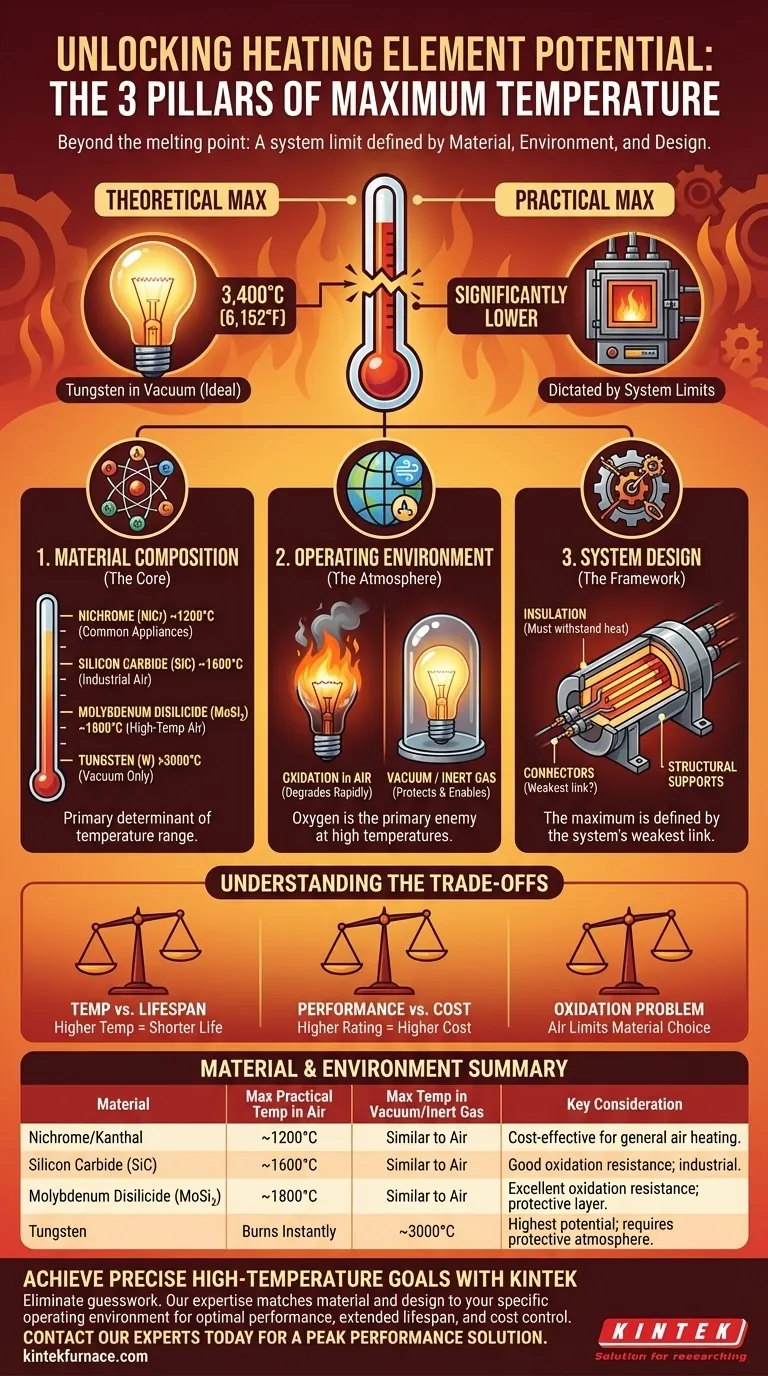
In theory, the maximum temperature of a heating element is limited by the melting point of its core material. Under ideal conditions, a tungsten heating element can reach an astonishing 3,400°C (6,152°F) in a vacuum. However, in practice, the true maximum temperature is much lower and is dictated by a combination of the material used, the element's design, and its operating environment.
The effective maximum temperature of a heating element is not a single number. It is a system limit determined by the interplay between the material's properties, the corrosive effects of the operating atmosphere, and the heat tolerance of the entire assembly.
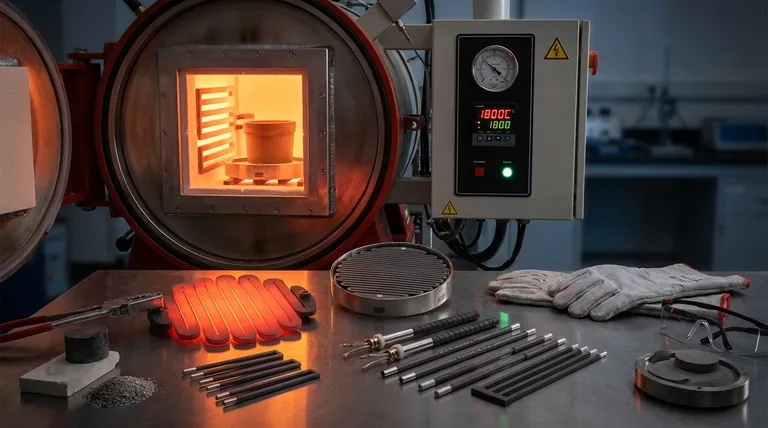

The Three Pillars of Temperature Limitation
Understanding the true temperature limit requires looking beyond a single material's melting point. Three factors work together to define the practical ceiling for any heating element.
