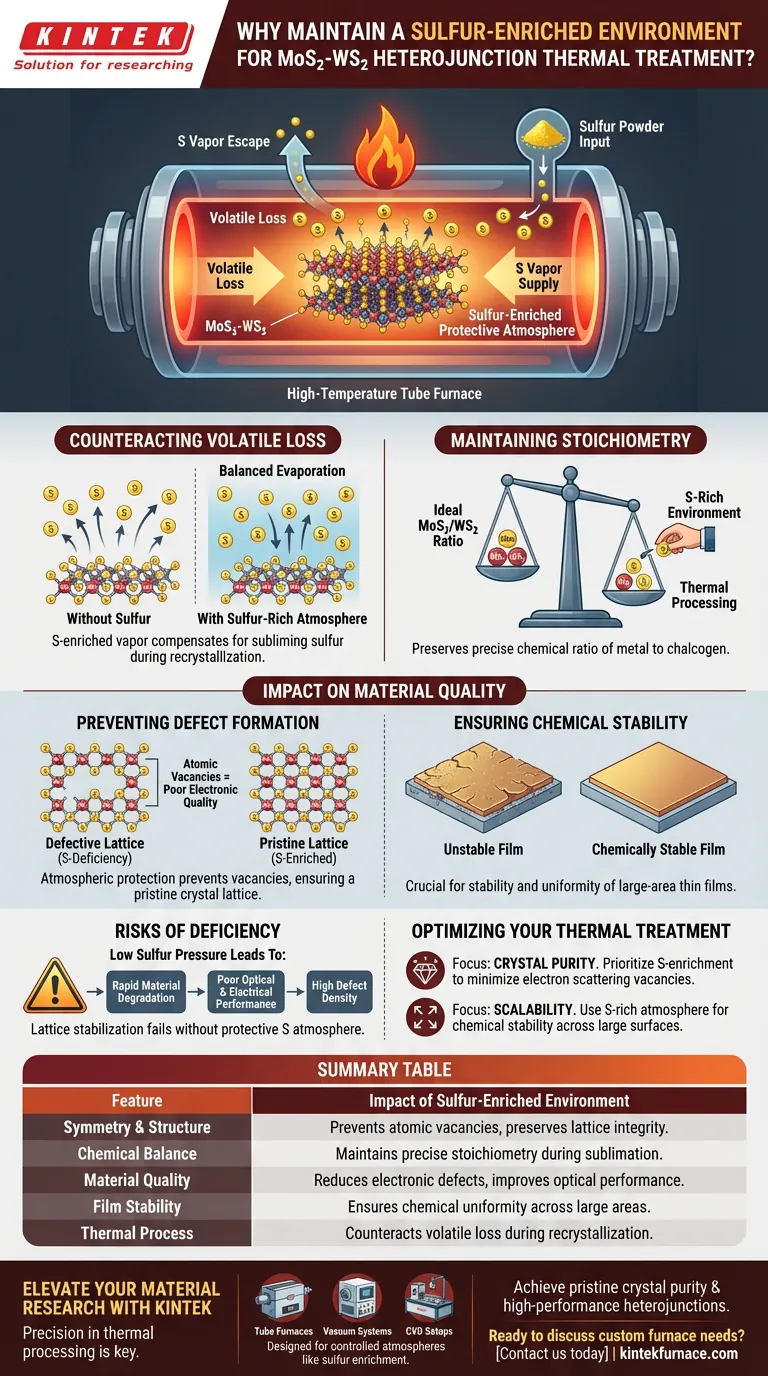
The primary purpose of maintaining a sulfur-enriched environment is to counteract the volatile loss of sulfur that inevitably occurs during high-temperature processing. By introducing sulfur powder into the tube furnace, you create a protective atmosphere that actively compensates for evaporating sulfur atoms, thereby preserving the material's fundamental chemical structure.
High-temperature treatment of MoS2-WS2 heterojunctions inherently drives sulfur out of the material. A sulfur-rich environment acts as a vital equilibrium buffer, preventing sulfur deficiency to ensure the structural integrity and chemical stability of the final thin film.
