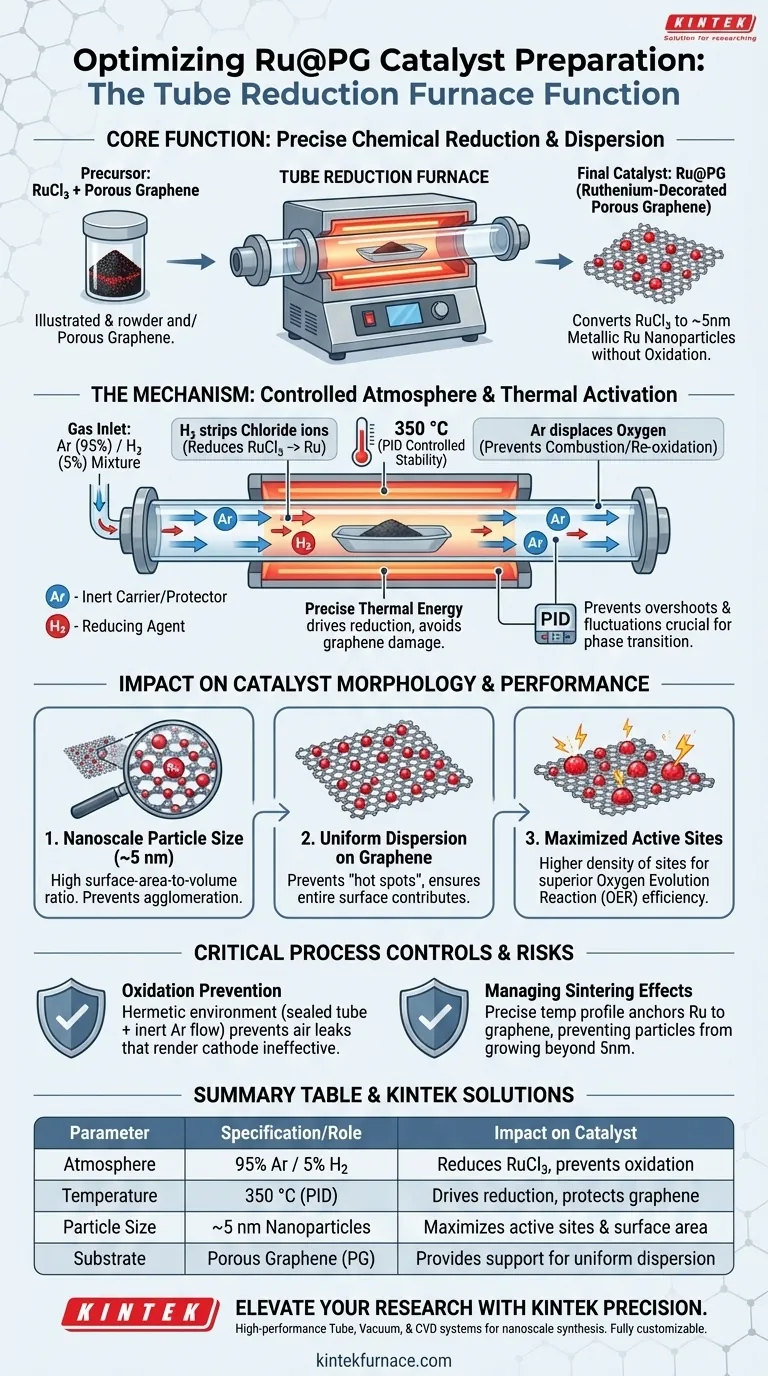
The primary function of a tube reduction furnace in this context is to facilitate the precise chemical reduction of ruthenium chloride ($RuCl_3$) precursors into metallic ruthenium nanoparticles. By utilizing a controlled 350 °C environment under a mixed hydrogen/argon atmosphere, the system ensures these nanoparticles are uniformly dispersed across the porous graphene sheets without undergoing oxidation.
The tube furnace acts as a precision reactor that converts precursor salts into highly active metallic catalysts. Its critical role is to produce extremely small (~5 nm) ruthenium particles with a high density of active sites, which are essential for maximizing the efficiency of the Oxygen Evolution Reaction (OER).
The Mechanism of Controlled Reduction
The Role of the Hydrogen/Argon Atmosphere
The specific gas mixture is the chemical engine of this process. Hydrogen acts as the reducing agent, stripping chloride ions from the precursor material to leave behind pure metallic ruthenium.
