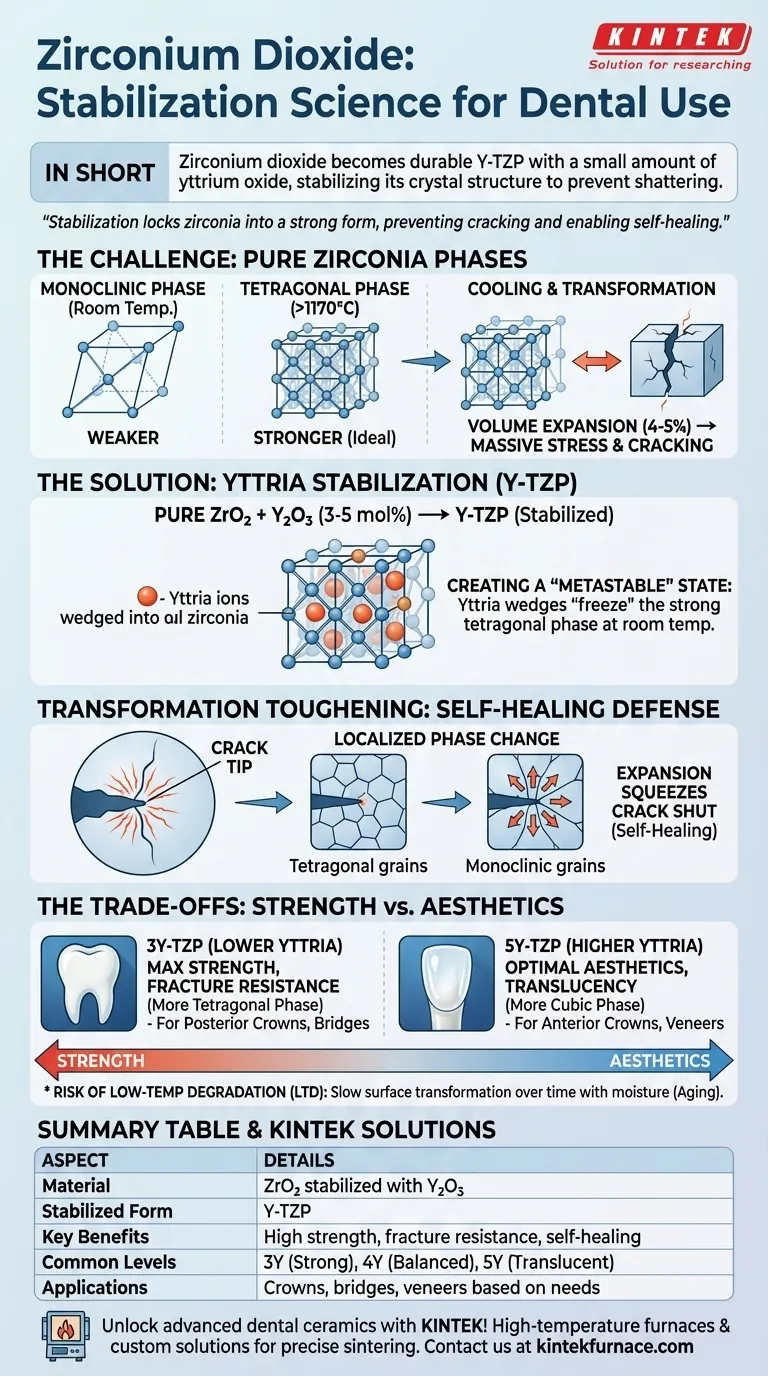
In short, zirconium dioxide is a high-performance ceramic that becomes a durable, fracture-resistant dental material known as Y-TZP when a small amount of yttrium oxide is added. This addition is not merely an ingredient; it is a critical process that "stabilizes" the material's crystal structure, preventing it from shattering under normal conditions.
The success of zirconia in dentistry hinges on a process called stabilization. By adding yttrium oxide, we lock zirconia into a strong, high-temperature crystalline form, which not only prevents it from cracking upon cooling but also gives it a unique, self-healing ability to stop fractures in their tracks.

The Challenge of Pure Zirconia: A Material in Three Phases
To understand why stabilization is necessary, you must first understand the unstable nature of pure zirconium dioxide (ZrO₂). It exists in three different crystal structures, or phases, depending on the temperature.
The Monoclinic Phase (Room Temperature)
At room temperature, pure zirconia naturally exists in a monoclinic crystal structure. While stable, this phase is mechanically weaker and does not possess the properties required for dental restorations.
