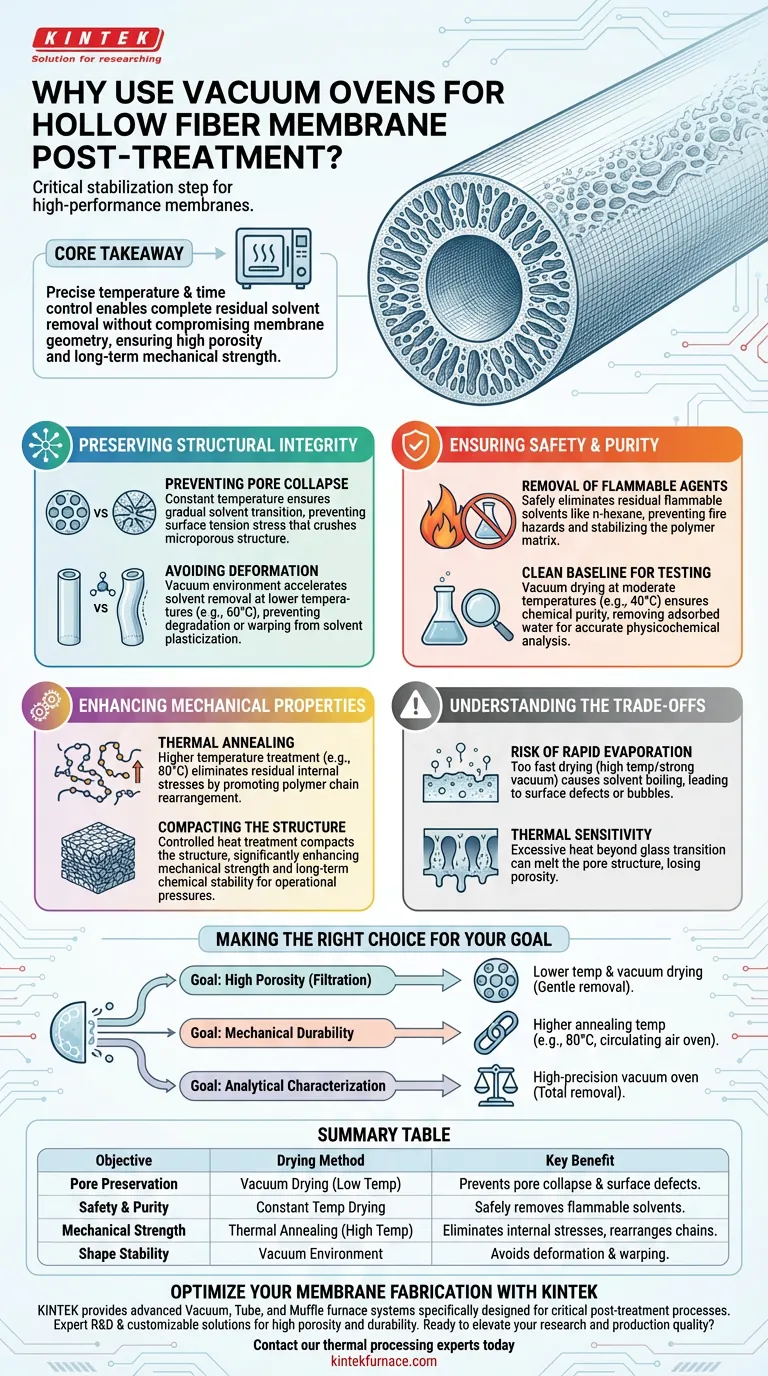
The use of vacuum ovens or constant temperature drying is a critical stabilization step in hollow fiber membrane fabrication. Its primary function is to safely remove residual flammable solvents, such as n-hexane, while preventing the fragile microporous structure from collapsing or shrinking violently under drying stress.
Core Takeaway By precisely controlling temperature and time, this equipment allows for the complete removal of solvents without compromising the membrane’s geometry. This balance is essential for preserving high porosity and setting the mechanical strength required for long-term performance.

Preserving Structural Integrity
Preventing Pore Collapse
The most critical function of controlled drying is maintaining the membrane's architecture.
If solvents evaporate too quickly or unevenly, the surface tension can generate stress that crushes the pores. Constant temperature drying ensures a gradual transition, preserving the microporous structure and high porosity vital for filtration efficiency.
Avoiding Plasticization and Deformation
Residual solvents can act as plasticizers, keeping the polymer soft and susceptible to deformation.
