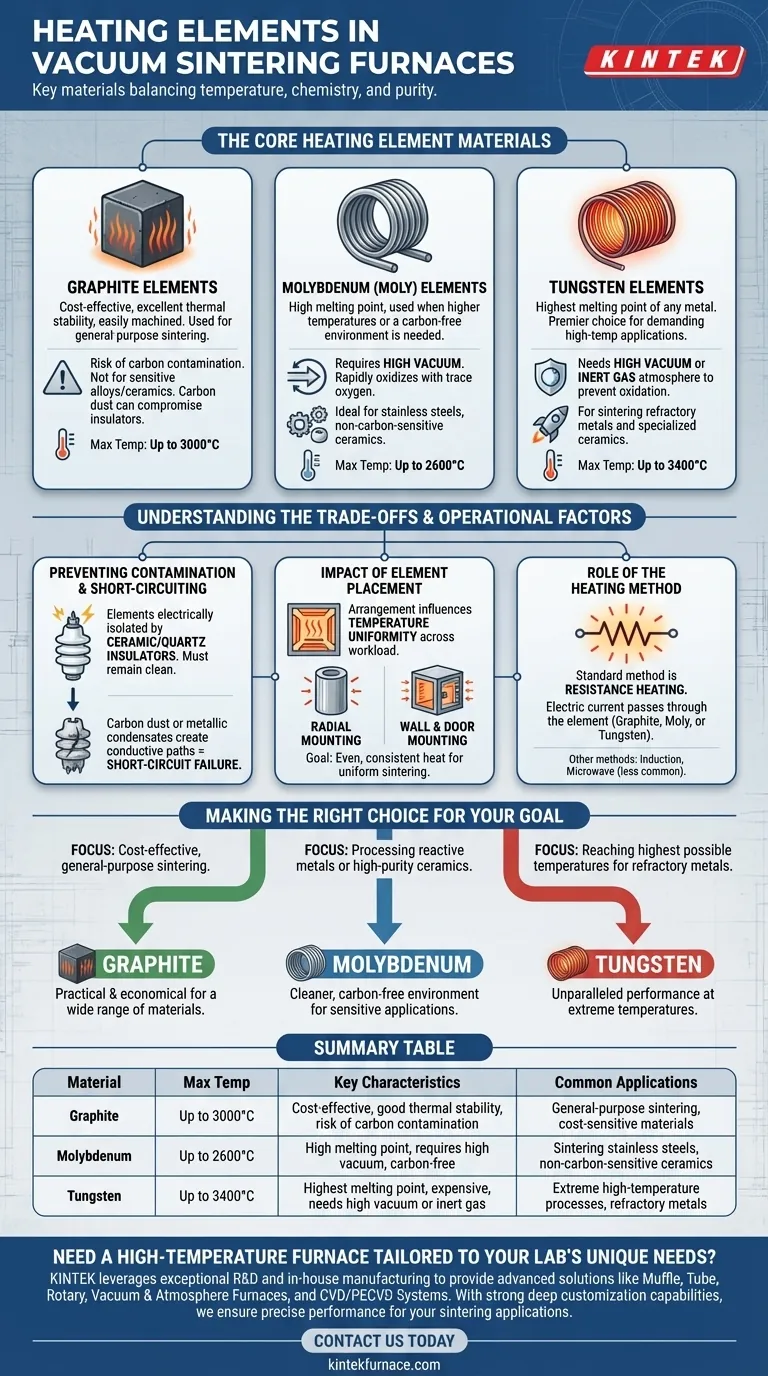
In a vacuum sintering furnace, the most common heating elements are made from graphite, molybdenum, and tungsten. The choice of material is not arbitrary; it is dictated by the maximum required temperature, the chemical properties of the material being processed, and the need to prevent contamination within the high-purity vacuum environment.
The selection of a heating element is a critical engineering decision that balances temperature requirements against potential chemical interactions. The goal is to heat the product effectively without introducing impurities or compromising the integrity of the furnace or the final part.
The Core Heating Element Materials
The three primary materials for resistance heating elements each serve a distinct set of applications, defined largely by their temperature limits and chemical reactivity.
Graphite Elements
Graphite is the most common and cost-effective heating element material for many vacuum furnace applications. It offers excellent thermal stability and is easily machined into complex shapes.
However, graphite can react with some materials and can be a source of carbon contamination, which is unacceptable for certain alloys and ceramics. Its use is also limited by the potential for carbon dust to compromise electrical insulators.
Molybdenum Elements
Molybdenum (often called "Moly") is used when higher temperatures are needed or when carbon contamination from graphite is a concern. It is a refractory metal with a very high melting point.
Molybdenum elements require a high-vacuum environment because they will rapidly oxidize in the presence of even trace amounts of oxygen at elevated temperatures. They are ideal for sintering stainless steels, certain ceramics, and other non-carbon-sensitive materials.
Tungsten Elements
Tungsten has the highest melting point of any metal, making it the premier choice for the most demanding high-temperature applications. It is used for sintering other refractory metals and specialized ceramics that require extreme processing temperatures.
Like molybdenum, tungsten must be operated in a high vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere to prevent oxidation. It is the most expensive of the three options but is indispensable for processes exceeding the capabilities of graphite or molybdenum.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a heating element involves more than just its material composition. The operational context, including placement and potential for contamination, is just as critical for achieving successful outcomes.
Preventing Contamination and Short-Circuiting
Heating elements are electrically isolated from the furnace body using ceramic or quartz insulators. These insulators must remain exceptionally clean.
Contamination from carbon dust (from graphite elements) or metallic condensates can create a conductive path, leading to electrical short-circuiting and furnace failure. This is a primary reason why molybdenum or tungsten are chosen for high-purity applications.
The Impact of Element Placement
The physical arrangement of the heating elements directly influences temperature uniformity across the workload.
Elements may be mounted radially to create a cylindrical hot zone, or they may be placed on the walls and doors of the furnace. The goal is to deliver even, consistent heat to ensure all parts are sintered uniformly, minimizing internal stresses and defects.
The Role of the Heating Method
While different materials are used, the most common heating method is resistance heating. This is where an electrical current is passed through the element (graphite, molybdenum, or tungsten), and its natural resistance to the flow of electricity generates intense heat.
Other, more specialized methods like induction heating (using magnetic fields) or microwave heating exist, but resistance heating remains the standard for most vacuum sintering furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements will determine the ideal heating element.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, general-purpose sintering: Graphite is often the most practical and economical choice for a wide range of materials.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals or high-purity ceramics: Molybdenum provides a cleaner, carbon-free environment suitable for more sensitive applications.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures for refractory metals: Tungsten is the definitive solution due to its unparalleled performance at extreme temperatures.
Understanding these material properties and operational principles empowers you to select the optimal heating system for achieving high-quality, repeatable sintering results.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Graphite | Up to 3000°C | Cost-effective, good thermal stability, risk of carbon contamination | General-purpose sintering, cost-sensitive materials |
| Molybdenum | Up to 2600°C | High melting point, requires high vacuum, carbon-free | Sintering stainless steels, non-carbon-sensitive ceramics |
| Tungsten | Up to 3400°C | Highest melting point, expensive, needs high vacuum or inert gas | Extreme high-temperature processes, refractory metals |
Need a high-temperature furnace tailored to your lab's unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise performance for your sintering applications. Contact us today to enhance your efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement



















