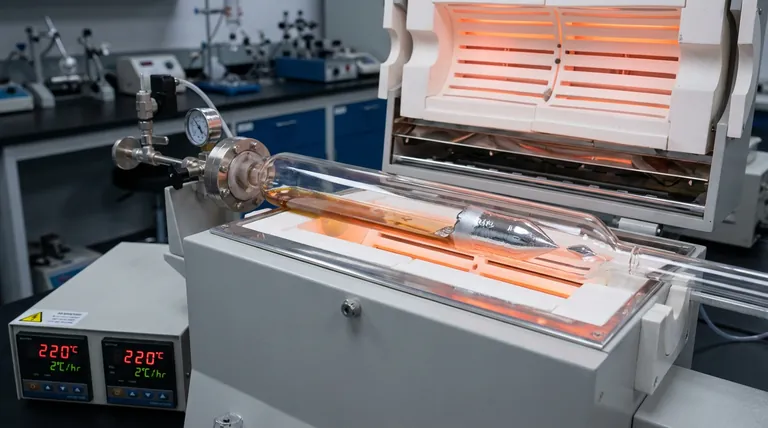
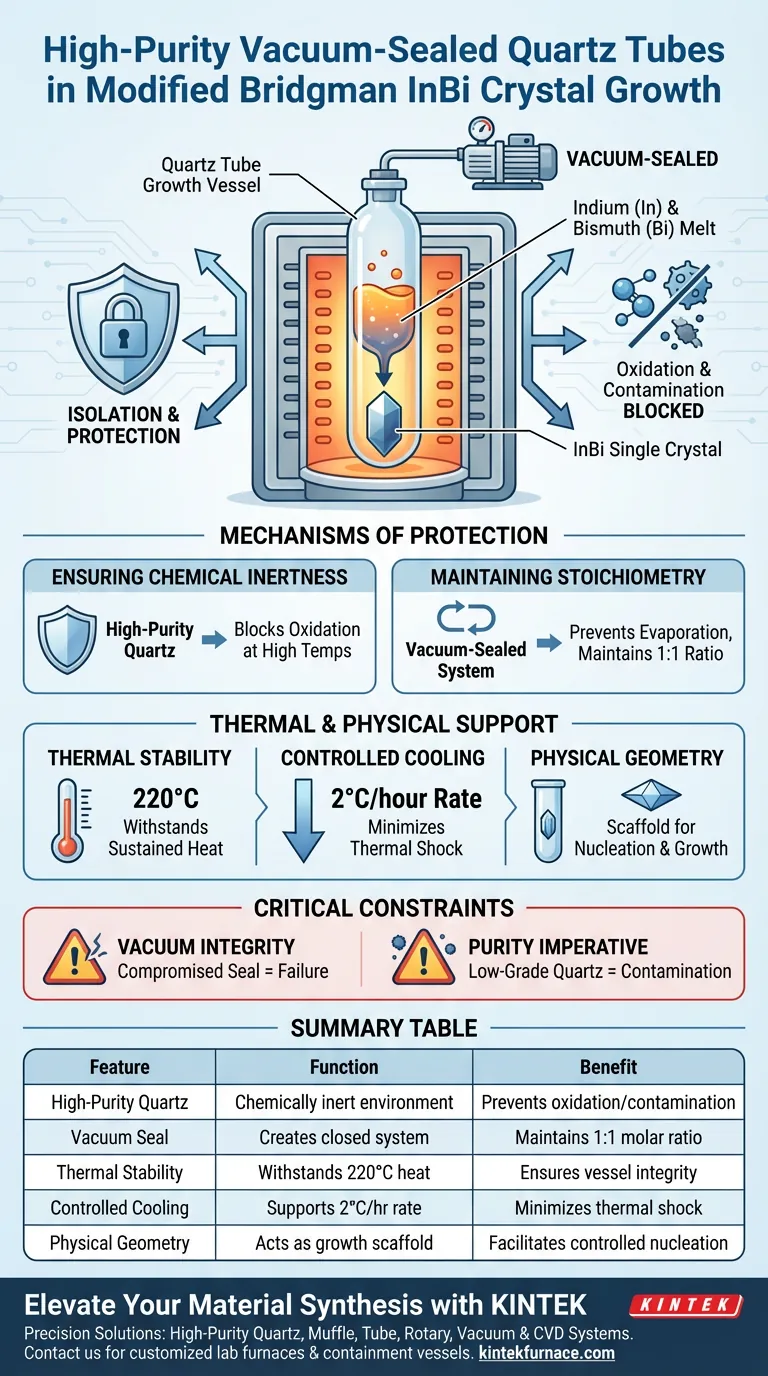
The high-purity vacuum-sealed quartz tube serves as the primary, chemically inert growth vessel. In the Modified Bridgman technique, its fundamental role is to isolate the indium (In) and bismuth (Bi) components from the external environment. This isolation prevents oxidation at high temperatures and ensures the mixture maintains a precise 1:1 molar ratio throughout the crystal growth process.
