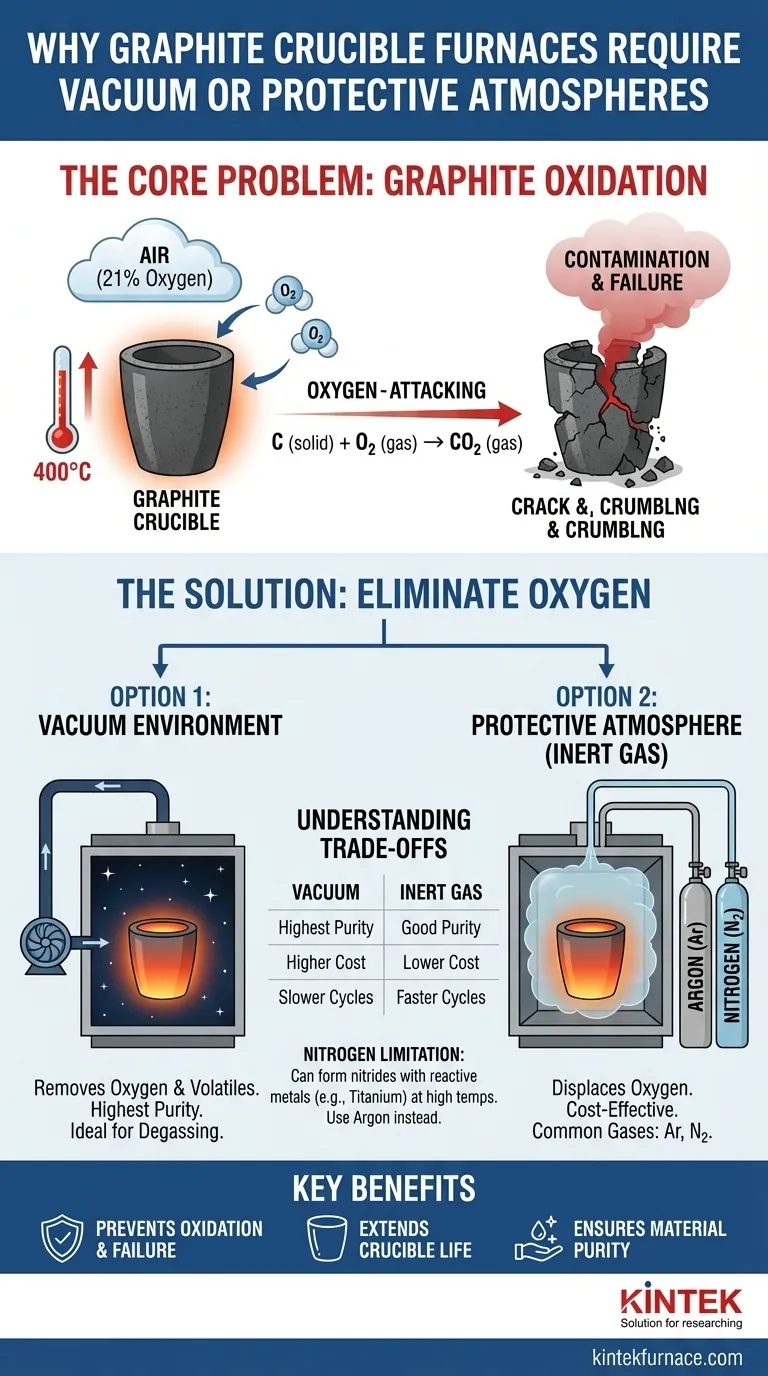
At its core, a graphite crucible requires a vacuum or protective atmosphere because graphite rapidly oxidizes—essentially, it burns away—when heated in the presence of oxygen. This controlled environment is not an optional enhancement; it is a fundamental operational requirement to prevent the complete structural failure of the crucible and the contamination of the material being processed.
While graphite offers exceptional thermal stability and conductivity for high-temperature applications, it is highly reactive with oxygen above 400°C. Using a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere is the only way to prevent the rapid chemical degradation of the crucible itself.

The Fundamental Problem: Graphite and Oxygen
The primary reason for using a controlled atmosphere is to manage a simple, destructive chemical reaction. Without this protection, a graphite furnace is unusable for high-temperature work.
