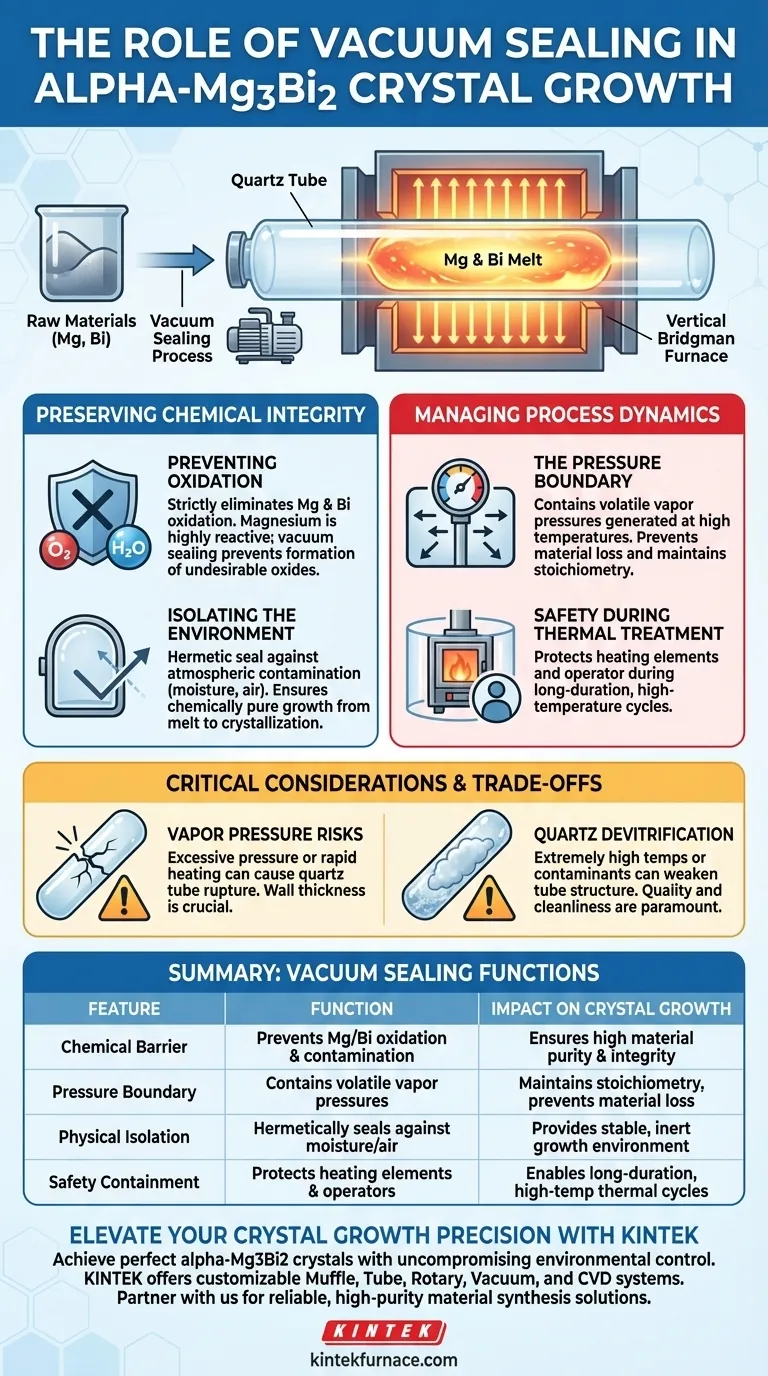
The primary purpose of vacuum sealing raw materials in a quartz tube for alpha-Mg3Bi2 crystal growth is to create an isolated, chemically inert environment. This step serves to strictly prevent the oxidation of metallic magnesium (Mg) and bismuth (Bi) during high-temperature melting, while simultaneously acting as a critical pressure boundary to ensure process safety during long-duration thermal treatments.
Core Insight Vacuum sealing serves a dual role: it acts as a chemical barrier against atmospheric contamination (specifically oxygen and moisture) and a physical containment vessel. Without this isolation, the high reactivity of magnesium would degrade the material purity, and the internal pressures generated during the vertical Bridgman process could compromise the growth furnace.

Preserving Chemical Integrity
To grow high-quality alpha-Mg3Bi2 crystals, maintaining the precise chemical composition of the melt is non-negotiable. The vacuum sealing process is the first line of defense in material synthesis.
