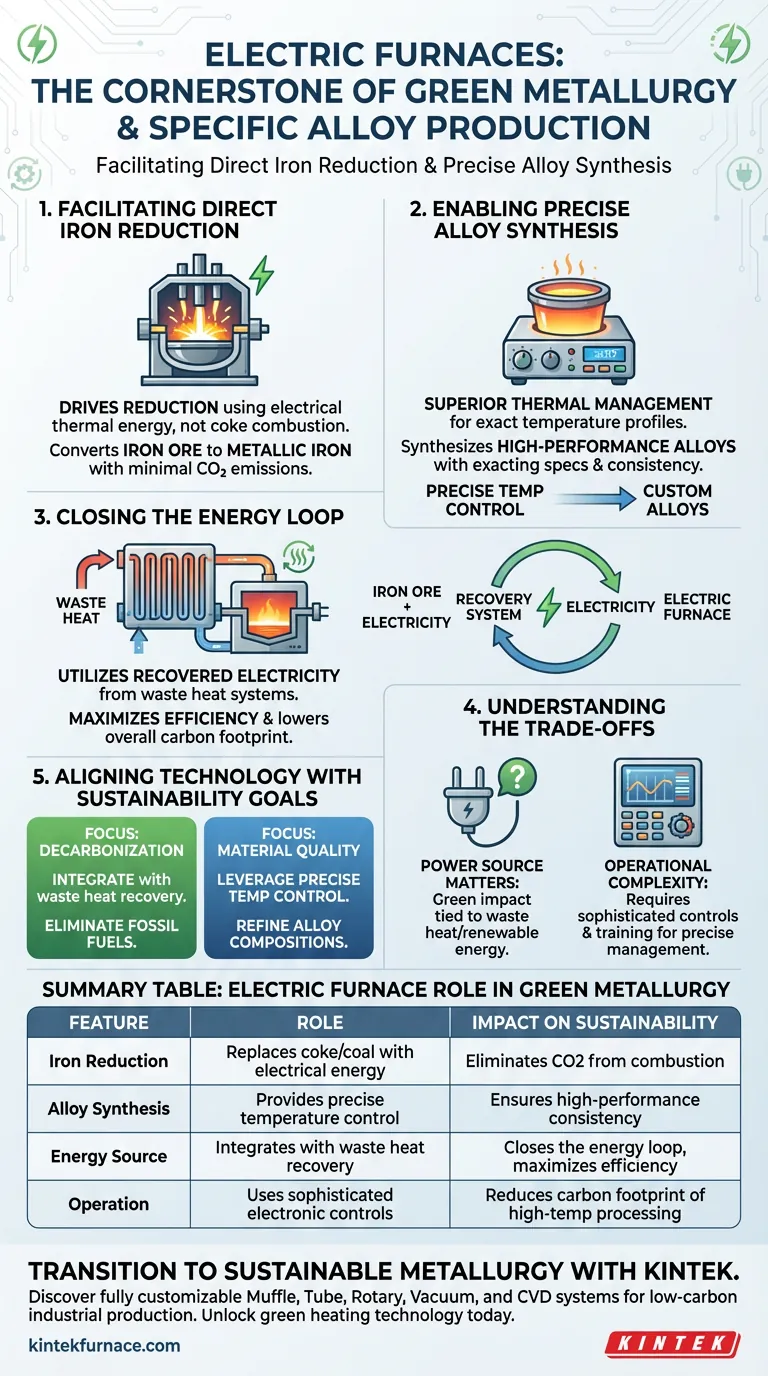
Electric furnaces function as the thermal cornerstone of modern green metallurgy. They provide the controlled, high-temperature environments required to facilitate the direct reduction of iron and the synthesis of specialized alloys, all while eliminating the reliance on traditional fossil-fuel combustion methods.
By replacing carbon-intensive heating with electrically generated heat—often powered by recovered waste heat systems—electric furnaces enable the precise metallurgical processing necessary to meet rigorous industrial decarbonization goals.

