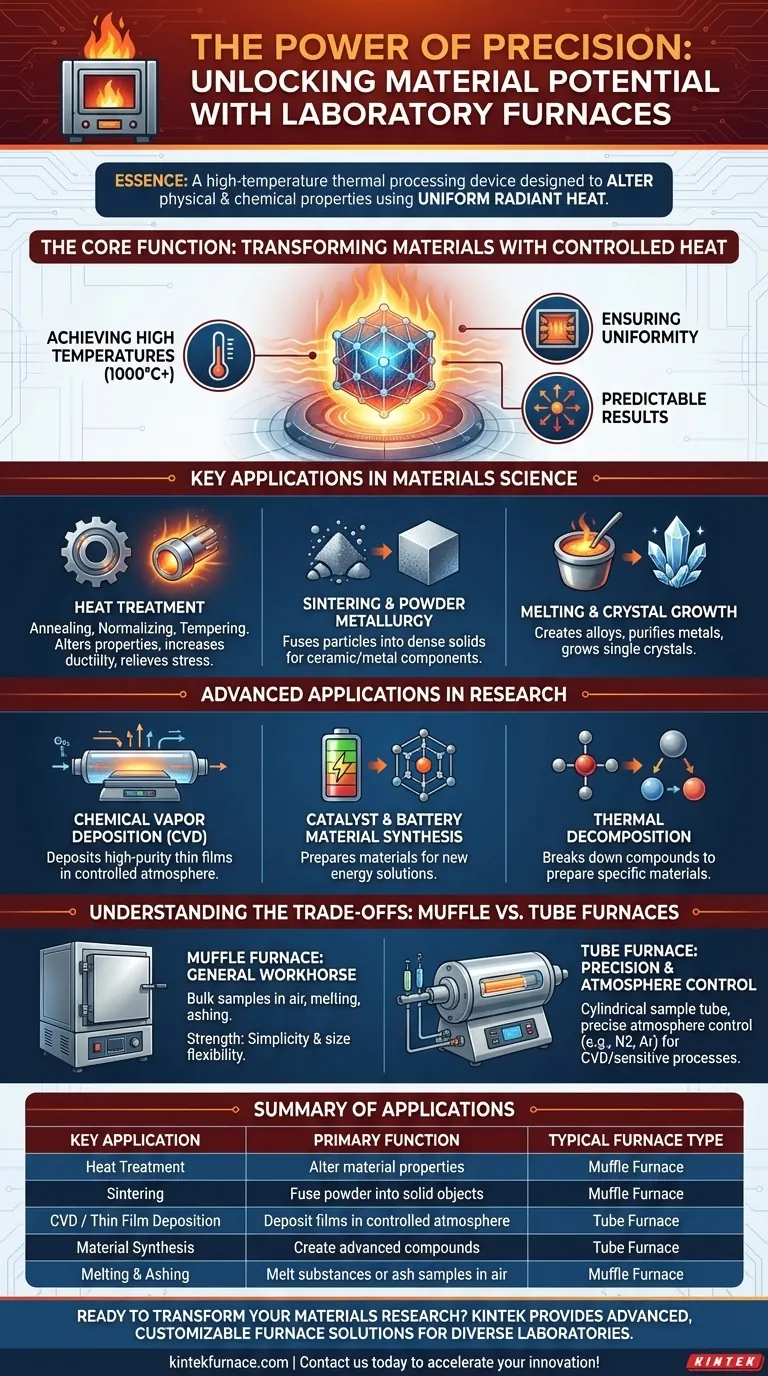
In essence, a laboratory furnace is a high-temperature thermal processing device used to alter the physical and chemical properties of materials. By using radiant heat to achieve uniform temperatures, often exceeding 1000°C, these furnaces enable critical processes such as melting metals, sintering ceramics, synthesizing advanced materials, and performing specific heat treatments.
The core function of a laboratory furnace is not simply to get things hot. Its true purpose is to create a precisely controlled and uniform high-temperature environment, which is the fundamental requirement for transforming a material's internal structure and composition.

The Core Function: Transforming Materials with Heat
A laboratory furnace's primary role is to deliver controlled, high-energy thermal input to a sample. This allows researchers and engineers to manipulate materials at a molecular or crystalline level.
