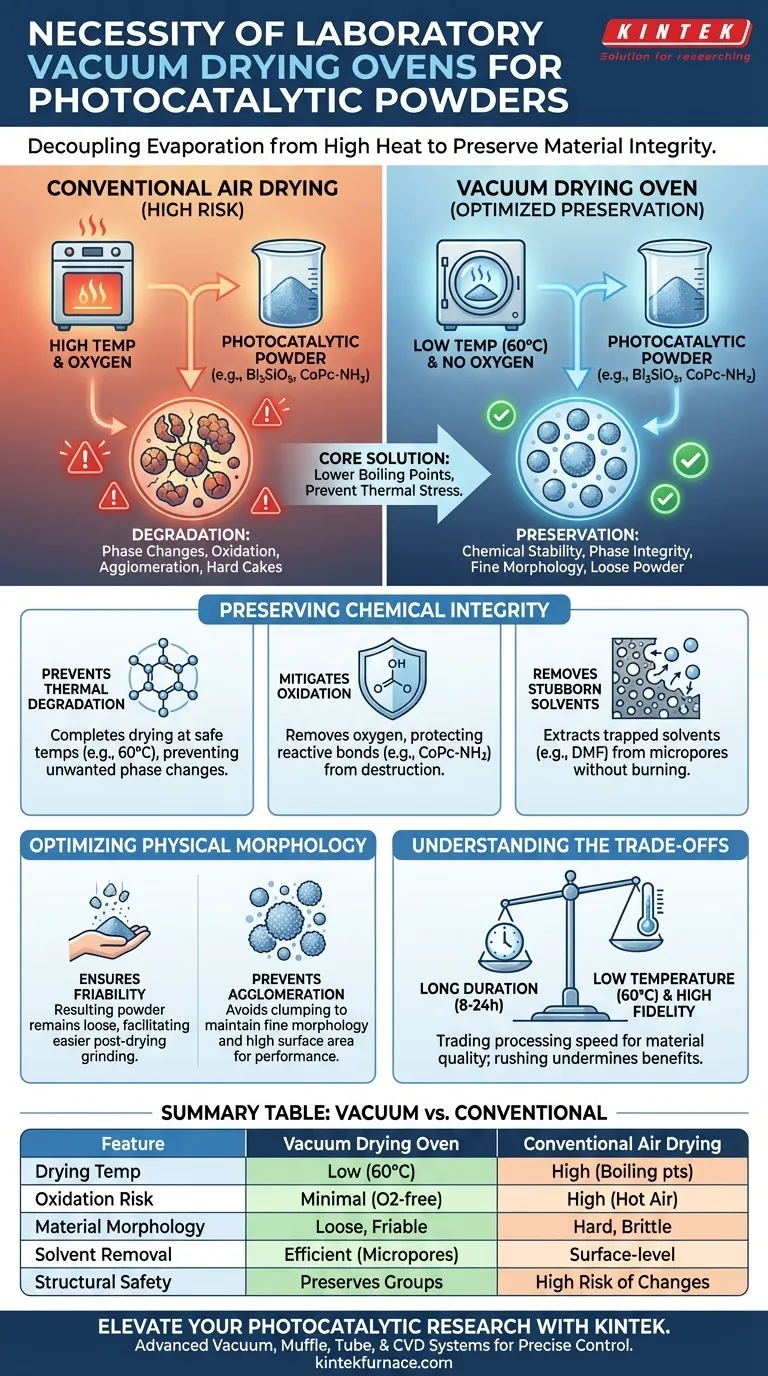
The necessity of a laboratory vacuum drying oven stems from its ability to lower the boiling point of solvents, enabling the dehydration of photocatalytic powders at significantly reduced temperatures. By processing materials like Bi2SiO5 or CN/BS composites at moderate heat (typically 60 °C), you remove moisture effectively without subjecting the sample to the thermal stress that causes degradation.
Core Takeaway Photocatalytic materials are highly sensitive to thermal stress and oxidative environments. A vacuum drying oven is strictly necessary to decouple evaporation from high heat, ensuring complete solvent removal while preserving the material's chemical structure, phase stability, and particle morphology.

Preserving Chemical and Structural Integrity
Preventing Thermal Degradation
Standard drying methods rely on high temperatures to evaporate moisture, which poses a severe risk to photocatalysts. By utilizing a vacuum environment, you reduce the boiling point of water and other solvents. This allows for complete drying at safe temperatures—such as 60 °C for Bi2SiO5—preventing unwanted phase changes that occur under high heat.
