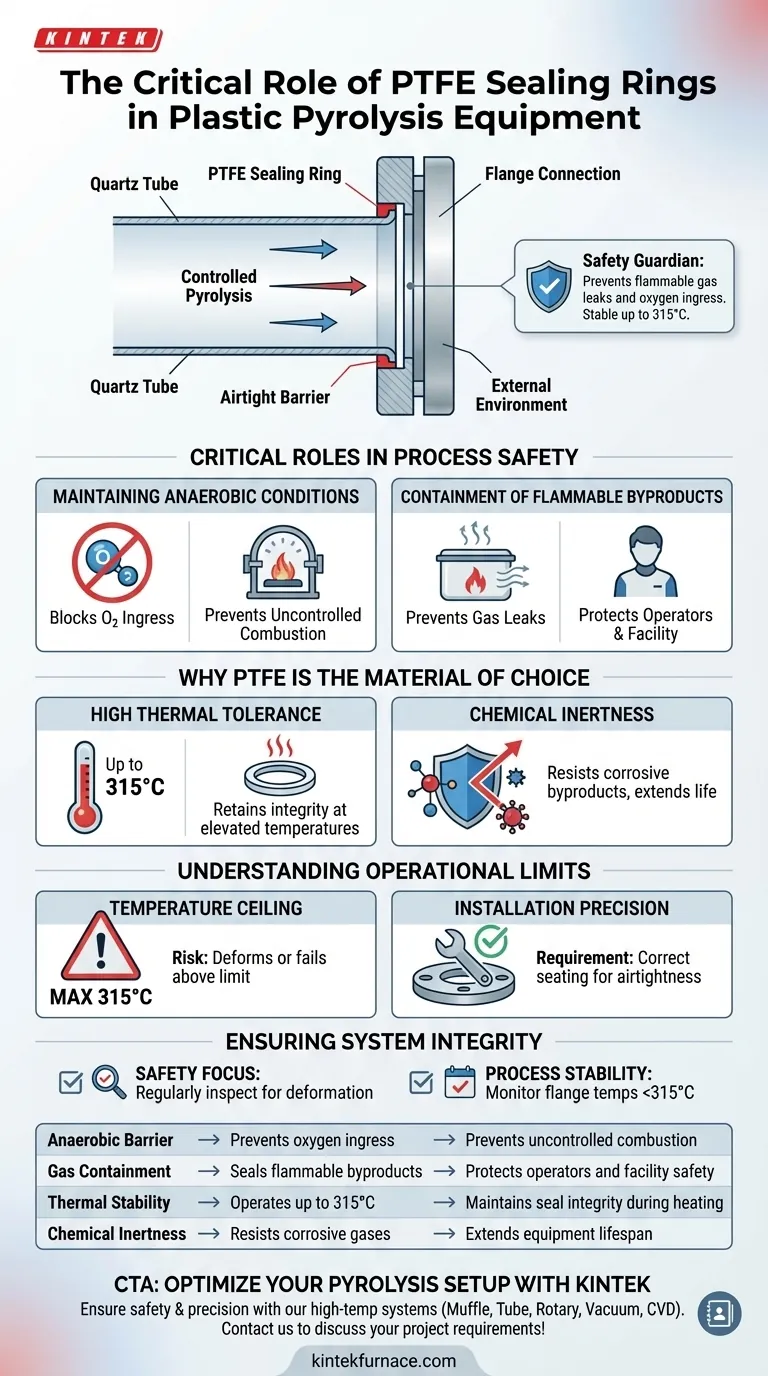
The primary function of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) sealing rings is to establish a critical, airtight barrier at the flange connections of the pyrolysis equipment's quartz tube. These components are essential for isolating the reaction chamber from the external environment. By creating this seal, they ensure the entire plastic decomposition process occurs in a controlled, closed loop system.
PTFE sealing rings act as the safety guardian of the pyrolysis process, leveraging high thermal and chemical resistance to prevent flammable gas leaks and oxygen ingress. This ensures the system operates stably under strict anaerobic conditions at temperatures up to 315°C.

Critical Roles in Process Safety
Maintaining Anaerobic Conditions
The fundamental requirement of pyrolysis is that it must occur in the absence of oxygen.
