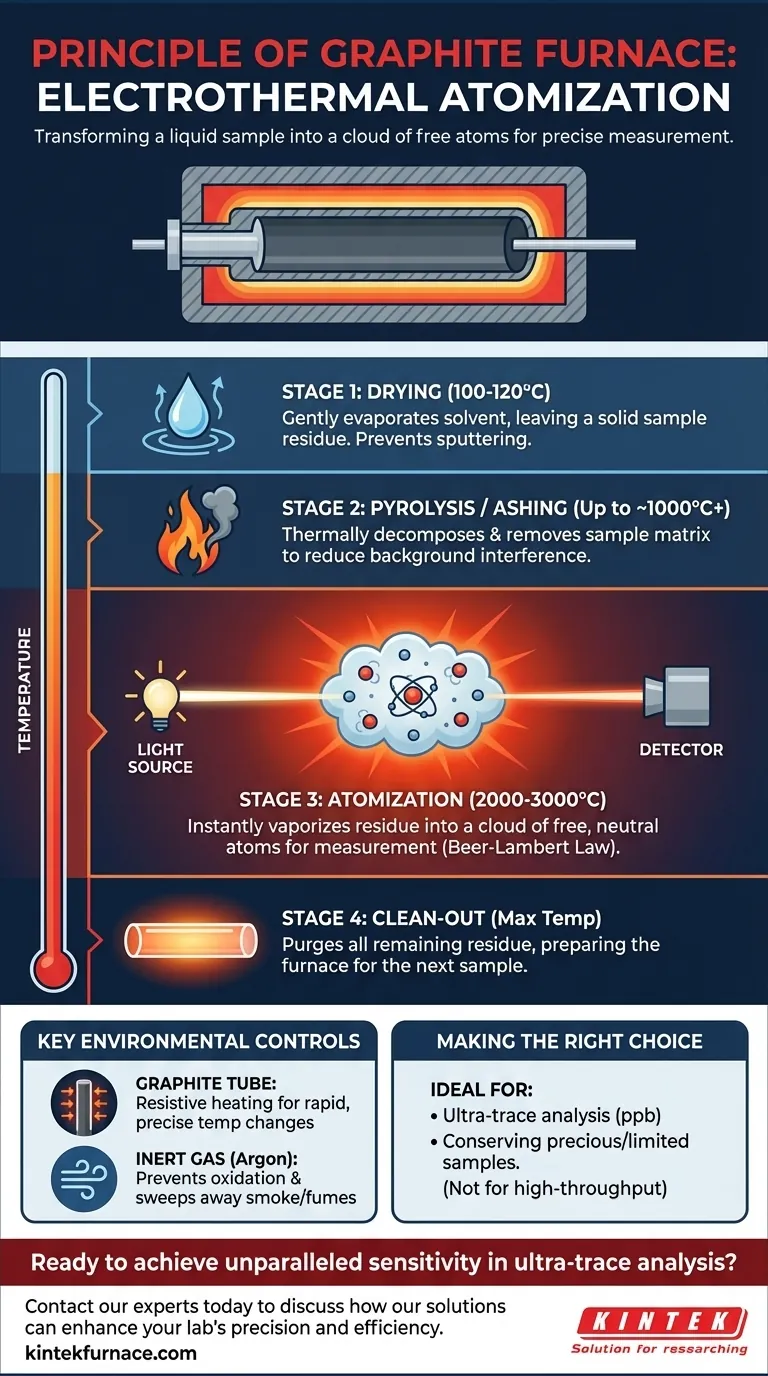
At its core, the principle of a graphite furnace is to use a precisely controlled, multi-stage heating program to transform a tiny liquid sample into a cloud of free, neutral atoms. This process, known as electrothermal atomization, occurs within a graphite tube purged with an inert gas. Once the atoms are isolated, a beam of light is passed through them, and their specific light absorption is measured to determine their concentration according to the Beer-Lambert Law.
The true genius of the graphite furnace is not just its ability to reach high temperatures. It is the sequential, programmed heating that systematically dries the sample, burns away interfering substances, and then, in a final, isolated step, atomizes the target element for an exceptionally sensitive and clean measurement.