Argon serves as an inert carrier gas. It displaces oxygen from the tube to prevent the combustion of hydrogen and protects the newly formed metallic ruthenium from immediately re-oxidizing.
Thermal Activation at 350 °C
The furnace maintains a steady temperature of 350 °C. This specific thermal energy is required to drive the reduction reaction between the hydrogen and the ruthenium chloride.
According to the primary technical data, this temperature is optimized to ensure complete reduction while avoiding excessive heat that could damage the graphene structure.
Precise PID Control
To maintain this specific 350 °C setpoint, the furnace utilizes a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) temperature control system.
This prevents temperature overshoots or fluctuations. Stability is vital because even minor deviations can alter the calcination process or affect the phase transition of the catalytic materials.
Impact on Catalyst Morphology
Achieving Nanoscale Particle Size
The ultimate goal of this setup is to restrict the size of the ruthenium particles to approximately 5 nm.
The controlled reduction environment prevents the metal atoms from agglomerating into large clumps. Smaller particles mean a higher surface-area-to-volume ratio.
Uniform Dispersion on Graphene
The furnace ensures that these nanoscale particles are spread evenly across the porous graphene support.
Uniform dispersion prevents "hot spots" and ensures that the entire surface area of the cathode contributes to the catalytic process.
Enhancement of Active Sites
By combining small particle size with uniform distribution, the process maximizes the density of catalytic active sites.
These active sites are the specific locations where the electrochemical reactions occur. A higher density directly correlates to superior performance in the Oxygen Evolution Reaction (OER).
Critical Process Controls and Risks
Oxidation Prevention
A major risk in catalyst preparation is the inadvertent oxidation of the metal during high-temperature treatment.
The sealed quartz or ceramic tube of the furnace creates a hermetic environment. If air leaks in, or if the inert argon flow is insufficient, the catalytic materials will oxidize, rendering the cathode ineffective.
Managing Sintering Effects
While heat is necessary for reduction, uncontrolled heat leads to sintering (particles fusing together).
The precise atmosphere and temperature profile allow for controlled sintering. This anchors the ruthenium to the graphene without allowing the particles to grow beyond the desired 5 nm threshold.
Optimizing Cathode Preparation
To achieve high-performance Ru@PG cathodes, you must align your processing parameters with your specific performance metrics.
- If your primary focus is maximizing OER Activity: Prioritize the precision of the reduction temperature (350 °C) to ensure particle sizes remain near 5 nm, as this dictates the density of active sites.
- If your primary focus is material consistency: Focus on the integrity of the inert atmosphere (Ar/H2 ratio) and the PID control to prevent oxidation and ensure uniform dispersion across every batch.
The effectiveness of your cathode is defined not just by the materials used, but by the strict thermal and atmospheric controls applied during the reduction phase.
Summary Table:
| Process Parameter | Specification/Role | Impact on Catalyst |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | 95% Argon / 5% Hydrogen | Reduces RuCl3 and prevents metal oxidation |
| Temperature | 350 °C (PID Controlled) | Drives reduction without damaging graphene |
| Particle Size | ~5 nm Nanoparticles | Maximizes active sites and surface area |
| Substrate | Porous Graphene (PG) | Provides support for uniform catalyst dispersion |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
High-performance catalysts like Ru@PG require absolute thermal and atmospheric control. KINTEK provides industry-leading Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of nanoscale materials synthesis. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, our high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to your specific gas flow and temperature profile requirements.
Ready to optimize your catalytic yields? Contact KINTEK Today to Discuss Your Custom Furnace Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Yanna Liu, Xiao Liang. Binder-Free Three-Dimensional Porous Graphene Cathodes via Self-Assembly for High-Capacity Lithium–Oxygen Batteries. DOI: 10.3390/nano14090754
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a vertical tube furnace preferred for quenching tests? Achieve Rapid, Repeatable Cooling for Accurate Results
- Why is atmosphere control critical for lignin carbonization? Expert Tips for High-Temperature Tube Furnace Success
- What role do furnace chamber working conditions play in selecting a vertical tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Process Success
- What role does a quartz tube reactor system play in evaluating MSR? Expert Guide to Kinetic Precision
- How do high-temperature tube furnaces optimize the performance of ceramic materials during post-sintering annealing?
- What optional accessories are available for three-zone split tube furnaces? Enhance Control and Efficiency for Your Lab
- How is a tube furnace utilized to construct DTB sites for Co/Co0.85Se@NC? Mastering Phase Engineering
- How does a vacuum tube furnace work? Master Precise High-Temp Material Processing



















