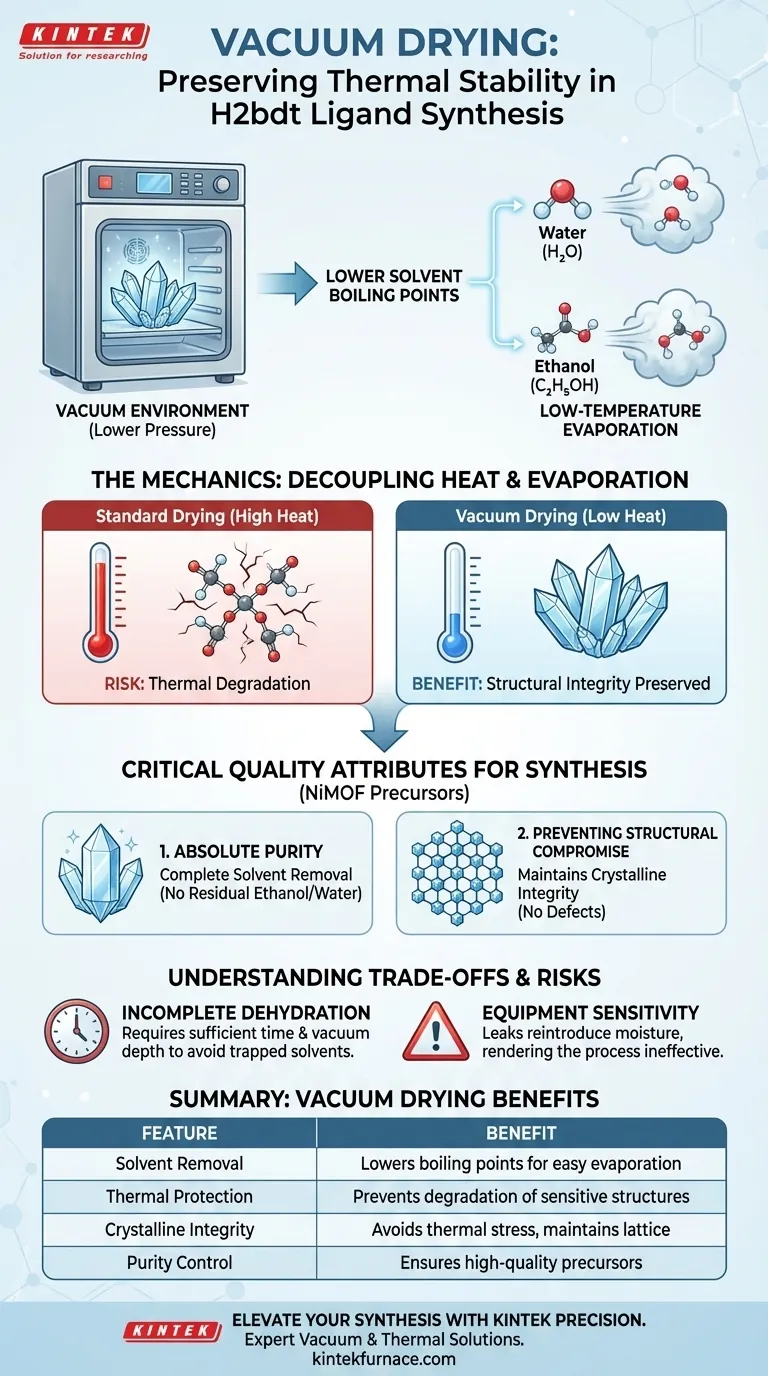
The primary function of a vacuum drying oven in this context is the preservation of thermal stability during purification. specifically, it is used to dry washed H2bdt ligand crystals by lowering the boiling points of residual solvents. This allows for the complete removal of ethanol and moisture at temperatures low enough to prevent the degradation of the sensitive organic molecules.
Core Insight: The value of vacuum drying lies in decoupling heat from evaporation. It enables the thorough removal of contaminants—specifically water and ethanol—without subjecting the H2bdt ligand to temperatures that would compromise its structural integrity, ensuring the high purity required for subsequent NiMOF synthesis.
The Mechanics of Low-Temperature Drying
Lowering Solvent Boiling Points
The defining characteristic of this process is the manipulation of pressure to alter physical properties. By creating a vacuum environment, the oven significantly reduces the atmospheric pressure surrounding the crystals.
