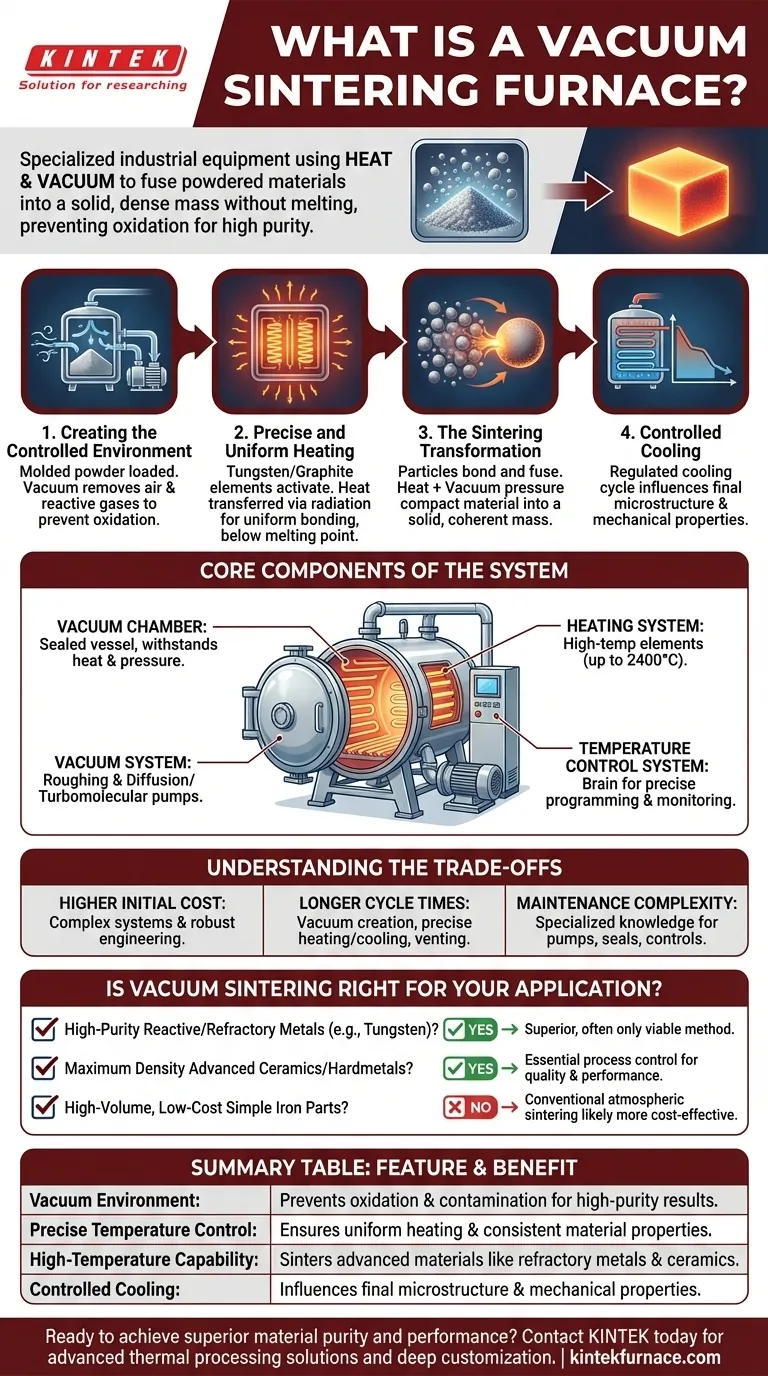
In essence, a vacuum sintering furnace is a specialized piece of industrial equipment that uses heat to fuse powdered materials into a solid, dense mass. It performs this process, known as sintering, inside a high-vacuum chamber, which is critical for preventing the oxidation and contamination that would otherwise occur in the presence of air. This method creates exceptionally pure, high-performance components without ever melting the base material.
The core purpose of a vacuum sintering furnace is not just to apply heat, but to create a perfectly controlled, inert environment. By removing reactive gases, it enables the manufacturing of advanced materials with superior strength and purity that are impossible to achieve in a conventional atmospheric furnace.

