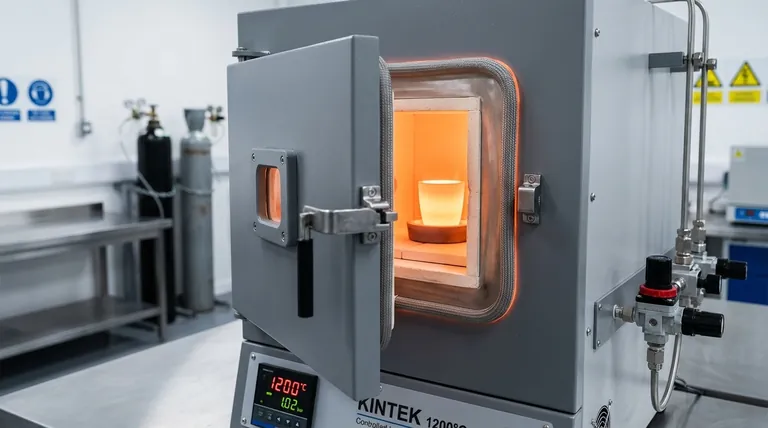
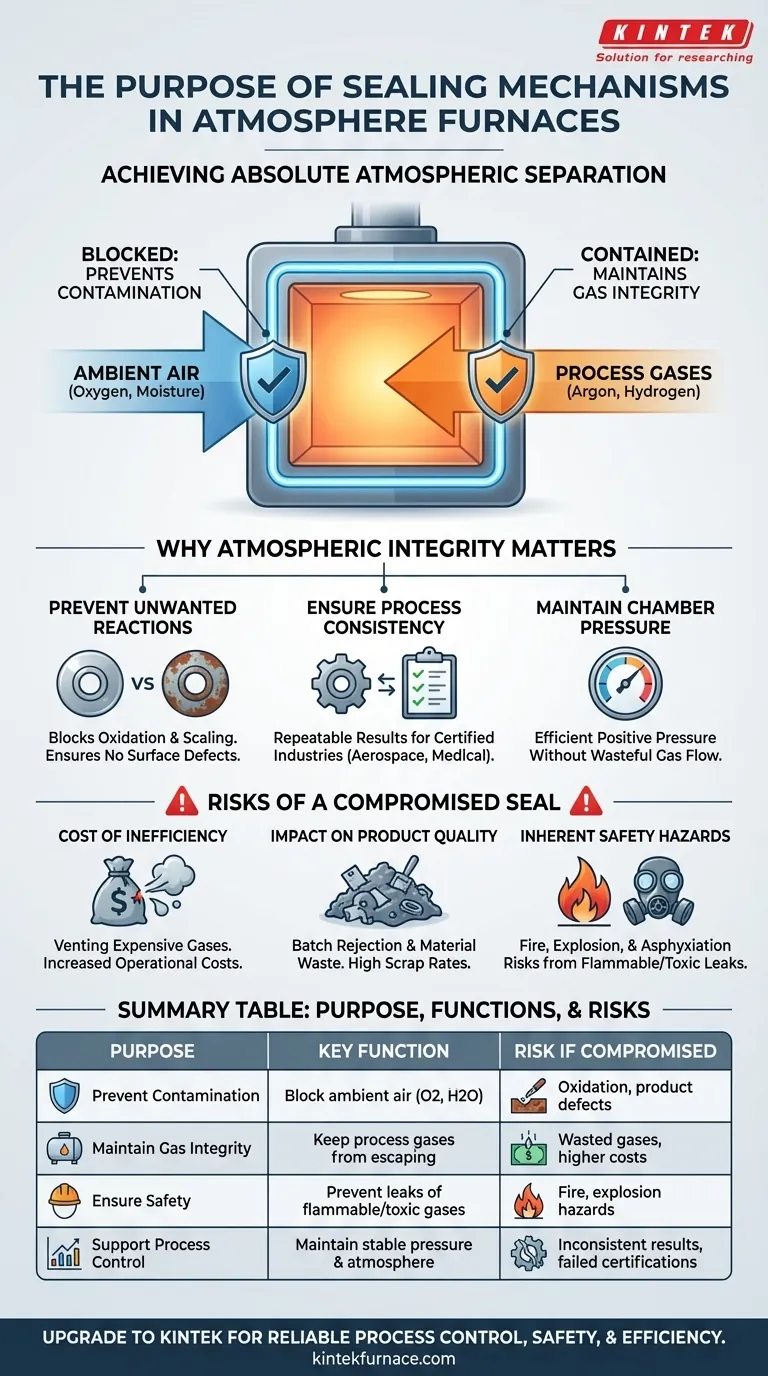
At its core, the purpose of a sealing mechanism in an atmosphere furnace is to achieve absolute atmospheric separation. These systems are designed to perform two critical and opposing functions simultaneously: they prevent the uncontrolled ambient air of the surrounding environment from contaminating the process, and they keep the carefully controlled process gases from escaping the furnace chamber.
