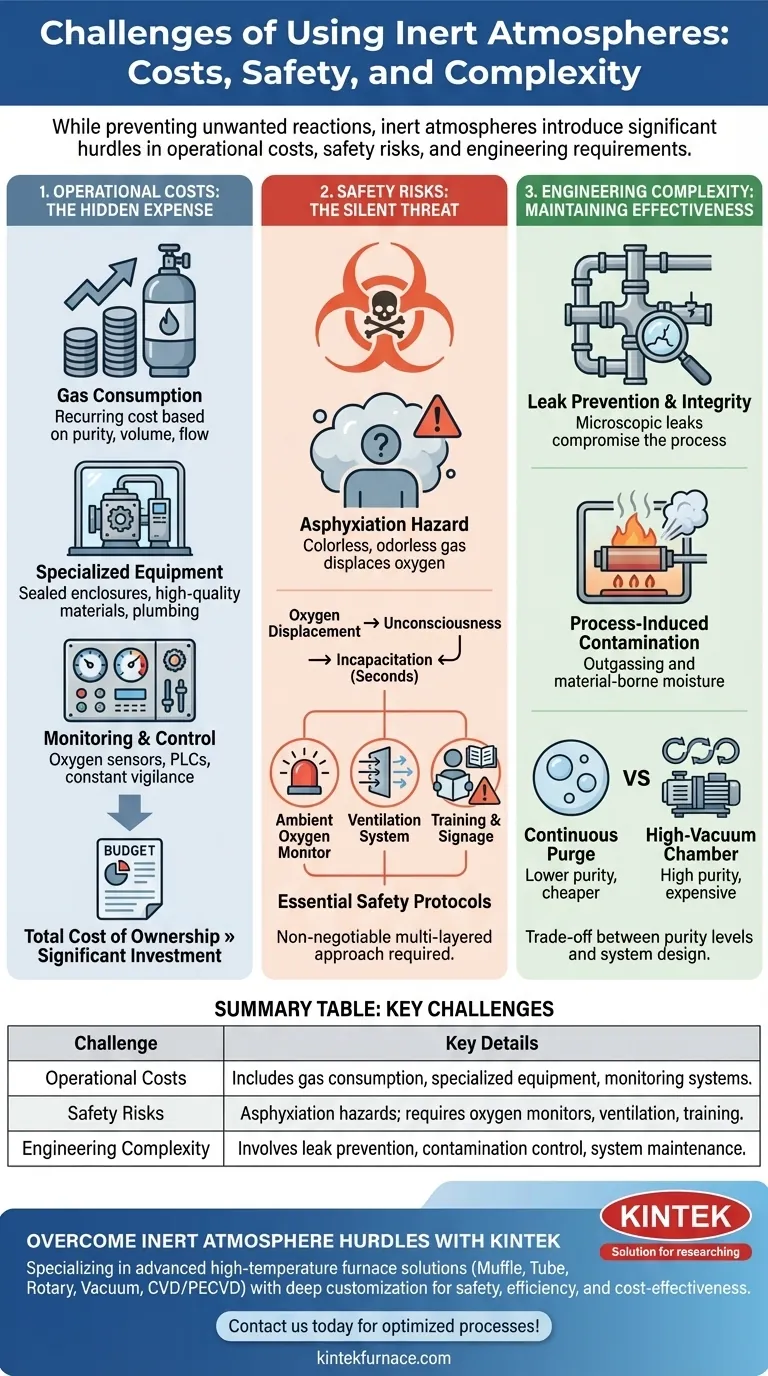
While incredibly effective for preventing unwanted chemical reactions, the primary challenges of using inert atmospheres are significant operational costs, critical safety risks like asphyxiation, and the engineering complexity required to implement and maintain them effectively. These are not minor considerations but fundamental hurdles that must be addressed in any system design.
The core challenge is not simply introducing an inert gas, but engineering a complete system that can reliably maintain a non-reactive environment while guaranteeing personnel safety and managing continuous operational costs.