The Goal: Isolating Atoms for Measurement
To accurately measure the amount of a specific element, it must first be liberated from its chemical bonds and physical matrix. The graphite furnace is an advanced tool designed to achieve this atomic isolation with extreme efficiency.
The Foundation: The Beer-Lambert Law
All atomic absorption spectroscopy, including the graphite furnace technique, is governed by the Beer-Lambert Law. This principle states that the amount of light absorbed by a cloud of atoms is directly proportional to the concentration of those atoms in the light's path.
To make this measurement, the element must be in a gaseous state of free, neutral atoms. It cannot be part of a molecule or an ion.
The Role of the Atomizer
The sole purpose of an atomizer is to convert a sample from its liquid or solid state into the required cloud of free atoms. The graphite furnace is a type of electrothermal atomizer, meaning it uses electricity to resistively heat a graphite tube and achieve this transformation.
The Graphite Furnace Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The power of the graphite furnace lies in its carefully programmed temperature sequence. A sample of just 5 to 20 microliters is injected into the graphite tube, and the furnace executes a multi-stage program.
Step 1: Drying
The temperature is first raised to just above the boiling point of the solvent, typically 100-120°C. This stage gently evaporates the liquid solvent (e.g., water or acid) without sputtering, leaving behind a solid residue of the sample.
Step 2: Pyrolysis (or Ashing)
Next, the temperature is increased significantly, often to several hundred or even over 1000°C. The goal here is to thermally decompose and remove as much of the sample matrix (salts, organic matter) as possible without losing the target analyte. This "ashing" stage is critical for reducing background noise and interferences later on.
Step 3: Atomization
This is the measurement step. The furnace temperature is rapidly ramped up to a very high level (e.g., 2000-3000°C). This intense heat instantly vaporizes the remaining residue, breaking all chemical bonds and creating the cloud of free, neutral atoms of your target element. The instrument's light source passes through the tube at this exact moment to measure the absorption.
Step 4: Clean-out
Finally, the furnace is heated to its maximum temperature for a few seconds. This high-temperature burn purges any remaining residue from the tube, ensuring it is clean and ready for the next sample.
Understanding the Key Environmental Controls
The entire process is only possible because of the carefully managed environment inside the furnace.
The Graphite Tube
The tube itself is made of high-purity graphite. It is held between two electrodes that pass a high current through it, causing it to heat up due to its own electrical resistance. This allows for the extremely rapid and precise temperature changes required for the process.
The Inert Gas Atmosphere
The furnace is continuously purged with an inert gas, almost always Argon. This has two critical functions. First, it creates a non-reactive atmosphere that prevents the hot graphite tube from being incinerated by oxygen in the air. Second, the gas flow helps sweep away the smoke and fumes created during the drying and pyrolysis stages.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (GFAAS) is a powerful tool, but it is not always the right one. Its utility depends entirely on your analytical objective.
- If your primary focus is ultra-trace analysis (parts-per-billion): GFAAS is the superior choice due to its exceptional sensitivity and low sample consumption.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput analysis (parts-per-million): A faster technique like Flame AAS is often more practical, as GFAAS has a much lower sample throughput (minutes per sample vs. seconds).
- If your primary focus is conserving a precious or limited sample: GFAAS is ideal, requiring only a few microliters for a complete and accurate analysis.
By mastering this controlled, sequential heating process, you gain the ability to accurately measure elements at concentrations far below what other methods can achieve.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Temperature Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Drying | 100-120°C | Evaporates solvent, leaving a solid sample residue. |
| Pyrolysis (Ashing) | Up to 1000°C+ | Removes sample matrix to reduce background interference. |
| Atomization | 2000-3000°C | Vaporizes the sample to create a cloud of free atoms for measurement. |
| Clean-out | Maximum Temperature | Purges residue to prepare the furnace for the next sample. |
Ready to achieve unparalleled sensitivity in ultra-trace analysis?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for analytical laboratories. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements—whether you're developing new GFAAS methods or require robust, reliable heating systems.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your lab's precision and efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