The integrity of the furnace seal is not a secondary detail; it is the fundamental enabler of process control. A compromised seal directly jeopardizes product quality, operational efficiency, and workplace safety, rendering the "atmosphere" aspect of the furnace ineffective.

The Critical Role of Atmospheric Integrity
An atmosphere furnace is, by definition, a tool for manipulating materials within a specific gaseous environment. The sealing mechanism is what makes this controlled environment possible.
Preventing Unwanted Chemical Reactions
Many advanced material processes, such as bright annealing or brazing, must occur in an environment free of oxygen. The primary role of the seal is to block ambient air—which contains approximately 21% oxygen and 78% nitrogen, plus moisture—from entering the hot zone.
Even a small leak can introduce contaminants that cause unwanted oxidation, scaling, or discoloration on the part's surface, ruining the final product.
Ensuring Process Consistency
High-value manufacturing demands repeatable results. A perfectly intact seal ensures the internal atmosphere remains stable and predictable from one batch to the next.
This atmospheric integrity is what guarantees that each part is exposed to the exact same conditions, which is critical for consistent processing results and achieving certifications in industries like aerospace or medical devices.
Maintaining Chamber Pressure
Many processes operate under a slight positive pressure. This design helps to push any potential contaminants out if a minor leak were to occur.
An effective sealing system is essential to maintain this pressure without requiring an excessive and wasteful flow of expensive process gases like argon or hydrogen.
Sealing as a Core Design Principle
The need for a robust seal is a primary differentiator between a simple furnace and a true atmosphere furnace.
Atmosphere vs. Standard Box Furnaces
A standard box furnace may have a basic seal on its door, but its main purpose is to contain heat. Its internal atmosphere is not a controlled variable.
In contrast, an atmosphere furnace is engineered around its sealing system. It requires a highly sealed structure, complete with gas inlets, outlets, and pressure control systems, to reliably manage the internal environment. This complexity is why they have a more involved manufacturing process and higher cost.
The Components of a Sealing System
These systems rely on components designed to withstand extreme conditions. This includes high-temperature seals and gaskets made from specialized materials that resist thermal degradation and chemical attack from the process gases.
Understanding the Risks of a Compromised Seal
A failing seal is not a minor inconvenience; it is a critical failure with significant consequences.
The Cost of Inefficiency
Controlled atmospheres are created using purified, and often expensive, gases. A leaking seal means you are constantly venting costly gas into the facility, driving up operational costs significantly. This is a direct and quantifiable financial loss.
The Impact on Product Quality
Atmospheric contamination is a leading cause of product rejection. A compromised seal can lead to an entire batch of parts being scrapped due to oxidation or other surface defects, resulting in wasted materials, time, and labor.
The Inherent Safety Hazards
Many atmosphere processes use flammable gases like hydrogen or dissociated ammonia. A leak in the furnace seal can release these gases into the surrounding work area, creating a serious risk of fire or explosion. Similarly, leaks of inert gases can create an asphyxiation hazard in confined spaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Understanding the purpose of sealing allows you to properly prioritize its role in your operation.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability and quality: View the sealing system not as a component, but as the very foundation of your process control.
- If your primary focus is operational cost and efficiency: Regularly inspect and maintain furnace seals to prevent the significant financial drain from wasted process gases.
- If your primary focus is safety: Treat any known seal degradation as an immediate and critical safety risk, especially when working with flammable or toxic atmospheres.
Ultimately, a robust sealing mechanism is what transforms a simple hot box into a precise, reliable metallurgical tool.
Summary Table:
| Purpose | Key Functions | Risks if Compromised |
|---|---|---|
| Prevent Contamination | Block ambient air (oxygen, moisture) | Oxidation, product defects |
| Maintain Gas Integrity | Keep process gases from escaping | Wasted gases, higher costs |
| Ensure Safety | Prevent leaks of flammable/toxic gases | Fire, explosion hazards |
| Support Process Control | Maintain stable pressure and atmosphere | Inconsistent results, failed certifications |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced atmosphere furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs for superior process control, safety, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity



