Preventing Oxidation
Magnesium and bismuth are susceptible to oxidation at high temperatures. Magnesium, in particular, is highly reactive with oxygen. If exposed to air during the melting phase, the raw materials would form oxides rather than the desired crystal compound. Vacuum sealing eliminates this variable entirely.
Isolating the Environment
The quartz tube acts as a hermetic seal against the ambient atmosphere. This isolation prevents moisture and other airborne contaminants from entering the melt. It ensures that the growth environment remains chemically pure from the initial melting stage through to crystallization.
Managing Process Dynamics
Beyond chemical purity, the quartz tube serves a structural function. The alpha-Mg3Bi2 growth process typically utilizes the vertical Bridgman technique, which imposes specific physical demands on the containment vessel.
The Pressure Boundary
During high-temperature synthesis, the volatile components within the tube can generate significant internal vapor pressure. The sealed quartz tube acts as a robust pressure boundary. It contains these vapors, preventing material loss that would alter the stoichiometry (the ratio of Mg to Bi) of the final crystal.
Safety During Thermal Treatment
The crystal growth process involves long-duration thermal treatments. The sealed tube protects the furnace heating elements and the operator by containing the melt. This ensures that the process remains safe and stable throughout the extended heating and cooling cycles required for single crystal growth.
Critical Considerations and Trade-offs
While vacuum sealing in quartz is the industry standard for this process, it is not without physical limitations that must be managed.
Vapor Pressure Risks
Although the tube acts as a pressure boundary, there is a limit to the internal pressure a quartz tube can withstand. If the temperature is raised too quickly or exceeds the design limits of the tube's wall thickness, the internal vapor pressure of the magnesium can cause the tube to rupture.
Quartz Devitrification
At extremely high temperatures or in the presence of certain contaminants, quartz can undergo devitrification (crystallization). This weakens the structural integrity of the tube. While quartz is generally suitable for Mg-Bi growth temperatures, the tube quality and cleanliness are paramount to prevent failure during long runs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Success in growing alpha-Mg3Bi2 depends on how strictly you manage the sealing and heating parameters.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Prioritize a high-vacuum base pressure (low background pressure) before sealing to remove every trace of oxygen and moisture, as magnesium is unforgiving of contaminants.
- If your primary focus is Process Safety: Calculate the expected vapor pressure of Magnesium at your peak temperature and ensure the quartz tube wall thickness provides a sufficient safety margin against rupture.
Ultimately, the sealed quartz tube is not just a container; it is an active component that defines the chemical purity and physical safety of your crystal growth process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function | Impact on Crystal Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Barrier | Prevents Mg/Bi oxidation and contamination | Ensures high material purity and integrity |
| Pressure Boundary | Contains volatile vapor pressures | Maintains stoichiometry and prevents material loss |
| Physical Isolation | Hermetically seals against moisture/air | Provides a stable, inert growth environment |
| Safety Containment | Protects heating elements and operators | Enables long-duration, high-temp thermal cycles |
Elevate Your Crystal Growth Precision with KINTEK
Achieving the perfect alpha-Mg3Bi2 crystal requires uncompromising environmental control and thermal stability. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with other high-performance lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique research requirements.
Don't let oxidation or pressure instability compromise your results. Partner with KINTEK for reliable, high-purity material synthesis solutions. Contact us today to discuss your project and request a custom quote!
Visual Guide
References
- Mingyuan Hu, Jiaqing He. Helical dislocation-driven plasticity and flexible high-performance thermoelectric generator in α-Mg3Bi2 single crystals. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55689-7
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum sintering and where is it commonly used? Discover High-Purity Material Processing
- What is the function of a vacuum oven in TiN/MoS2 coating? Master the Curing Process for Superior Film Integrity
- What is the principle of graphite furnace? Master Ultra-Trace Element Analysis with Precise Heating
- What are the primary applications of vacuum furnaces? Achieve High-Purity Heat Treatment for Aerospace and Medical
- How does the vacuum pumping system perform in terms of pump down times? Achieve Faster Evacuation for Your Lab
- What operational flexibility do multiple-chamber vacuum furnaces provide? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Processing
- How does the pressure environment affect the metallic thermal reduction for titanium? Master Precision Control
- How do the radiant heating and controlled cooling functions of a vacuum brazing furnace benefit Kovar-to-SS joints?



















