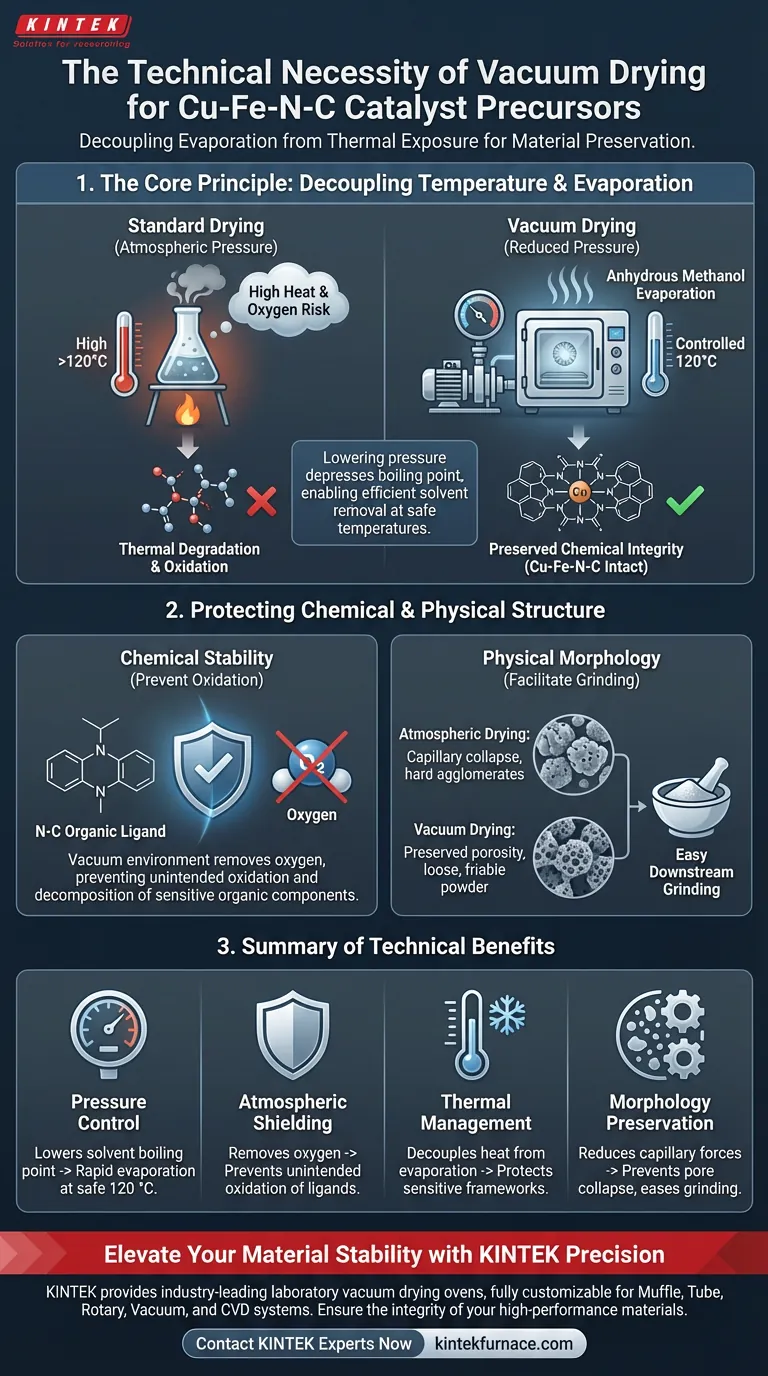
The technical necessity of a laboratory vacuum drying oven lies in its ability to decouple evaporation rates from high thermal exposure. By significantly reducing environmental pressure, the oven allows residual anhydrous methanol solvent to evaporate rapidly at a controlled temperature of 120 °C. This specific environment is critical for preventing the unintended oxidation or decomposition of the organic components within the Cu-Fe-N-C precursor, ensuring the chemical structure remains intact for subsequent processing.
Core Takeaway Vacuum drying is not simply a faster method of moisture removal; it is a preservation strategy for sensitive chemical architectures. By lowering the boiling point of solvents, it protects the precursor's organic framework from thermal degradation and oxidative stress, ensuring the material retains the specific physical properties required for effective grinding.
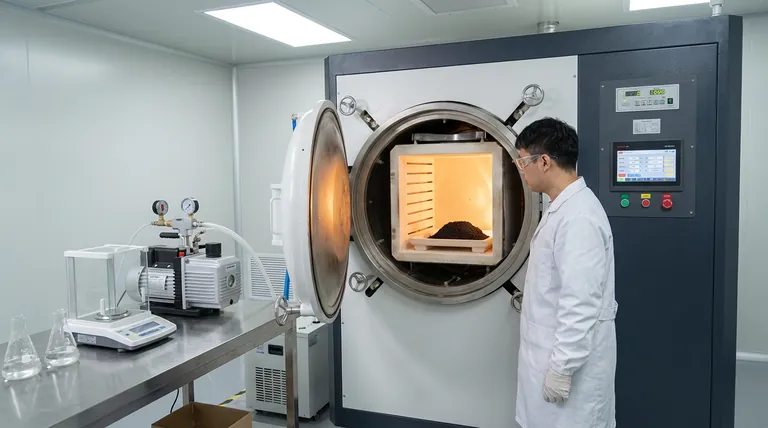

The Thermodynamics of Preservation
Decoupling Temperature and Evaporation
The primary technical challenge in processing Cu-Fe-N-C precursors is removing the solvent without destroying the material. Standard drying relies on heat to reach the solvent's boiling point.