The Mechanics of Sulfur Compensation
Counteracting Volatile Loss
During thermal treatments like recrystallization, the temperatures required to process MoS2 and WS2 are high enough to cause sulfur atoms to sublime.
Without intervention, these atoms escape the solid material and enter the gas phase.
The sulfur-enriched atmosphere provides a reservoir of sulfur vapor that compensates for this loss immediately, effectively balancing the evaporation rate.
Maintaining Stoichiometry
The functionality of MoS2-WS2 heterojunctions relies on a precise chemical ratio, known as stoichiometry.
Thermal processing threatens this balance by selectively removing the lighter, more volatile sulfur component.
By maintaining a sulfur-rich environment, you ensure the material retains the correct ratio of metal to chalcogen atoms.
Impact on Material Quality
Preventing Defect Formation
When sulfur atoms leave the crystal lattice without replacement, they leave behind atomic "holes" known as vacancies.
These sulfur deficiency defects severely degrade the electronic quality of the material.
The protective sulfur atmosphere prevents these defects from forming, resulting in a pristine crystal lattice.
Ensuring Chemical Stability
The primary reference highlights that this atmospheric protection is critical for the stability of large-area thin films.
Thin films are particularly vulnerable to degradation because of their high surface-to-volume ratio.
A sulfur-enriched environment ensures the film remains chemically stable and uniform across its entire area.
Understanding the Risks of Deficiency
The Consequence of Low Sulfur Pressure
If the tube furnace environment lacks sufficient sulfur, the "protective" mechanism fails.
This leads to rapid degradation of the material's properties as the lattice attempts to stabilize itself with fewer sulfur atoms.
The result is often a film with poor optical and electrical performance due to a high density of defects.
Optimizing Your Thermal Treatment
To ensure the highest quality MoS2-WS2 heterojunctions, consider the following regarding your specific goals:
- If your primary focus is crystal purity: Prioritize the sulfur enrichment to minimize vacancy defects, which act as scattering centers for electrons.
- If your primary focus is scalability: Use the sulfur-rich atmosphere to ensure chemical stability across the entire surface of large-area thin films.
By controlling the sulfur environment, you turn a destructive high-temperature process into a constructive recrystallization step.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact of Sulfur-Enriched Environment |
|---|---|
| Symmetry & Structure | Prevents atomic vacancies and preserves crystal lattice integrity. |
| Chemical Balance | Maintains precise metal-to-chalcogen stoichiometry during sublimation. |
| Material Quality | Reduces electronic defects and improves optical performance. |
| Film Stability | Ensures chemical uniformity across large-area thin films. |
| Thermal Process | Counteracts volatile loss during high-temperature recrystallization. |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision in thermal processing is the difference between a defective sample and a high-performance heterojunction. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-precision Tube Furnaces, Vacuum systems, and CVD setups specifically designed for controlled atmospheres like sulfur enrichment.
Whether you need customizable high-temp furnaces for recrystallization or large-scale thin film production, our engineering team ensures your equipment meets your unique stoichiometry requirements.
Ready to achieve pristine crystal purity? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Matteo Gardella, F. Buatier de Mongeot. Large area van der Waals MoS<sub>2</sub>–WS<sub>2</sub> heterostructures for visible-light energy conversion. DOI: 10.1039/d3lf00220a
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
People Also Ask
- What type of pumps are used in low vacuum atmosphere furnaces? Rotary Vane Pumps for Efficient Heat Treatment
- What protective function does furnace atmosphere provide? Essential for Preventing Oxidation and Decarburization
- What challenges are associated with using inert atmospheres? Overcome Costs, Safety, and Complexity
- Why is atmosphere control critical for heat treatment quality? Unlock Precision and Durability
- Why are sealing mechanisms critical in atmosphere furnaces? Ensure Purity, Safety, and Efficiency
- What is the function of low-oxygen controlled powder sintering in Cu-Fe-Zn alloys? Master Interstitial Strengthening
- What is the purpose of sealing mechanisms in atmosphere furnaces? Ensure Process Purity and Safety
- What safety features are included in the box type annealing atmosphere furnace? Ensure Operator and Equipment Protection



















