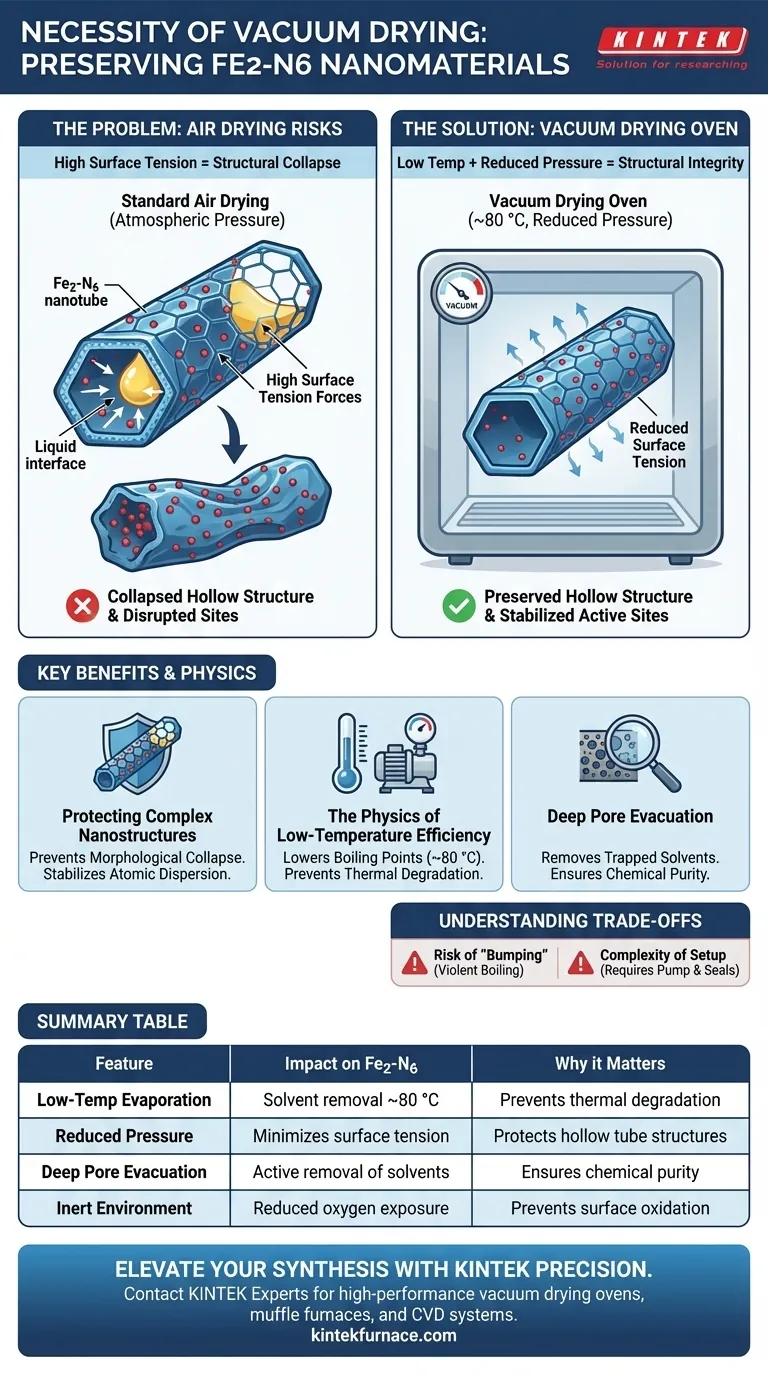
Preserving structural integrity is the primary necessity. For synthesized Fe2-N6 nanomaterials, the laboratory vacuum drying oven is essential to enable the rapid evaporation of residual water and solvents at low temperatures (approximately 80 °C) by reducing atmospheric pressure. This specific process prevents the collapse of hollow tube structures caused by surface tension, thereby safeguarding the spatial distribution stability of the atomically dispersed metal sites.
The vacuum environment fundamentally alters the evaporation kinetics, lowering solvent boiling points to bypass the high surface tension forces that typically destroy hollow nanostructures during standard air drying.

Protecting Complex Nanostructures
Preventing Morphological Collapse
The most critical function of vacuum drying for Fe2-N6 is mitigating surface tension. As liquids evaporate from the pores of nanomaterials under standard atmospheric pressure, the retreating liquid interface creates significant tension forces.