A vacuum oven alters this dynamic by lowering the ambient pressure. This depresses the boiling point of the anhydrous methanol, allowing it to vaporize efficiently at 120 °C. This ensures complete solvent removal without requiring temperatures that would otherwise damage the catalyst.
Protecting Organic Integrity
The "N-C" (Nitrogen-Carbon) components of the precursor are often organic and thermally sensitive. High temperatures combined with atmospheric oxygen can lead to rapid oxidation or decomposition.
By operating in a vacuum, you remove the oxygen source and keep the thermal energy below the threshold of organic degradation. This maintains the precise chemical stoichiometry required for the catalyst to function correctly.
Physical Structure and Processability
Preventing Structural Collapse
Beyond chemical protection, the drying method dictates the physical morphology of the powder. High-temperature drying at atmospheric pressure can cause capillary forces to collapse pores or lead to hard agglomeration (clumping).
Vacuum drying promotes a gentler evaporation process. This preserves the internal porous structure of the material, which is vital for maintaining a high specific surface area—a key metric for catalytic activity.
Facilitating Downstream Grinding
The primary reference notes that the end goal of this drying stage is to prepare the powder for grinding.
Vacuum drying tends to result in a "looser" internal structure rather than a hard, sintered cake. This friability is technically necessary because it allows the precursor to be ground easily into a fine, uniform powder, ensuring consistent particle size distribution in the final application.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Solvent Bumping
While vacuum drying is efficient, applying a deep vacuum too quickly can cause "bumping"—where the solvent boils violently rather than evaporating steadily. This can splash the precursor material inside the oven, leading to sample loss or cross-contamination.
Equipment Complexity vs. Necessity
Vacuum ovens add complexity compared to standard convection ovens. They require vacuum pumps, seal maintenance, and careful monitoring of pressure levels. However, for Cu-Fe-N-C precursors, this added complexity is a non-negotiable requirement due to the sensitivity of the organic components to oxidation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The choice of drying parameters should be dictated by the specific vulnerabilities of your material.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Stability: Prioritize vacuum levels that allow evaporation at temperatures well below the decomposition threshold of your organic ligands (e.g., maintaining 120 °C to protect Cu-Fe-N-C structures).
- If your primary focus is Physical Morphology: Ensure a gradual reduction in pressure to prevent pore collapse, ensuring the resulting powder is loose and porous for easy grinding.
By controlling pressure, you transform drying from a destructive heating process into a precise, structure-preserving step.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Technical Necessity | Benefit to Cu-Fe-N-C Precursors |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure Control | Lowers solvent boiling point | Rapid evaporation of methanol at a safe 120 °C |
| Atmospheric Shielding | Removes oxygen from chamber | Prevents unintended oxidation of nitrogen-carbon ligands |
| Thermal Management | Decouples heat from evaporation | Protects sensitive organic frameworks from degradation |
| Morphology Preservation | Reduces capillary forces | Prevents pore collapse and facilitates easy grinding |
Elevate Your Material Stability with KINTEK Precision
Preserving the delicate chemical architecture of Cu-Fe-N-C catalysts requires precise thermal and atmospheric control. KINTEK provides industry-leading laboratory vacuum drying ovens designed to protect your most sensitive precursors from oxidation and structural collapse.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all fully customizable to meet your unique research or production requirements. Ensure the integrity of your high-performance materials and optimize your downstream grinding processes today.
Ready to refine your laboratory thermal processing?
Visual Guide
References
- Kun Liu, Xin Chen. Highly efficient Fe–Cu dual-site nanoparticles supported on black pearls 2000 (carbon black) as oxygen reduction reaction catalysts for Al–air batteries. DOI: 10.1039/d3ra07925b
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the limitations of PVD coating? Overcome Challenges for Optimal Surface Engineering
- What is the function of a laboratory vacuum drying oven in BAFPAE processing? Maintain Precursor Purity and Stability
- What is the use of a laboratory furnace? Unlock Precise Material Transformation
- What role does a constant temperature water bath play in simulated hot-rolling oxidation? Master Precision Humidity
- Why is a high-purity argon flow required during the thermal reduction of nitrogen-doped graphene oxide?
- What are the technical advantages of using the molten salt method? Elevate Your Biomass Carbon Support Synthesis
- What key data does a Simultaneous Thermal Analyzer (STA) provide for lignite combustion? Assess Fire Risk with Precision
- How do precision electric drying ovens control the precipitation of strengthening phases in recycled aluminum alloys?



