Understanding Oxidation
Graphite is a form of carbon. When heated in air (which contains about 21% oxygen), it begins to react with oxygen at temperatures as low as 400°C (752°F). This process, known as oxidation, accelerates dramatically as temperatures increase.
The Chemical Reaction
The reaction is straightforward: solid carbon (C) from the crucible combines with gaseous oxygen (O₂) from the air to create carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas.
C (solid) + O₂ (gas) → CO₂ (gas)
This reaction effectively converts the solid structural material of your crucible into a gas, causing it to weaken, thin, and eventually fail.
Consequences of Uncontrolled Oxidation
Operating a graphite furnace in open air leads to catastrophic failure and contamination.
First, the crucible is consumed. It will literally lose mass and structural integrity until it can no longer contain the molten material.
Second, the process creates severe contamination. The resulting carbon dioxide or carbon monoxide can dissolve into the molten material, introducing impurities that ruin the final product, especially in high-purity applications like semiconductor or alloy production.
How Controlled Atmospheres Solve the Problem
A vacuum or a protective gas atmosphere solves this problem by removing one of the key reactants: oxygen.
The Role of a Vacuum
Creating a vacuum inside the furnace chamber is the most effective way to remove oxygen. By pumping out the air, you eliminate the oxygen available to react with the hot graphite.
This method is the gold standard for applications requiring the absolute highest purity, as it also helps pull unwanted dissolved gases out of the molten material itself—a process called degassing.
The Role of a Protective Atmosphere
An alternative and often more cost-effective method is to fill the furnace chamber with a non-reactive, or inert, gas.
This gas displaces the oxygen-rich air, blanketing the graphite components and the workload in an environment where oxidation cannot occur. The furnace is typically purged with the inert gas to flush out the air before heating begins.
Common Inert Gases: Argon and Nitrogen
Argon (Ar) and **Nitrogen (N₂) ** are the most common gases used. They are chosen because they are chemically stable and do not react with graphite, even at extreme temperatures. Argon is generally preferred for its heavier weight (which helps it displace air more effectively) and its complete inertness with almost all materials.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a vacuum and an inert gas involves balancing purity requirements, cost, and material compatibility.
Vacuum vs. Inert Gas
A vacuum system offers the highest level of purity but requires more complex, expensive, and slower-cycling equipment (pumps, seals, and chambers).
An inert gas system is generally simpler, faster to operate, and less costly. However, it relies on the purity of the source gas and is less effective at removing volatile contaminants that may outgas from the molten material.
The Limitation of Nitrogen
While nitrogen is inert with graphite, it can react with certain molten metals at very high temperatures to form nitrides. For example, when melting titanium, aluminum, or certain specialty steels, using nitrogen can introduce nitride impurities. In these cases, argon is the superior choice.
Material Compatibility Is Key
The choice of atmosphere must always consider the material being heated. The goal is to create an environment that is non-reactive with both the graphite crucible and the material inside it.
Choosing the Right Environment for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the specific goals of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest material purity: A vacuum environment is superior as it actively removes oxygen and other volatile contaminants from the melt.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production and preventing basic oxidation: A protective atmosphere of argon or nitrogen is a highly effective and more economical solution.
- If you are working with reactive metals like titanium at high temperatures: Use a vacuum or an argon atmosphere, as nitrogen can form undesirable metal nitrides.
By controlling the atmosphere, you transform graphite from a vulnerable material into a powerful and reliable tool for high-temperature processing.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Reason | Prevents oxidation of graphite above 400°C, which causes structural failure and contamination. |
| Atmosphere Types | Vacuum (removes oxygen) or inert gases like argon/nitrogen (displace oxygen). |
| Key Benefits | Extends crucible life, maintains material purity, and enables high-temperature applications. |
| Considerations | Vacuum for highest purity; inert gas for cost-effectiveness; material compatibility is crucial. |
Upgrade your high-temperature processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable graphite crucible furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, preventing oxidation and contamination while enhancing efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific applications and deliver superior performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas



