For delicate structures like the hollow tubes found in Fe2-N6, these forces can cause the walls to cave in. Vacuum drying accelerates evaporation at lower temperatures, minimizing the duration and intensity of these capillary forces to preserve the material's intended morphology.
Stabilizing Atomic Dispersion
Fe2-N6 nanomaterials rely on the precise arrangement of atomically dispersed metal sites. The physical stability of the support structure is directly linked to the stability of these active sites.
If the hollow tube structure collapses during drying, the spatial distribution of these metal sites can be disrupted or obscured. Maintaining the structural framework ensures these sites remain accessible and active for subsequent applications.
The Physics of Low-Temperature Efficiency
Lowering Boiling Points
By reducing the pressure within the oven, the boiling points of water and residual solvents are significantly lowered. This allows for thorough dehydration at approximately 80 °C.
This is critical because achieving the same level of dryness at atmospheric pressure would require much higher temperatures. Such high heat could lead to unwanted phase changes or thermal degradation of the material.
Deep Pore Evacuation
Standard drying often clears surface moisture but traps solvents deep within the nanopores. The vacuum environment creates a pressure differential that actively draws solvents out from these deep structures.
This ensures the removal of contaminants without requiring extended exposure to heat, which is vital for maintaining the "loose" powder consistency required for further processing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of "Bumping"
While rapid evaporation is beneficial, applying a vacuum too aggressively to a slurry can cause the solvent to boil violently, known as bumping. This can physically displace the sample or splatter it within the chamber.
Complexity of Setup
Compared to a standard convection oven, vacuum drying requires more complex hardware, including a vacuum pump and airtight seals. Failure to maintain a consistent vacuum seal will negate the benefits and may lead to inconsistent drying rates across the sample batch.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the quality of your Fe2-N6 nanomaterials, tailor your drying parameters to your specific objectives:
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Maintain a steady temperature of 80 °C under vacuum to minimize surface tension and prevent the collapse of hollow tubes.
- If your primary focus is Chemical Purity: Ensure the vacuum phase is maintained long enough to fully evacuate solvents from deep pores, preventing interference in electrochemical testing.
- If your primary focus is Prevention of Oxidation: Utilize the vacuum to minimize oxygen exposure during the heating phase, protecting surface functional groups.
By controlling pressure and temperature simultaneously, you ensure the Fe2-N6 material retains the precise architecture required for peak performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Impact on Fe2-N6 Nanomaterials | Why it Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Temp Evaporation | Solvent removal at ~80 °C | Prevents thermal degradation and phase changes |
| Reduced Pressure | Minimizes surface tension forces | Protects hollow tube structures from collapsing |
| Deep Pore Evacuation | Active removal of trapped solvents | Ensures chemical purity for electrochemical testing |
| Inert Environment | Reduced oxygen exposure | Prevents unwanted oxidation of surface functional groups |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Maintaining the structural integrity of advanced nanomaterials like Fe2-N6 requires exact thermal and atmospheric control. KINTEK provides industry-leading laboratory solutions, including high-performance vacuum drying ovens, muffle furnaces, and CVD systems, all customizable to your specific research needs.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our systems ensure your atomically dispersed metal sites and delicate hollow structures remain intact through every processing phase. Don't compromise on your material's performance.
Contact KINTEK Experts Today to find the perfect high-temperature solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
References
- Yan Yan, Jie Zeng. General synthesis of neighboring dual-atomic sites with a specific pre-designed distance via an interfacial-fixing strategy. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-55630-y
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 1200℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do aerospace industries benefit from high-temperature furnaces? Unlock Superior Strength and Durability
- What are the requirements for sulfur powder loading in MoS2 synthesis? Master the 50-150 mg Precision Range
- What is the primary function of a forced air oven in SnmCunOx-t synthesis? Master Chemical Foaming
- What is the role of temperature control equipment in 60Si2CrV steel processing? Ensure Hardness and Longevity
- What is the primary role of a ball mill in raw material preparation for vacuum carbothermic reduction of magnesium? Ensure a Complete and Rapid Reaction
- What is the primary purpose of operating a laboratory oven at 383 K for 24 hours? Precision Drying for Carbon Prep
- Why is a high-temperature annealing process in a vacuum oven required for CMSMs? Unlock Membrane Precision
- What is the primary function of a high-precision drop furnace? Master Flash Smelting Simulation Kinetics



