Achieving High Temperatures
Unlike an oven, a furnace operates at significantly higher temperatures. This capability is essential for processes that require substantial energy, such as melting metals or firing high-performance ceramics.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
The internal chamber is designed to distribute radiant heat evenly. This temperature uniformity is critical for ensuring that an entire sample undergoes the same transformation, leading to consistent and predictable results.
Key Applications in Materials Science
Much of modern materials engineering relies on the precise thermal processing that furnaces provide.
Heat Treatment
Processes like annealing, normalizing, and tempering involve carefully heating and cooling a material to alter its properties. This can increase ductility, relieve internal stresses, or improve hardness without changing the material's shape.
Sintering and Powder Metallurgy
Furnaces are used to sinter powdered materials, such as ceramics or metals. At high temperatures, the individual particles fuse together to form a solid, dense object, a foundational process in creating everything from ceramic components to metal parts.
Melting and Crystal Growth
For creating alloys or purifying metals, a muffle furnace can melt the raw materials within a crucible. In advanced applications, controlled cooling cycles within a furnace are used to grow large, single crystals for electronics or optics.
Advanced Applications in Research
In specialized research fields, furnaces are indispensable tools for innovation and discovery.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
A tube furnace is often used for CVD. In this process, volatile precursor gases react and decompose on a heated substrate inside the tube, depositing a high-purity thin film on its surface.
Catalyst and Battery Material Synthesis
Furnaces are central to new energy research. They are used for preparing and modifying materials for lithium-ion batteries (like lithium iron phosphate) and for developing and testing materials for fuel cells.
Thermal Decomposition
Researchers use furnaces to study thermal decomposition, breaking down compounds with heat to precisely prepare other materials, such as specific oxides, nitrides, and carbides.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Muffle vs. Tube Furnaces
The choice of furnace type depends entirely on the requirements of the experiment. The two most common types are muffle and tube furnaces.
Muffle Furnaces: The General Workhorse
A muffle furnace contains the heating elements on the outside of a primary chamber, or "muffle." This design is excellent for heating bulk samples in air, melting materials in a crucible, or ashing samples. Its strength is simplicity and sample size flexibility.
Tube Furnaces: Precision and Atmosphere Control
A tube furnace heats a cylindrical tube, often made of ceramic or quartz, through which the sample is placed. Its primary advantage is the ability to tightly control the atmosphere by flowing specific gases (e.g., nitrogen, argon) through the tube, making it ideal for sensitive processes like CVD or catalyst research.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal process is critical for achieving your desired material outcome.
- If your primary focus is modifying the properties of a solid part (e.g., making it tougher or less brittle): Your goal is heat treatment, requiring controlled heating and cooling cycles.
- If your primary focus is creating a solid object from a powder: You will be using a sintering process to fuse the particles together at high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is creating a thin film or a specialized compound in a controlled atmosphere: You need a tube furnace for processes like Chemical Vapor Deposition or specific synthesis reactions.
- If your primary focus is melting a substance or processing bulk samples in air: A muffle furnace is the most direct and effective tool for the job.
Ultimately, the laboratory furnace is an indispensable tool that enables the precise manipulation and creation of materials, driving innovation across science and engineering.
Summary Table:
| Key Application | Primary Function | Typical Furnace Type |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Treatment | Alter material properties (annealing, tempering) | Muffle Furnace |
| Sintering | Fuse powder particles into solid objects | Muffle Furnace |
| CVD / Thin Film Deposition | Deposit high-purity films in controlled atmosphere | Tube Furnace |
| Material Synthesis | Create advanced compounds (battery materials, catalysts) | Tube Furnace |
| Melting & Ashing | Melt substances or ash samples in air | Muffle Furnace |
Ready to Transform Your Materials Research?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our furnace solutions can accelerate your innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a muffle furnace in LSCF modification? Achieve Precise Thermal Foundation for Advanced Ceramics
- How does high-temperature heating facilitate the conversion of rice husks into inorganic precursors for silica extraction?
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- How is the thermal stability of KBaBi compounds evaluated? Discover Precise XRD & Heat Treatment Limits
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace used for Ni-BN powder preheating? Achieve defect-free coating density.



