By acting as both a protective barrier and a physical scaffold, the quartz tube enables the synthesis of high-quality crystals. It eliminates the risk of oxidation and component loss, which are the two primary causes of structural defects and compositional inaccuracy in InBi growth.

Mechanisms of Protection and Control
Ensuring Chemical Inertness
The most immediate threat to growing Indium-Bismuth (InBi) crystals is environmental contamination.
High-purity quartz provides a chemically inert environment. This property effectively blocks the oxidation of Indium and Bismuth, which are reactive at elevated temperatures.
Maintaining Stoichiometry
Successful crystal growth requires a precise chemical composition.
The vacuum-sealed nature of the tube creates a closed system. This prevents the evaporation or loss of volatile components, forcing the materials to maintain the required 1:1 molar ratio essential for the target crystal structure.
Thermal and Physical Support Functions
Withstanding Thermal Regimes
The vessel must endure sustained heat without degrading or reacting with the contents.
The quartz material is selected for its ability to withstand specific thermal treatments, including sustained heating at 220°C.
Facilitating Controlled Cooling
Crystal quality is defined by the cooling process.
The tube provides the necessary stability to undergo slow, controlled cooling rates, specifically 2°C per hour. This slow rate is critical for minimizing thermal shock and allowing the crystal lattice to form correctly.
Supporting Nucleation
Physical geometry plays a role in how the crystal begins to form.
The tube provides the physical support structure required for controlled nucleation and growth, defining the shape and containment of the melt as it solidifies.
Understanding the Constraints
Dependence on Vacuum Integrity
The efficacy of this technique relies entirely on the quality of the seal.
If the vacuum seal is compromised even slightly, the inert environment is lost. This leads to immediate oxidation of the In and Bi components, rendering the growth attempt a failure.
The Imperative of Purity
Not all quartz is suitable for this application.
The tube must be of high purity. Lower-grade quartz can introduce contaminants into the melt at high temperatures, altering the electrical or structural properties of the final InBi crystal.
Optimizing Your Growth Strategy
To ensure high-quality InBi single crystal growth using the Modified Bridgman technique, prioritize the specifications of your containment vessel.
- If your primary focus is Compositional Accuracy: Rigorously test the integrity of the vacuum seal to guarantee the 1:1 molar ratio is preserved against evaporation.
- If your primary focus is Structural Perfection: Ensure the quartz grade can maintain physical stability during the slow 2°C/hour cooling phase without inducing stress on the nucleating crystal.
The quartz tube is not merely a container; it is the fundamental environmental control system that dictates the success of the entire crystallization process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in InBi Growth | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| High-Purity Quartz | Provides a chemically inert environment | Prevents oxidation and contamination of In and Bi |
| Vacuum Seal | Creates a closed system | Maintains 1:1 molar ratio by preventing evaporation |
| Thermal Stability | Withstands sustained heat (220°C) | Ensures vessel integrity during high-temperature synthesis |
| Controlled Cooling | Supports 2°C per hour cooling rate | Minimizes thermal shock for perfect lattice formation |
| Physical Geometry | Acts as a growth scaffold | Facilitates controlled nucleation and crystal shaping |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision in crystal growth begins with the quality of your thermal environment. At KINTEK, we understand that even the slightest impurity or vacuum compromise can derail your research. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-purity vacuum-sealed quartz solutions and high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for the Modified Bridgman technique and beyond.
Whether you need customized lab high-temp furnaces or specialized containment vessels for InBi growth, our team is ready to support your unique research requirements. Contact KINTEK today to secure the equipment precision your laboratory demands.
Visual Guide
References
- Thomas J. Rehaag, Gavin R. Bell. Cleaved surfaces and homoepitaxial growth of InBi(001). DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/adfc2d
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is lab vacuum used for? Mastering Environmental Control for Purity and Precision
- What are the main reasons for the alumina furnace tube being prone to breaking? Prevent Costly Failures with Expert Tips
- What are the main types of laboratory furnaces? Find Your Perfect High-Temperature Solution
- Why are laboratory heating and stirring devices necessary for Pechini and sol-gel synthesis? Ensure Precise Homogeneity
- What are the key characteristics of the alumina furnace tube? Essential for High-Temp Lab Success
- What is the advantage of the circulating water multifunctional vacuum pump being one machine for multiple purposes? Streamline Lab Work Efficiently
- How does a high-precision heating stage contribute to the drying and crystallization of FAPbBr3 nanosheets?
- Why is graphite foil used to line graphite molds before loading titanium alloy powder? Ensure Purity and Protect Molds



















