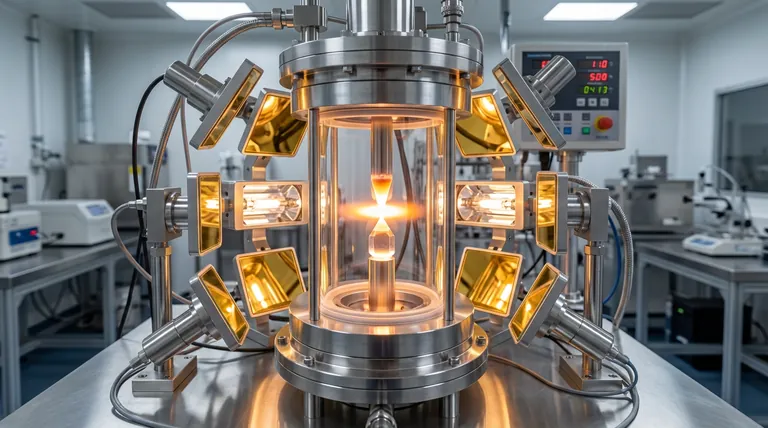
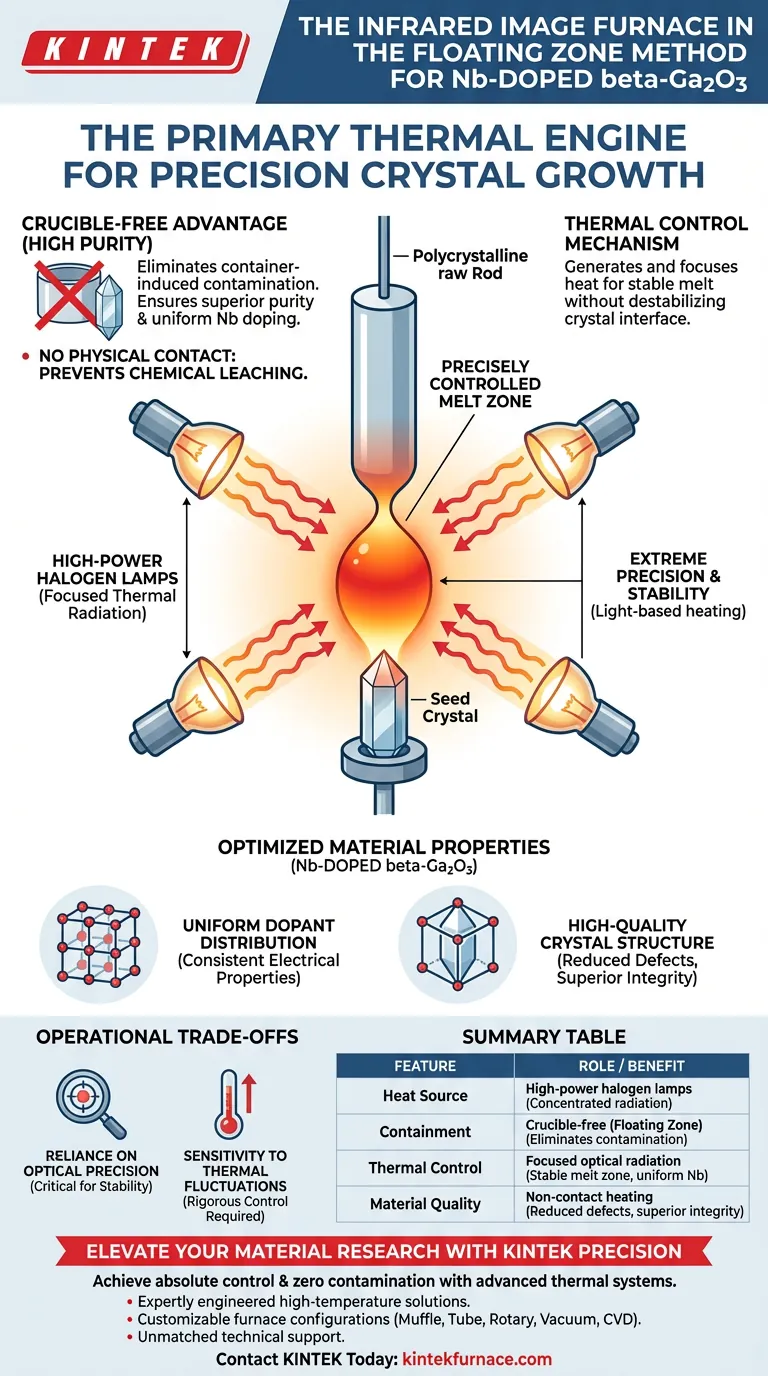
The infrared image furnace functions as the primary thermal engine in the Floating Zone Method, responsible for generating and focusing the heat necessary for crystal growth. By utilizing high-power halogen lamps, the furnace creates highly concentrated thermal radiation to establish a precisely controlled melt zone between the raw material rod and the seed crystal.
