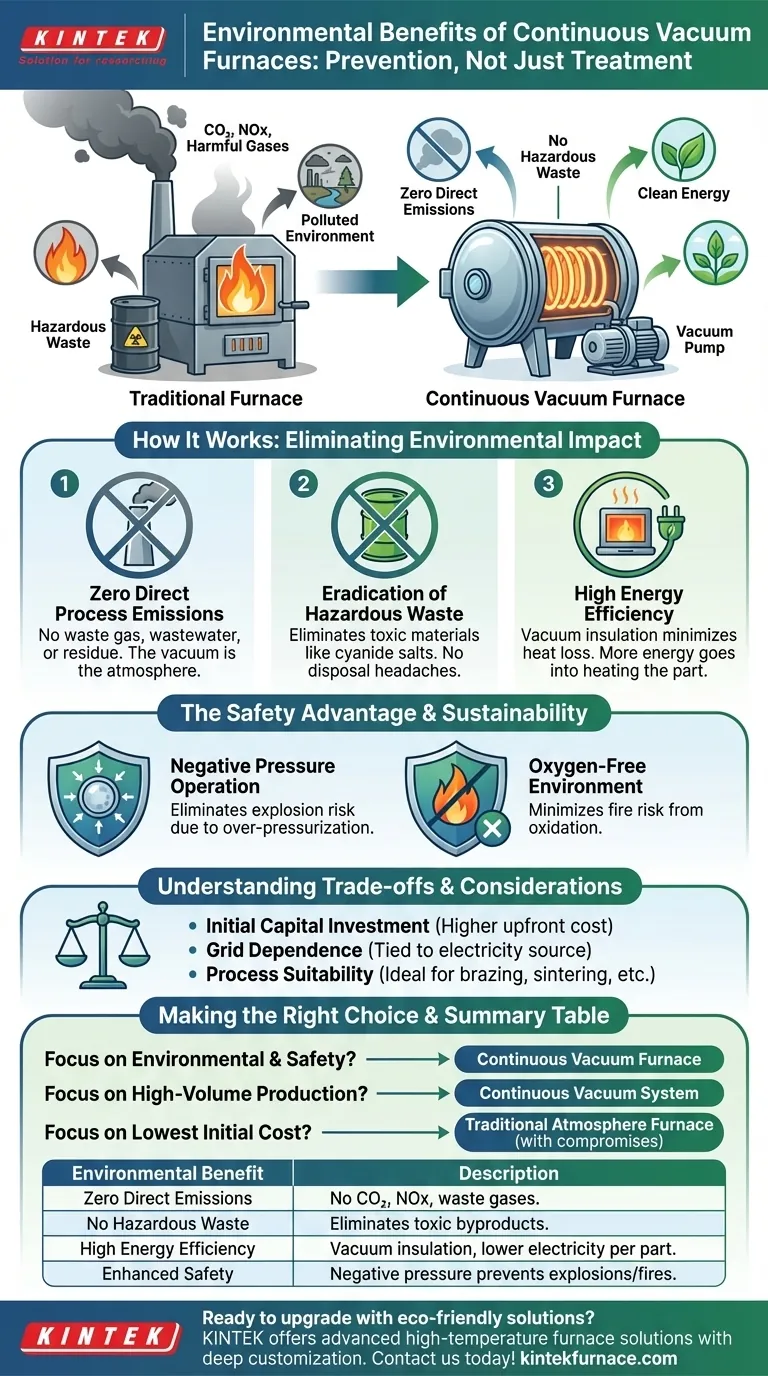
At their core, continuous vacuum furnaces offer significant environmental benefits by fundamentally changing the nature of the heat treatment process. Instead of burning fuel or using chemical atmospheres, they use a clean vacuum environment, which results in zero direct process emissions, eliminates hazardous waste byproducts, and achieves high energy efficiency.
The primary environmental advantage of a continuous vacuum furnace is not in treating pollution, but in preventing its creation altogether. By replacing combustible fuels and chemical atmospheres with a clean vacuum, these systems eliminate the source of emissions and hazardous waste inherent in traditional furnace technologies.

How Vacuum Furnaces Eliminate Environmental Impact
The environmental benefits of a vacuum furnace stem directly from its core operating principle: creating a controlled environment devoid of air and other reactive gases. This elegant solution sidesteps many of the ecological drawbacks of older methods.
Zero Direct Process Emissions
Traditional furnaces often rely on the combustion of fossil fuels for heat and the use of specific gas atmospheres (like endothermic gas) for process control. This combustion directly produces pollutants such as CO₂, NOx, and other harmful flue gases.
