At its core, the vacuum pump is the component responsible for creating the controlled, low-pressure environment inside a vacuum heat treatment furnace. By systematically removing air and other gases from the sealed heating chamber, the pump system eliminates reactive elements like oxygen that would otherwise compromise the integrity of the material being treated. This creates the pristine conditions necessary for high-performance metallurgy.
The true role of the vacuum pump is not merely to remove air, but to enable a level of process control and material purity that is impossible to achieve in a standard atmosphere. It is the key to preventing unwanted chemical reactions, like oxidation, and enhancing the final mechanical properties of the workpiece.

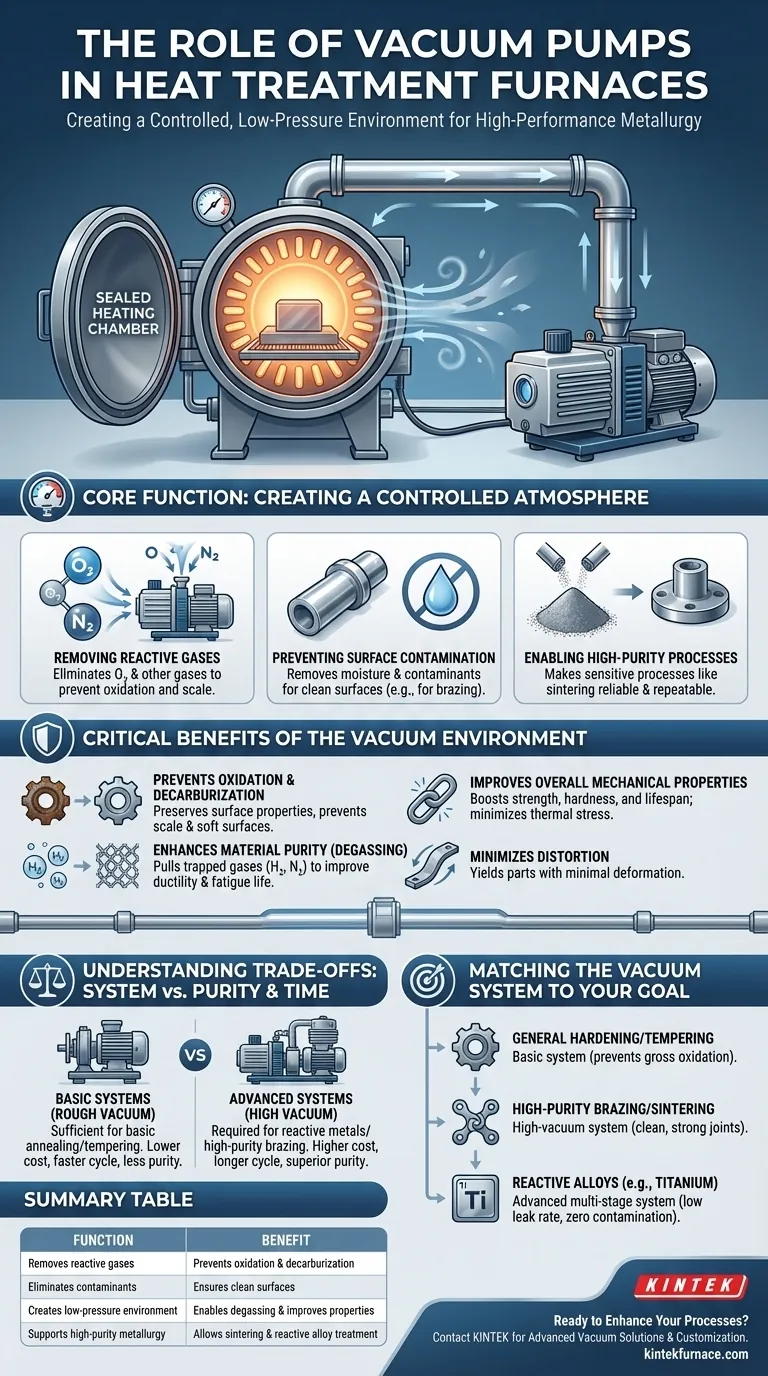
The Core Function: Creating a Controlled Atmosphere
A vacuum heat treatment furnace relies on its pump system to establish and maintain a specific low-pressure environment. This is not a passive state but an active process managed throughout the treatment cycle.