1. Material Composition (The Core)
The material at the heart of the element is the primary determinant of its potential temperature range. Different materials are chosen for specific temperature brackets.
Common alloys like Nichrome (nickel-chromium) are used in everyday appliances and can operate reliably up to about 1200°C (2192°F).
For higher-temperature industrial applications, more exotic materials are necessary. Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) and Silicon Carbide (SiC) are ceramics that can operate in air at temperatures approaching 1800°C (3272°F).
At the extreme end is Tungsten, which boasts a melting point of 3422°C. This allows it to reach the highest temperatures, but as we will see, only under very specific conditions.
2. Operating Environment (The Atmosphere)
The atmosphere surrounding the element is often the most significant limiting factor. The primary enemy at high temperatures is oxygen.
Oxidation is a chemical reaction that degrades or destroys the heating element, much like rust corrodes iron. This process accelerates dramatically as temperature increases.
This is why a Tungsten element, which can reach over 3000°C, would burn up almost instantly in open air. To reach its potential, it must be operated in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon) to protect it from oxygen.
Materials like MoSi₂ and SiC are valuable because they form a protective glassy layer of silicon dioxide on their surface, which inhibits further oxidation and allows for high-temperature use in air.
3. System Design (The Framework)
A heating element is more than just its conductive core. It is an assembly that includes insulating materials, structural supports, and electrical connectors.
The maximum operating temperature of the entire system is defined by its weakest link.
If the insulating ceramic cannot withstand the heat, or if the lead connectors will melt or oxidize, the element's core cannot be run at its full material potential. The overall design must be engineered to tolerate the intended operating temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a heating element involves balancing competing priorities. The highest temperature is not always the best choice.
Temperature vs. Lifespan
Operating any heating element near its maximum rated temperature will drastically shorten its operational lifespan. Material degradation, even in protected environments, is inevitable.
For greater reliability and longevity, engineers typically select an element with a maximum temperature rating significantly higher than the intended operating temperature.
Performance vs. Cost
There is a direct and steep correlation between temperature rating and cost. Nichrome is relatively inexpensive, while high-performance materials like Molybdenum Disilicide and Tungsten are orders of magnitude more costly.
The cost of creating a controlled atmosphere (vacuum or inert gas) for materials like Tungsten adds another layer of expense and complexity to the system.
The Oxidation Problem
For most applications that operate in air, the choice of material is limited to those with inherent resistance to oxidation, like Nichrome, Kanthal (FeCrAl), or ceramic elements. This is the single biggest trade-off for achieving high temperatures without the complexity of a controlled atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements will determine the best path forward.
- If your primary focus is general heating up to 1200°C (e.g., ovens, kilns, dryers): Standard alloys like Nichrome or Kanthal offer the best balance of cost, lifespan, and performance in air.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature industrial processes in air (1200°C to 1800°C): Ceramic elements like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) or Silicon Carbide (SiC) are the necessary choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute maximum temperature in a lab or specialized vacuum furnace: Tungsten is the undisputed champion, but it demands a non-oxidizing environment.
Ultimately, choosing the right heating element is about matching the material and system design to the specific realities of your operating environment.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Practical Temp in Air (°C) | Max Temp in Vacuum/Inert Gas (°C) | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nichrome/Kanthal | Up to ~1200°C | Similar to Air | Cost-effective for general heating in air. |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Up to ~1600°C | Similar to Air | Good oxidation resistance; common in industrial furnaces. |
| Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Up to ~1800°C | Similar to Air | Excellent oxidation resistance; forms protective layer. |
| Tungsten | Burns instantly | Up to ~3000°C | Highest temperature potential; requires protective atmosphere. |
Achieve Your Precise High-Temperature Goals with KINTEK
Selecting the right heating element is critical to your process's success, efficiency, and cost. The wrong choice can lead to premature failure, inconsistent results, and unnecessary expense.
KINTEK's expertise eliminates the guesswork. We leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide you with the optimal high-temperature solution. Our advanced product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental and production requirements perfectly.
Let us help you:
- Extend element lifespan by matching the material and design to your specific operating environment.
- Optimize performance and ensure temperature uniformity for reliable results.
- Control costs without compromising on quality or capability.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application. We'll provide a solution engineered for peak performance and durability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism



