Using a vacuum environment accelerates solvent removal at lower temperatures (e.g., 60°C). This prevents the fibers from degrading or warping due to solvent plasticization, ensuring the membrane retains the correct shape when removed from the collector.
Ensuring Safety and Purity
Removal of Flammable Agents
Post-treatment often involves solvent exchange with volatile liquids like n-hexane.
Controlled drying safely eliminates these residual flammable solvents. This is not only a safety protocol to prevent fire hazards but also a chemical necessity to stabilize the polymer matrix.
Establishing a Clean Baseline for Testing
For experimental accuracy, membranes must be free of physically adsorbed water and solvent molecules.
Vacuum drying at moderate temperatures (e.g., 40°C) ensures the material is chemically pure. This allows for accurate measurement of physicochemical parameters, such as swelling rates and water vapor transmission rates (WVTR), without interference from trapped moisture.
Enhancing Mechanical Properties
Thermal Annealing
Beyond simple drying, these ovens provide a uniform thermal field for annealing membranes.
Treatment at higher temperatures (e.g., 80°C) promotes the rearrangement of polymer chains. This process eliminates residual internal stresses generated during the membrane-forming process, leading to a more stable material.
Compacting the Structure
Controlled heat treatment helps "lock in" the final properties of the membrane.
By compacting the membrane structure, the drying process significantly enhances both mechanical strength and long-term chemical stability. This is particularly important for composite membranes that must withstand operational pressures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Rapid Evaporation
While efficiency is important, drying too fast is detrimental.
If the temperature is too high or the vacuum too strong initially, solvents may boil within the matrix. This causes surface defects or bubbles, damaging the skin layer of the membrane.
Thermal Sensitivity
Heat is necessary for annealing, but excessive heat can be destructive.
Overheating the polymer beyond its glass transition temperature without careful control can lead to a loss of porosity. The goal is to remove the solvent, not to melt the pore structure you worked hard to create.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Depending on the specific requirements of your membrane application, your drying strategy should adjust:
- If your primary focus is High Porosity (Filtration): Prioritize lower temperatures and vacuum drying to gently remove solvents without collapsing the micropores.
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Durability: Utilize a circulating air oven at higher annealing temperatures (e.g., 80°C) to relieve internal stress and compact the polymer chains.
- If your primary focus is Analytical Characterization: Use a high-precision vacuum oven to ensure total solvent and moisture removal for reproducible gravimetric data.
Successful post-treatment is defined by the balance between thorough solvent removal and the preservation of the membrane's delicate porous architecture.
Summary Table:
| Objective | Drying Method | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Pore Preservation | Vacuum Drying (Low Temp) | Prevents pore collapse and surface defects from drying stress. |
| Safety & Purity | Constant Temp Drying | Safely removes flammable solvents like n-hexane for a clean baseline. |
| Mechanical Strength | Thermal Annealing (High Temp) | Eliminates internal stresses and promotes polymer chain rearrangement. |
| Shape Stability | Vacuum Environment | Avoids deformation and warping caused by solvent plasticization. |
Optimize Your Membrane Fabrication with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between a high-performance membrane and a collapsed structure. KINTEK provides advanced Vacuum, Tube, and Muffle furnace systems specifically designed for critical post-treatment processes like solvent removal and thermal annealing.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our equipment is fully customizable to meet your unique lab requirements—ensuring you achieve high porosity and mechanical durability every time.
Ready to elevate your research and production quality? Contact our thermal processing experts today to find the perfect solution for your high-temperature laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Synthesis and Characterization of Polysulfone/Peat Clay Hollow Fibre Membranes: The Effect of Composition and Morphology. DOI: 10.37934/arfmts.126.2.86105
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace for Dental Laboratories
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-precision vacuum drying oven play in composite electrolyte membranes? Ensure High Purity & Integrity
- What are the primary functions of a laboratory drying oven in banana peel activated carbon? Optimize Every Process Step
- How do continuous vacuum furnaces contribute to metal annealing and hardening? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Purity
- What is the function of a vacuum drying oven in processing mixed TiB2-SiC slurries? Protect Material Integrity
- What are the features of a Front Loading/Horizontal Furnace? Unlock Precision Heat Treatment
- Why is short-term annealing followed by water quenching necessary for Ti-15Mo alloys? Lock in Peak Material Performance
- How does a graphite resistance furnace facilitate the nitridation of silicon powder? Achieve Ceramic Excellence
- What environmental benefits do continuous vacuum furnaces provide? Achieve Zero Emissions and High Efficiency



