This pressure drop depresses the boiling points of residual solvents, primarily water and ethanol. Consequently, these liquids can vaporize and exit the crystal lattice at much lower temperatures than would be required at standard atmospheric pressure.
Protecting Organic Stability
H2bdt is an organic ligand, meaning its molecular structure can be sensitive to excessive thermal energy. Standard drying methods often require high heat to drive off moisture, which poses a risk of thermal decomposition.
The vacuum drying oven circumvents this by facilitating drying under low-temperature conditions. This ensures the crystals are dried effectively without reaching the thermal threshold that would denature or degrade the organic backbone of the ligand.
Critical Quality Attributes for Synthesis
Achieving Absolute Purity
The synthesis of downstream materials, such as Nickel Metal-Organic Frameworks (NiMOF), requires precursors of exceptionally high purity.
The vacuum oven ensures the complete removal of washing agents. If residual ethanol or moisture remains adsorbed on the crystal surface, it acts as an impurity that can interfere with the coordination chemistry during the subsequent synthesis steps.
Preventing Structural Compromise
Beyond simple purity, the physical structure of the crystal must be maintained.
By avoiding high-temperature stress, the vacuum process preserves the crystalline integrity of the H2bdt ligand. This "gentle" yet deep drying prevents the formation of defects or alterations in the crystal lattice that could propagate errors into the final NiMOF structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Incomplete Dehydration
While vacuum drying allows for lower temperatures, it often requires longer processing times to achieve "deep drying." A common pitfall is terminating the cycle too early.
If the vacuum level is insufficient or the time is too short, capillary water or deeply trapped solvent molecules may remain within the crystal structure, leading to inconsistent synthesis results later.
Equipment Sensitivity
Vacuum drying relies heavily on the integrity of the oven's seals and pump performance.
Unlike a standard convection oven, a minor leak in a vacuum oven creates a dynamic equilibrium where moisture from the lab environment is continuously reintroduced. This can render the drying process ineffective, regardless of the temperature setting.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the successful preparation of H2bdt ligands, align your drying parameters with your specific purity requirements.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Prioritize a deeper vacuum level over increased temperature to ensure the total volatilization of ethanol without risking thermal degradation.
- If your primary focus is Process Speed: You may moderately increase the temperature, but you must stay strictly below the known decomposition threshold of the H2bdt molecule to avoid destroying the yield.
Success in organic ligand synthesis depends not just on creating the molecule, but on isolating it without destroying it in the process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Drying Benefit for H2bdt |
|---|---|
| Solvent Removal | Lowers boiling points of water/ethanol for easy evaporation |
| Thermal Protection | Prevents degradation of sensitive organic molecular structures |
| Crystalline Integrity | Avoids thermal stress to maintain lattice structure for NiMOF synthesis |
| Purity Control | Ensures complete removal of contaminants for high-quality precursors |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
High-purity organic ligands like H2bdt demand precise thermal management to avoid structural compromise. KINTEK provides industry-leading laboratory vacuum systems designed to decouple heat from evaporation, ensuring your sensitive materials are dried thoroughly without thermal stress.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your unique research needs. Don't risk the integrity of your precursors with inconsistent drying.
Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect high-temp solution for your lab
Visual Guide
References
- Carolina Manquian, Dinesh Pratap Singh. Synthesis and Optimization of Ni-Based Nano Metal–Organic Frameworks as a Superior Electrode Material for Supercapacitor. DOI: 10.3390/nano14040353
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- What is a vacuum sintering furnace? Achieve High-Purity, Dense Materials
- Why is a vacuum resistance furnace necessary for Ti-Zr-Nb alloy annealing? Ensure Purity & Uniformity
- What types of heating elements are used in vacuum sintering furnaces? Choose the Right One for High-Temp Success
- How does the vacuum furnace improve the performance of heat-treated products? Achieve Superior Control and Quality
- What role does a vacuum chamber play in the Flash Joule Heating (FJH) process for LIG? Master Graphene Synthesis
- What is the primary application of a vacuum oven for CPD/C60 encapsulation? Lock Nano-Fillers in PU Membranes
- How is furnace brazing utilized in the electronics and semiconductor industries? Master Precision Joining for High-Reliability Components



