How a Vacuum Sintering Furnace Operates
The operation of a vacuum sintering furnace is a multi-stage process designed for absolute precision and control. It transforms loose powder into a fully dense, high-integrity solid.
Creating the Controlled Environment
The process begins by loading the molded powder material into the furnace's sealed vacuum chamber. A powerful vacuum system, typically involving multiple pumps, then removes the air and any other atmospheric gases.
This step is the most critical distinction of vacuum sintering. It prevents unwanted chemical reactions, like oxidation, which ensures the chemical purity of the final product.
Precise and Uniform Heating
Once the vacuum is established, the heating system activates. Heating elements, often made of tungsten or graphite, raise the chamber's temperature according to a pre-programmed profile.
In a vacuum, heat is transferred primarily through radiation, allowing it to heat the material uniformly from all sides. This avoids hot spots and ensures consistent bonding throughout the component. The temperature is brought just below the material's melting point.
The Sintering Transformation
At the target temperature, the individual particles of the powder begin to bond and fuse. This diffusion process eliminates the pores between particles, causing the component to shrink and increase in density.
The combination of heat and the external pressure of the vacuum compacts the material into a solid, coherent mass without seams, joints, or fillers.
Controlled Cooling
After a specified time at the sintering temperature, a controlled cooling cycle begins. The rate of cooling is just as important as the heating, as it influences the final microstructure and mechanical properties of the material. A water-cooling system circulates fluid through the furnace walls to manage this process safely and efficiently.
Core Components of the System
A vacuum sintering furnace is an integrated system where each component plays a vital role in achieving the final result.
The Vacuum Chamber
This is the sealed, heavy-duty vessel where the entire process takes place. It is engineered to withstand both the extreme internal heat and the immense external pressure created by the vacuum.
The Heating System
This includes the heating elements that can reach temperatures as high as 2400°C. They are designed for long life and stability in a vacuum environment.
The Vacuum System
A series of pumps work together to first remove the bulk of the air (roughing pumps) and then create the high vacuum needed for the process (diffusion or turbomolecular pumps).
The Temperature Control System
This is the brain of the furnace. It is a sophisticated controller that allows operators to program, monitor, and regulate precise heating rates, holding times, and cooling profiles to meet exact material specifications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum sintering is a specialized process with specific considerations. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
Higher Initial Cost
Vacuum sintering furnaces are complex machines that represent a significant capital investment. The cost is substantially higher than for conventional atmospheric furnaces due to the vacuum systems, advanced controls, and robust chamber engineering.
Longer Cycle Times
Achieving a high vacuum, executing a precise heating and cooling profile, and venting the chamber takes time. As a result, total cycle times are typically longer than for atmospheric processes.
Maintenance Complexity
The high-performance components, including vacuum pumps, seals, and control systems, require specialized knowledge for operation and maintenance. Keeping the system leak-free and calibrated is essential for consistent results.
Is Vacuum Sintering the Right Process for Your Application?
Choosing the right manufacturing process depends entirely on your material requirements and production goals.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity components from reactive or refractory metals (like tungsten and molybdenum): Vacuum sintering is the superior, and often only, viable method.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and superior mechanical properties in advanced ceramics or hardmetals: The process control offered by vacuum sintering is essential for quality and performance.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production of simple iron-based parts: Conventional atmospheric sintering is likely a more cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, adopting vacuum sintering is an investment in absolute process control to achieve material properties and purity that are otherwise unattainable.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Vacuum Environment | Prevents oxidation and contamination for high-purity results |
| Precise Temperature Control | Ensures uniform heating and consistent material properties |
| High-Temperature Capability | Sinters advanced materials like refractory metals and ceramics |
| Controlled Cooling | Influences final microstructure and mechanical properties |
Ready to achieve superior material purity and performance with a vacuum sintering furnace?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced thermal processing solutions. Our product line, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our high-temperature furnace solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What tasks does a high-temperature vacuum sintering furnace perform for PEM magnets? Achieve Peak Density
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- How does the ultra-low oxygen environment of vacuum sintering affect titanium composites? Unlock Advanced Phase Control



