The Hidden Costs: Beyond the Gas Itself
Adopting an inert atmosphere is an investment that extends far beyond the price of nitrogen or argon gas. The total cost of ownership is often driven by the supporting infrastructure.
Direct Gas Consumption
The price of the inert gas is a recurring operational expense. Costs are dictated by the required purity level, the volume needed, and the flow rate necessary to displace oxygen and compensate for any system leaks.
Specialized Equipment and Infrastructure
Standard equipment is rarely sufficient. Achieving an inert environment often requires sealed enclosures like gloveboxes, specially designed heat-treating furnaces, or vacuum systems capable of first removing ambient air before backfilling with the inert gas.
This includes specialized plumbing, high-quality seals, and non-reactive materials to prevent contamination and leaks, all of which add significant capital expense.
Monitoring and Control Systems
You cannot simply fill a chamber and hope for the best. Maintaining the atmosphere requires constant vigilance, typically through automated systems. This means investing in oxygen sensors, pressure gauges, and programmable logic controllers (PLCs) to manage gas flow and purge cycles.
The Silent Risk: Managing Asphyxiation Hazards
The most severe challenge is the risk to human life. Because inert gases displace oxygen, they create an immediate and silent threat in any enclosed or poorly ventilated space.
The Danger of Oxygen Displacement
Inert gases like nitrogen and argon are colorless and odorless. They do not trigger a choking sensation or other warning signs from the body before a person loses consciousness. An individual can walk into an oxygen-deficient environment and become incapacitated in seconds.
Essential Safety Protocols
Mitigating this risk is non-negotiable. It requires a multi-layered safety approach including ambient oxygen monitors with alarms, robust ventilation systems, clear warning signage, and rigorous training for all personnel working near the equipment.
The Engineering Hurdle: Maintaining Effectiveness
Creating an inert atmosphere is one challenge; maintaining its purity during operation is another entirely. The effectiveness of the system is constantly threatened by contamination.
The Constant Battle Against Leaks
Even microscopic leaks in seals, welds, or fittings can allow atmospheric oxygen to seep into the chamber, compromising the entire process. Designing, building, and maintaining a truly leak-tight system is a significant engineering effort.
Process-Induced Contamination
The process itself can be a source of contamination. Materials brought into the chamber can carry absorbed moisture and air, which is then released. Heating components can also cause them to "outgas," releasing trapped gases that pollute the inert environment.
The Trade-off Between Purity and Complexity
Simpler methods like continuous gas bubbling or purging may be cheaper but are often less effective at achieving very low oxygen levels. High-purity applications demand more complex and expensive systems, such as a high-vacuum chamber that is pumped down and backfilled multiple times to ensure purity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your strategy for implementing an inert atmosphere must be aligned with your specific technical requirements and safety obligations.
- If your primary focus is absolute purity for sensitive electronics or chemical synthesis: You must invest in a high-integrity, sealed system like a glovebox or vacuum furnace with continuous oxygen monitoring.
- If your primary focus is bulk oxidation prevention in processes like welding or heat treating: A continuous purge system may be sufficient, but you must validate its effectiveness and prioritize robust safety monitoring for personnel.
- If your primary focus is safety in any application: Non-negotiable elements include ambient oxygen monitors, engineered ventilation, and comprehensive personnel training on the dangers of asphyxiation.
Ultimately, a successful inerting strategy depends on treating the atmosphere not as a simple utility, but as a critical, engineered system.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Operational Costs | Includes gas consumption, specialized equipment (e.g., sealed enclosures), and monitoring systems (e.g., oxygen sensors). |
| Safety Risks | Asphyxiation hazards from oxygen displacement; requires oxygen monitors, ventilation, and training. |
| Engineering Complexity | Involves leak prevention, contamination control, and system maintenance for purity and effectiveness. |
Struggling with inert atmosphere challenges in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs, ensuring safety, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you overcome these hurdles and optimize your processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment



