PTFE sealing rings specifically block external oxygen from entering the reaction chamber. If oxygen were to breach the system, the process could shift from controlled pyrolysis to uncontrolled combustion, posing severe safety risks.
Containment of Flammable Byproducts
During the breakdown of plastics, the system generates various volatile and flammable gases.
These sealing rings prevent these hazardous gases from leaking out at the flange connections. This containment is vital for protecting operators and the surrounding facility from potential fire hazards or toxic exposure.
Why PTFE is the Material of Choice
High Thermal Tolerance
Pyrolysis is an energy-intensive process requiring elevated temperatures to break chemical bonds.
PTFE is selected for this application because it retains its structural integrity and sealing properties up to 315°C. This allows the equipment to operate effectively within the standard temperature ranges required for many plastic decomposition reactions.
Chemical Inertness
The breakdown of plastics can produce aggressive chemical byproducts that would degrade lesser materials.
PTFE offers excellent chemical resistance, ensuring that the seal does not corrode or weaken when exposed to the harsh gases generated inside the quartz tube. This durability ensures a long service life and reduces maintenance frequency.
Understanding the Operational Limits
The Temperature Ceiling
While PTFE is robust, it is not invincible against extreme heat.
The primary limitation to be aware of is the 315°C threshold. If your specific pyrolysis protocol requires temperatures exceeding this limit at the flange connection points, the PTFE rings may soften, deform, or lose their sealing capability.
Installation Precision
The effectiveness of the seal relies heavily on proper installation at the flanges.
Even with the right material properties, the rings must be seated correctly to ensure airtightness. A misalignment during the setup of the quartz tube can negate the benefits of the material, leading to leaks despite the high-quality composition of the ring.
Ensuring System Integrity
To maximize the safety and efficiency of your plastic pyrolysis equipment, consider these operational priorities:
- If your primary focus is Safety: Regularly inspect the PTFE rings for signs of deformation to ensure no flammable gases are escaping into the workspace.
- If your primary focus is Process Stability: Monitor the flange temperatures to ensure they remain strictly below 315°C to preserve the vacuum or anaerobic state.
By rigorously respecting the thermal limits of your sealing components, you guarantee a secure and efficient chemical conversion process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Pyrolysis | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Anaerobic Barrier | Prevents oxygen ingress | Prevents uncontrolled combustion |
| Gas Containment | Seals flammable byproducts | Protects operators and facility safety |
| Thermal Stability | Operates up to 315°C | Maintains seal integrity during heating |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosive gases | Extends equipment lifespan and reliability |
Optimize Your Pyrolysis Setup with KINTEK
Ensure the highest safety and process precision with laboratory equipment engineered for extreme conditions. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized lab high-temp furnaces—all fully customizable to meet your unique research or production needs.
Whether you are processing complex plastics or developing new chemical conversion protocols, our technical team is ready to provide the durable, high-performance solutions your facility demands.
Ready to upgrade your thermal processing system? Contact KINTEK experts today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Hitesh Panchal. Fuel Extraction from Plastic Waste. DOI: 10.22214/ijraset.2025.66489
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- 304 316 Stainless Steel High Vacuum Ball Stop Valve for Vacuum Systems
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three Section Clamp
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of an enhanced hydrothermal reactor with magnetic stirring? Optimize MoS2/C Synthesis Yield
- Why is a ceramic crucible necessary for the thermal processing of silica extracted from sugarcane bagasse?
- Why is a laboratory vacuum degasser necessary for biochar? Ensure Accurate BET Structural Characterization
- Why are graphite crucible furnaces used in vacuum or protective atmosphere environments? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Purity
- What is the role of High-Strength Graphite Molds in Al-Ti-Zr sintering? Mastering Vacuum Hot Pressing Performance
- What advantages does a vacuum drying oven offer for BiFeO3 electrode sheets? Optimize Your Battery Research
- Why is a Mass Flow Controller (MFC) important for gas-phase corrosion research? Ensure Data Integrity & Precision
- Why Use a Capped Alumina Crucible for Glycine Pyrolysis? Optimize Your Carbon-Based Composite Synthesis



