The furnace’s ability to generate heat without physical contact eliminates the need for a crucible, preventing container-induced contamination and ensuring the high purity and uniform niobium (Nb) doping required for superior beta-Ga2O3 crystals.

The Mechanism of Thermal Control
Generating Concentrated Radiation
The core operation of the infrared image furnace relies on high-power halogen lamps. These lamps do not simply heat the ambient air; they generate intense thermal radiation.
Creating the Melt Zone
This radiation is optically focused to a specific point. This creates a localized, high-temperature melt zone suspended directly between the polycrystalline raw rod and the single crystal seed.
Precision and Stability
Because the heat is delivered via light rather than a physical heating element, the temperature profile can be manipulated with extreme precision. This allows for the exact thermal conditions required to sustain the melt without destabilizing the crystal interface.
Achieving High Purity Through Design
The Crucible-Free Advantage
The most critical role of this furnace is its ability to facilitate "crucible-free" growth. In traditional methods, the melt often reacts with the container walls, leaching impurities into the crystal.
Preventing Contamination
By suspending the melt using surface tension and focused radiation, the infrared image furnace removes physical contact with any vessel. This effectively prevents chemical contamination, which is a common failure point in growing oxide single crystals.
Optimizing Material Properties
Uniform Dopant Distribution
For Nb-doped beta-Ga2O3, the goal is not just to grow a crystal, but to alter its electrical properties with niobium. The floating zone technique ensures that the Nb dopant is distributed uniformly throughout the crystal lattice.
High-Quality Crystal Structure
The combination of contamination control and stable thermal gradients results in high-quality single crystals. This equipment is the standard for producing materials where structural integrity and purity are non-negotiable.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Reliance on Optical Precision
While the lack of a crucible improves purity, it removes the physical support for the melt. The process relies entirely on the precise focus of the halogen lamps to maintain the melt zone's stability.
Sensitivity to Thermal Fluctuations
Because the volume is small and the heat source is concentrated radiation, the system requires rigorous control. Any deviation in the lamp output or focus can disrupt the melt zone, unlike large-volume crucible methods that have higher thermal inertia.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Whether you are setting up a growth facility or selecting a material source, understanding the capabilities of this furnace is essential.
- If your primary focus is electrical consistency: The infrared image furnace is critical for ensuring the Nb dopant is evenly spread, preventing localized variances in conductivity.
- If your primary focus is extreme lattice purity: Rely on this method to eliminate foreign contaminants that would otherwise introduce defects from containment vessels.
The infrared image furnace is not just a heater; it is the precision tool that bridges the gap between raw powder and high-performance semiconductor material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in Floating Zone Method | Benefit for Nb-doped Ga2O3 |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | High-power halogen lamps | Concentrated radiation for precise melting |
| Containment | Crucible-free (Floating Zone) | Eliminates contamination for high purity |
| Thermal Control | Focused optical radiation | Stable melt zone and uniform Nb distribution |
| Material Quality | Non-contact heating | Reduced defects and superior lattice integrity |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Achieving the perfect crystal structure requires more than just heat—it requires absolute control and zero contamination. At KINTEK, we specialize in the R&D and manufacturing of advanced thermal systems designed for the most demanding lab environments.
Whether you are pioneering semiconductor research with beta-Ga2O3 or exploring new materials, our range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems can be fully customized to meet your unique specifications.
Partner with KINTEK for:
- Expertly engineered high-temperature solutions.
- Customizable furnace configurations for specialized crystal growth.
- Unmatched technical support from lab equipment specialists.
Contact KINTEK Today to discuss your project and discover how our high-performance furnaces can drive your innovation forward.
Visual Guide
References
- Qinglin Sai, H.F. Mohamed. Conduction mechanism and shallow donor defects in Nb-doped β-Ga2O3 single crystals. DOI: 10.1063/5.0200755
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is Barium Titanate annealed after SPS? Restore Material Stoichiometry and Electrical Performance
- Why must the filling of the working medium into a sodium heat pipe be performed inside a protective glovebox?
- What are the technical characteristics of Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) equipment for perovskite? Precision Thin Films
- Why is an industrial-grade forced air drying oven required for Ca2.5Ag0.3Sm0.2Co4O9 ceramic? Precision Pre-Treatment
- Why must the entire system be maintained at a high temperature during the filling process of a sodium heat pipe?
- What role does a high-temperature furnace play in the chemical activation of carbon materials? Master KOH Activation
- What is the role of a customized drying station with nitrogen purging? Optimize Polymer Blend Membrane Processing
- What role does the soaking zone of a walking-beam furnace play in the final quality of heated Titanium/Steel clad plates?



