Removing Reactive Gases
The primary task of the vacuum pump is to evacuate the atmosphere from the furnace chamber. Air is approximately 21% oxygen, a highly reactive gas that readily causes oxidation (rust or scale) on the surface of hot metals.
By removing the air, the pump effectively eliminates the risk of oxidation, ensuring the treated part maintains a bright, clean surface finish without the need for post-process cleaning.
Preventing Surface Contamination
Beyond oxygen, the atmosphere contains moisture and other potential contaminants. The vacuum system removes these elements, preventing unwanted surface reactions that can negatively impact material properties.
This is especially critical for processes like brazing, where a perfectly clean surface is required to create a strong, flux-free metallurgical bond between components.
Enabling High-Purity Processes
Certain advanced metallurgical processes are only possible in a vacuum. For example, sintering powdered metals to form a solid, high-density part relies on a vacuum to prevent gas pockets and ensure component integrity.
The pump system makes these sensitive, high-value processes reliable and repeatable.
Why This Vacuum Environment is Critical
Creating a vacuum is fundamental to achieving the superior results associated with this heat treatment method. The benefits are directly tied to the pristine environment the pumps create.
Preventing Oxidation and Decarburization
As mentioned, the vacuum prevents scale formation. It also prevents decarburization—the loss of carbon from the surface of steel alloys at high temperatures, which can make the material soft and brittle.
This protection ensures the material's surface properties are preserved or enhanced, not degraded, by the heat treatment.
Enhancing Material Purity (Degassing)
The low-pressure environment actively pulls trapped gases, like hydrogen and nitrogen, out of the metal itself. This process is known as degassing.
Removing these dissolved gases can significantly improve the material's ductility and fatigue life, and it is a crucial step in preventing issues like hydrogen embrittlement.
Improving Overall Mechanical Properties
By preventing contamination and purifying the material, the vacuum environment directly contributes to improved strength, hardness, and lifespan of the finished component. The process yields parts with minimal thermal stress and deformation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The quality of the vacuum system is not uniform; it involves a trade-off between process requirements and system complexity. The level of vacuum needed dictates the type and cost of the pumps.
Pump System vs. Process Purity
A simple mechanical pump may be sufficient for basic annealing or tempering, where a "rough" vacuum prevents the worst of the oxidation.
However, treating highly reactive metals or performing high-purity brazing requires a more complex multi-stage pump system (e.g., a mechanical pump paired with a diffusion or turbomolecular pump) to achieve a "high" vacuum.
Cycle Time vs. Final Pressure
Achieving a very high vacuum (very low pressure) takes more time. The pump system's efficiency directly impacts the furnace's overall cycle time.
There is a balance between the time spent pumping down to the target pressure and the throughput requirements of the manufacturing operation. Choosing the right pump is about meeting the metallurgical need without creating a production bottleneck.
Matching the Vacuum System to Your Metallurgical Goal
The pump system must be specified based on the intended application. Consider the desired outcome to determine the necessary level of vacuum.
- If your primary focus is general hardening or tempering: A basic system that prevents gross oxidation and decarburization is often sufficient.
- If your primary focus is high-purity brazing or sintering: A high-vacuum system is non-negotiable to ensure clean, strong joints and dense components.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive alloys (e.g., titanium): You need an advanced, multi-stage high-vacuum system with a low leak rate to prevent any contamination.
Ultimately, the vacuum pump system is the heart of the furnace, creating the ideal environment that makes superior heat treatment results possible.
Summary Table:
| Function | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Removes reactive gases (e.g., oxygen) | Prevents oxidation and decarburization |
| Eliminates contaminants (e.g., moisture) | Ensures clean surfaces for processes like brazing |
| Creates low-pressure environment | Enables degassing and improves mechanical properties |
| Supports high-purity metallurgy | Allows sintering and treatment of reactive alloys |
Ready to enhance your heat treatment processes with reliable vacuum solutions? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, backed by strong R&D and deep customization to meet your unique needs. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your metallurgical outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is the heat treatment in a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Metallurgical Properties
- Why use a vacuum furnace? Achieve Unparalleled Material Purity and Process Control
- How does vacuum heat treatment improve mechanical properties of metals? Enhance Strength and Durability
- What does a vacuum furnace do? Achieve Superior Material Processing in a Pure Environment



