The Mechanisms of Green Metal Processing
Facilitating Direct Reduction of Iron
The primary function of the electric furnace in this context is to drive the direct reduction of iron.
Unlike blast furnaces that rely on coke for both heat and chemical reduction, electric furnaces use electrical energy to generate the necessary thermal environment.
This process converts iron ore into metallic iron without the massive carbon dioxide emissions associated with burning coal or gas.
Enabling Precise Alloy Synthesis
Producing alloys with specific, high-performance properties requires exact thermal management.
Electric furnaces offer superior control over temperature profiles compared to combustion-based alternatives.
This precision allows metallurgists to synthesize alloys with exacting specifications, ensuring consistency and quality in the final material.
Closing the Energy Loop
A critical differentiator in green metallurgy is the source of the electricity used.
These furnaces are designed to utilize electricity recovered from waste heat systems within the industrial plant.
By recycling energy that would otherwise be lost, the system maximizes efficiency and significantly lowers the overall carbon footprint of production.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Dependency on Power Sources
While electric furnaces are "green" technology, their environmental impact is tied to their power source.
If the electricity does not come from waste heat recovery or renewable sources, the decarbonization benefits are diminished.
Operators must ensure the energy input aligns with the facility's sustainability targets.
Operational Complexity
Achieving the precision mentioned earlier requires sophisticated control systems.
Moving from traditional combustion to electric heating changes the operational dynamics of a foundry or steel plant.
This often requires updated infrastructure and specialized training for operators to manage the precise temperature gradients effectively.
Aligning Technology with Sustainability Goals
To effectively leverage electric furnaces in your metallurgy operations, consider your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is decarbonization: Prioritize integrating the furnace with waste heat recovery systems to eliminate reliance on external fossil-fuel energy.
- If your primary focus is material quality: Leverage the furnace's precise temperature control capabilities to refine alloy compositions that are difficult to produce in combustion furnaces.
Ultimately, the electric furnace is not just a melting tool; it is the enabling technology that bridges the gap between high-performance metal production and a low-carbon industrial future.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electric Furnace Role in Green Metallurgy | Impact on Sustainability |
|---|---|---|
| Iron Reduction | Replaces coke/coal with electrical thermal energy | Eliminates CO2 from fossil-fuel combustion |
| Alloy Synthesis | Provides precise temperature and profile control | Ensures high-performance material consistency |
| Energy Source | Integrates with waste heat recovery systems | Closes the energy loop and maximizes efficiency |
| Operation | Uses sophisticated electronic control systems | Reduces carbon footprint of high-temp processing |
Transition to Sustainable Metallurgy with KINTEK
Ready to lead the shift toward low-carbon industrial production? Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Whether you are focusing on direct iron reduction or complex alloy synthesis, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique metallurgical needs.
Unlock the precision and efficiency of green heating technology today. Contact our experts now to discover how KINTEK can enhance your lab's capabilities and help you meet rigorous decarbonization goals.
Visual Guide
References
- Viktoriia Ye. Khaustova, I.V. Shulga. Directions for the development of coke and non-coke metallurgy. DOI: 10.31081/1681-309x-2025-0-4-3-13
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- How does the sintering process enhance conventional ceramics with Alumina? Boost Strength and Insulation
- Why is thermal annealing of native substrates required for β-Ga2O3? Optimize Your Epitaxial Growth Foundation
- What is zirconium dioxide and how is it stabilized for dental use? Discover the Science Behind Durable Dental Ceramics
- What is the necessity of a laboratory vacuum drying oven for photocatalytic powders? Protect Your Material Integrity
- Why is a slow heating rate utilized for rice husk biochar? Optimize Pore Structure and Adsorption Performance
- Why must T91 steel ingots undergo long-term homogenization? Ensure High-Performance Microstructural Uniformity
- What is the technical necessity of using a laboratory vacuum drying oven for Cu-Fe-N-C catalyst precursors?
- What is the primary function of a high-purity inert glove box? Ensure Success in LiF-BeF2 Molten Salt Systems



