Mitigating Oxidation
Many photocatalytic powders possess reactive functional groups that are vulnerable to oxygen at elevated temperatures. For example, reduced amino functional groups in CoPc-NH2 powders can oxidize if dried in hot air, destroying the catalyst's utility. The vacuum oven removes oxygen from the chamber, protecting these delicate chemical bonds during the heating process.
Removing Stubborn Solvents
Complex synthesis often involves high-boiling point solvents like dimethylformamide (DMF) trapped in micropores. Atmospheric drying cannot remove these solvents efficiently without burning the sample. Vacuum drying extracts these residual solvents from particle interstices effectively, even at lower temperatures like 60°C.
Optimizing Physical Morphology
Ensuring Friability for Processing
Post-drying processing, such as grinding, requires the material to be chemically stable and physically manageable. The primary reference notes that vacuum drying ensures the resulting powder remains "loose." This loose structure is critical for easier subsequent grinding, whereas air drying often results in hard, brittle cakes.
Preventing Agglomeration
Maintaining a high surface area is vital for photocatalytic performance. Vacuum drying prevents the "clumping" or agglomeration of particles that often happens during slow, high-heat air evaporation. This is essential for maintaining fine morphology, such as when loading particles onto a matrix like C3N4.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Time vs. Temperature Exchange
While vacuum drying preserves quality, it is not a rapid process. References indicate drying times ranging from 8 hours to as long as 24 hours depending on the material and solvent. You are trading processing speed for material fidelity; rushing this process with higher heat or lower time undermines the benefits of the vacuum environment.
Complexity of Solvent Evaporation
Simply applying a vacuum does not guarantee success; the temperature must still be tuned to the specific solvent. While water may evaporate easily at 60°C under vacuum, other solvents trapped deep in micropores may require extended duration (up to 24 hours) to fully migrate out. Incomplete drying due to impatience can leave residual solvents that interfere with catalytic activity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring your drying protocols, align your settings with your specific material constraints:
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Prioritize lower temperatures (approx. 60°C) over long durations (24h) to protect sensitive functional groups from oxidation.
- If your primary focus is Physical Processing: Ensure the vacuum level is sufficient to keep the powder loose, preventing agglomeration that complicates grinding.
A vacuum drying oven is not merely a drying tool; it is a preservation instrument that ensures your photocatalyst reaches the experiment phase with its intended properties intact.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Drying Oven | Conventional Air Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Drying Temperature | Low (typically 60°C) | High (Standard boiling points) |
| Oxidation Risk | Minimal (Oxygen-free environment) | High (Exposure to hot air) |
| Material Morphology | Loose, friable powder | Hard, brittle cakes |
| Solvent Removal | Efficient for micropores/high BP | Surface-level only |
| Structural Safety | Preserves delicate functional groups | High risk of phase changes |
Elevate Your Photocatalytic Research with KINTEK
Don't let thermal stress or oxidation compromise your material performance. KINTEK provides advanced, customizable vacuum drying solutions engineered for the delicate needs of laboratory R&D.
Backed by expert manufacturing, our systems ensure precise temperature control and superior vacuum stability for high-sensitivity powders. Whether you need specialized Vacuum, Muffle, Tube, or CVD systems, our high-temperature lab furnaces are designed to protect your material's chemical and physical integrity.
Ready to optimize your synthesis workflow? Contact KINTEK today for a customized solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Shaowei Qin, Jianhui Jiang. A high-performance g-C3N5/Bi2SiO5 heterojunction photocatalyst induced by constructing S-scheme electron-highways. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-85268-9
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are a laboratory oven and Canadian Balsam used together for wood slides? Master Permanent Microscopy Techniques
- Why is a 105 °C drying process in an electric drying oven significant? Prevent Refractory Structural Failure
- How does high-temperature heating facilitate the conversion of rice husks into inorganic precursors for silica extraction?
- What is the function of an industrial drying oven in ZnZrOx catalyst prep? Ensure Uniform Metal Precursor Adsorption
- What are the advantages of the Laser Hearth Method for Zirconia? Achieve High Purity & Density for Advanced Research
- Why are automated Mass Flow Controllers (MFCs) essential in mixed-gas nitriding? Achieve Process Precision
- Why is a vacuum drying apparatus necessary for iridium salt precursor impregnation? Unlock Superior Template Loading
- Why are industrial-grade drying and crushing equipment necessary for pretreatment? Optimize Chemical Reactions



