The Tetragonal Phase (High Temperature)
When heated above 1170°C, zirconia transforms into a tetragonal phase. This structure is significantly stronger and tougher, making it the ideal state for a dental crown. This is the phase that exists during the high-heat manufacturing process called sintering.
The Problem of Phase Transformation
Here lies the critical problem: when pure zirconia cools back down to room temperature, it wants to revert from the strong tetragonal phase to the weaker monoclinic phase. This transformation is accompanied by a significant volume expansion of about 4-5%, which introduces massive internal stresses and causes the material to crack and fail catastrophically.
The Solution: Yttria Stabilization
To make zirconia viable for dentistry, we must prevent this destructive phase transformation. This is achieved by adding a precise amount of a stabilizing agent, most commonly yttrium oxide (Y₂O₃).
Introducing Yttrium Oxide (Y₂O₃)
By adding a small percentage of yttrium oxide (typically 3 to 5 mole percent), a new material is created: Yttria-stabilized Tetragonal Zirconia Polycrystal (Y-TZP). This is the material commonly referred to as "zirconia" in dentistry.
Creating a "Metastable" State
The yttria wedges itself into the crystal lattice, effectively "freezing" the zirconia in its strong tetragonal phase even after it cools to room temperature. This is known as a metastable state—it's not the naturally preferred state, but it is stable enough for clinical use.
Transformation Toughening: Zirconia's Unique Defense
This metastability gives zirconia a remarkable property called transformation toughening. When a microscopic crack begins to form under stress (e.g., from chewing), the high energy at the crack tip triggers a localized phase change.
The material at the tip of the crack instantly transforms from the metastable tetragonal phase back to the more stable monoclinic phase. This transformation causes a localized volume expansion right where it's needed, creating a compressive force that squeezes the crack tip shut and stops it from propagating further. It is, in effect, a self-healing mechanism.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The amount of yttria added is not arbitrary; it's a careful balancing act between strength and aesthetics.
Strength vs. Translucency
Lower amounts of yttria (e.g., 3Y-TZP) result in a material that is almost entirely in the strong tetragonal phase. This makes it incredibly tough and fracture-resistant, but also more opaque.
Higher amounts of yttria (e.g., 5Y-TZP) create a mix of the tetragonal phase and a third, cubic phase. The cubic phase is weaker but much more translucent. This results in a more aesthetically pleasing material that looks more like a natural tooth, but at the cost of reduced fracture strength.
The Risk of Low-Temperature Degradation (LTD)
Over time, the presence of water (saliva) can cause a slow, superficial transformation of the tetragonal phase back to the monoclinic phase. This phenomenon, known as "aging," can slightly reduce the material's surface integrity. Modern dental zirconia formulations are engineered to be highly resistant to this, but it remains a fundamental property of the material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding how zirconia is stabilized allows you to select the appropriate material for a specific clinical need.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and durability (e.g., posterior crowns, multi-unit bridges): Choose a lower-yttria zirconia (3Y-TZP) for its superior fracture resistance due to a higher concentration of the tough tetragonal phase.
- If your primary focus is optimal aesthetics (e.g., anterior crowns, veneers): Opt for a higher-yttria zirconia (4Y-TZP or 5Y-TZP) that incorporates the more translucent cubic phase, sacrificing some strength for a more lifelike appearance.
- If your primary focus is balancing strength and aesthetics: Consider a multi-layered zirconia disc, which uses a stronger, more opaque composition in the cervical third and a more translucent composition in the incisal third.
Mastering the science of stabilization empowers you to harness the full potential of zirconia for predictable and highly successful patient outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Material | Zirconium dioxide (ZrO₂) stabilized with yttrium oxide (Y₂O₃) |
| Stabilized Form | Yttria-stabilized Tetragonal Zirconia Polycrystal (Y-TZP) |
| Key Benefits | High strength, fracture resistance, transformation toughening for self-healing |
| Common Yttria Levels | 3Y-TZP (high strength), 4Y-TZP (balanced), 5Y-TZP (high translucency) |
| Applications | Dental crowns, bridges, veneers based on strength and aesthetic needs |
Unlock the potential of advanced dental ceramics with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong customization capabilities ensure precise sintering and processing of materials like zirconia to meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your dental material outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the step-by-step process for making porcelain dental restorations? Master Precision and Aesthetics
- What are some recent innovations in dental lab equipment furnaces? Boost Efficiency with Smart Automation
- What happens if the timing is incorrect during a dental furnace operation? Avoid Ruined Restorations
- What are the risks of inadequate dental furnace ventilation? Protect Your Lab Quality & Team Safety
- How does precise temperature control in a porcelain furnace benefit sintering? Achieve Perfect Dental Restorations



















