, inhibiting vertical stacking and forcing the material to grow laterally into ultra-thin Mn3O4 nanosheets.
The "hydrate-assisted thinning" strategy fundamentally alters the growth kinetics of the crystal. By releasing water to reduce the free energy associated with vertical growth, the precursor ensures the material expands horizontally rather than thickening, enabling the formation of atomically thin structures.
The Mechanics of Dimensional Control
The Internal Water Source
Unlike standard precursors, hydrate precursors contain water molecules trapped within their crystal lattice.
During the heating phase of synthesis, these molecules are released into the reaction environment. This provides an immediate, localized source of water vapor exactly where the nucleation is occurring.
Modifying Surface Energy
The key to this process is the interaction between the released water and the growing material.
The water molecules adsorb onto the surface of the Mn3O4. This adsorption process significantly reduces the free energy associated with vertical growth, effectively creating an energetic barrier against upward expansion.
Inhibiting Vertical Stacking
Because the energy required to grow vertically is increased relative to lateral growth, the crystal is forced to adopt a specific morphology.
The system inhibits the stacking of atomic layers on top of one another. Instead, the material follows the path of least resistance, promoting lateral growth across the substrate.
The Role of the CVD Environment
While the hydrate provides the mechanism for thinning, the Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) system provides the necessary control.
The CVD environment regulates the furnace temperature and pressure to ensure the water release coincides perfectly with nucleation kinetics. This precision allows for the synthesis of large-area, high-quality single crystals on substrates like mica.
Understanding the Constraints
Kinetic Sensitivity
The success of this method relies on a precise balance between heating rate and water release.
If the precursor is heated too aggressively, water may be driven off before it can effectively adsorb and inhibit vertical growth. Conversely, insufficient heat may fail to liberate the water molecules required for the thinning mechanism.
Precursor Consistency
Using hydrates introduces a variable regarding the stoichiometry of the precursor material.
You must ensure the specific hydration state (e.g., 4H2O) is consistent. Variations in the hydration level of the precursor can lead to inconsistent film thicknesses or incomplete lateral coverage.
Optimizing Synthesis for Your Objectives
To apply this hydrate-assisted strategy effectively, consider your specific experimental goals:
- If your primary focus is atomic-level thinness: Prioritize the selection of a hydrate precursor with a stable water-release profile that matches your target reaction temperature.
- If your primary focus is film uniformity: rigorous control of the CVD gas flow and pressure is essential to manage the distribution of the released water vapor across the substrate.
By leveraging the chemical potential of hydrate precursors, you gain precise control over crystal dimensionality, turning a simple heating process into a tool for advanced nanomaterial fabrication.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role of Hydrate Precursors (e.g., MnCl2·4H2O) |
|---|---|
| Primary Mechanism | Acts as a controlled internal source of water molecules during heating |
| Surface Interaction | Water adsorbs onto crystal surfaces to lower vertical growth free energy |
| Growth Direction | Inhibits vertical stacking while promoting lateral expansion |
| Final Morphology | Facilitates the formation of large-area, atomically thin nanosheets |
| Key Variables | Heating rate, hydration state consistency, and CVD pressure control |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise dimensional control in Mn3O4 nanosheet synthesis requires more than just the right precursor—it demands a high-performance thermal environment. At KINTEK, we understand the delicate kinetics of hydrate-assisted thinning.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to regulate temperature and pressure with the exactitude needed for sophisticated nanomaterial fabrication. Whether you are aiming for atomic-level thinness or large-scale film uniformity, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Ready to achieve superior crystal growth? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom furnace solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Jiashuai Yuan, Wei Liu. Controllable synthesis of nonlayered high-κ Mn3O4 single-crystal thin films for 2D electronics. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-56386-9
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-precision furnace critical for refractory castables? Ensure Structural Integrity & Mineral Stability
- Why is HR-TEM used after high-temperature heat treatment? Visualize structural evolution and material integrity.
- Why is an air-ventilated oven necessary for GFPP surface modification? Achieve Maximum Solar Reflectance
- What is the importance of the feeding system and ore distributing device? Unlock Peak Oil Shale Retorting Efficiency
- What role does an infrared image furnace play in the Floating Zone Method? Mastering Nb-doped beta-Ga2O3 Crystal Growth
- What is the function of a forced drying oven in SiOC coating conversion? Ensure Flawless Solvent Removal
- Process conditions for HEA cladding thermal experiments: Ensuring 800°C stability and 1680-hour endurance.
- What are the advantages of directly adding heat carriers to oil sludge? Boost Efficiency & Preserve Resource Value