A vacuum furnace, being electrically powered and operating in a vacuum, produces no waste gas, wastewater, or waste residue during its operation. The "atmosphere" is the vacuum itself, eliminating the need for combustible or chemical gas mixtures and their associated emissions.
Eradication of Hazardous Waste
Many conventional heat-treating processes, particularly older ones like salt bath hardening or pack carburizing, generate significant toxic waste. This includes land-contaminating cyanide salts and difficulties in disposing of contaminated fixtures and waste materials.
Continuous vacuum furnaces completely eliminate the use and disposal of these toxic materials. This not only prevents environmental contamination but also removes a major operational headache and long-term liability associated with managing hazardous waste.
High Energy Efficiency
Vacuum is an exceptional thermal insulator. This, combined with modern furnace construction, results in excellent thermal insulation and minimal heat loss to the surrounding environment. This means more of the energy consumed goes directly into heating the workpiece.
This inherent high energy utilization rate reduces the overall electricity required per part. While the furnace consumes electricity, its efficiency minimizes the indirect environmental footprint associated with power generation.
The Safety Advantage: A Key Part of Sustainability
A modern definition of sustainability includes not just environmental protection but also social responsibility, where workplace safety is paramount. Vacuum furnaces provide a demonstrably safer operating environment.
Operating at Negative Pressure
Atmosphere furnaces operate at a positive pressure, creating a risk of explosion if pressure builds uncontrollably. Vacuum furnaces operate at a negative pressure.
This design inherently eliminates the risk of explosion due to over-pressurization. A leak in a vacuum system results in air flowing in, not a dangerous gas flowing out.
An Oxygen-Free Environment
The low-oxygen vacuum environment significantly reduces operational hazards. It minimizes the risk of fire that can be caused by the rapid oxidation of hot materials or flammable lubricants when exposed to air in a conventional furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While the benefits are clear, a comprehensive evaluation requires acknowledging the trade-offs. No technology is a universal solution, and vacuum furnaces are no exception.
Initial Capital Investment
Continuous vacuum furnace systems represent a significant upfront capital investment. They are complex machines that are more expensive to purchase than many traditional atmosphere furnaces. This cost must be weighed against the long-term operational savings, reduced compliance costs, and elimination of waste disposal fees.
Dependence on the Electrical Grid
While highly efficient, these furnaces are entirely dependent on electricity. Therefore, their "green" credentials are tied to the source of that electricity. If the power grid relies heavily on fossil fuels, the furnace still has an indirect carbon footprint, albeit a smaller one due to its efficiency.
Process Suitability
Vacuum processing is ideal for a wide range of applications, including brazing, sintering, hardening, and annealing. However, it is not suitable for all metallurgical processes. Certain case hardening methods, for example, may still require specialized atmosphere furnaces, though hybrid technologies are closing this gap.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate furnace technology requires balancing your operational goals with your commitment to environmental and safety standards.
- If your primary focus is environmental compliance and workplace safety: A continuous vacuum furnace is the definitive choice, as it eliminates direct emissions, hazardous waste, and common explosion or fire risks.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, high-quality production: The process control and automation of a continuous vacuum system deliver superior part consistency and throughput for mass manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial capital cost: Traditional atmosphere furnaces may present a lower upfront investment, but this comes with the known compromises of ongoing emission management, waste disposal, and higher safety risks.
Investing in continuous vacuum technology is a strategic decision that aligns operational excellence with modern environmental and social responsibility.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Zero Direct Emissions | No CO₂, NOx, or waste gases produced during operation. |
| No Hazardous Waste | Eliminates toxic byproducts like cyanide salts from processes. |
| High Energy Efficiency | Vacuum insulation reduces heat loss, lowering electricity use per part. |
| Enhanced Safety | Negative pressure design prevents explosions and fire risks. |
Ready to upgrade your lab with eco-friendly and efficient furnace solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to learn how our vacuum furnaces can reduce your environmental impact and enhance operational safety!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the proper procedures for handling the furnace door and samples in a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Integrity & Safety
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in LP-DED? Optimize Alloy Integrity Today
- What are the components of a vacuum furnace? Unlock the Secrets of High-Temperature Processing
- Why does heating steel rod bundles in a vacuum furnace eliminate heat transfer paths? Enhance Surface Integrity Today
- What are the general operational features of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity & Precision



















