At its core, a vacuum tube furnace is a high-temperature oven that heats materials inside a sealed tube from which all air has been removed. By creating this vacuum, the furnace prevents the material from oxidizing or reacting with atmospheric gases during the intense heating process, ensuring its properties remain pure and unaltered.
The true purpose of a vacuum tube furnace is not just to generate heat, but to create an exceptionally pure and controlled environment. This allows for high-temperature material processing that would be impossible in a normal atmosphere, where reactions like oxidation are unavoidable.
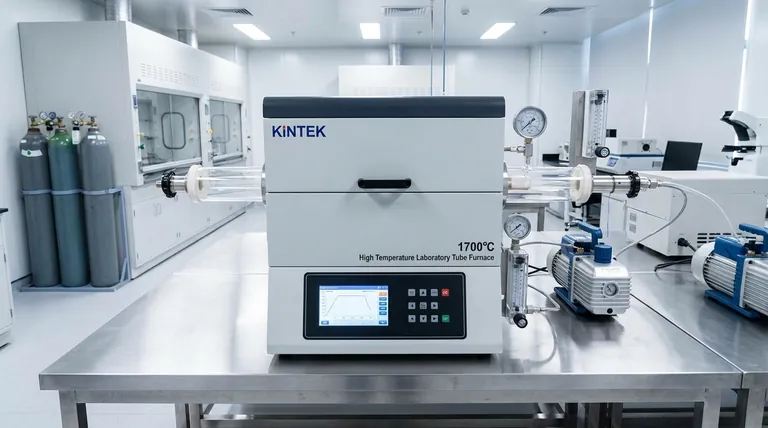

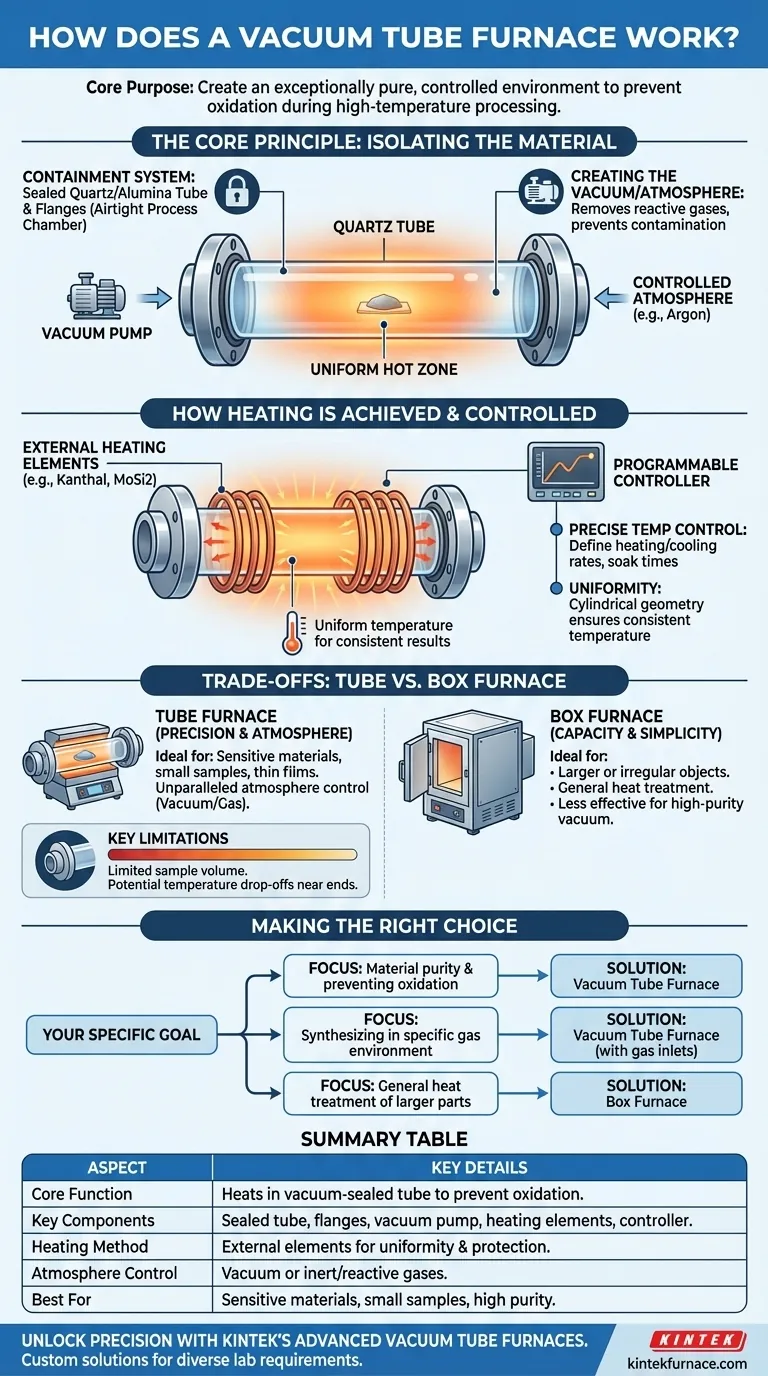
The Core Principle: Isolating the Material
The defining feature of a vacuum tube furnace is its ability to create a pristine processing environment, completely isolated from the outside air. This is achieved through two key systems working in tandem.
The Containment System: Tube and Flanges
The heart of the furnace is a sealed tube, typically made of quartz for temperatures up to around 1200°C or a ceramic like corundum (alumina) for even higher temperatures. This tube acts as the process chamber.
To ensure it's airtight, each end of the tube is sealed with a stainless steel flange. These flanges are fitted with vacuum-grade gaskets and ports for connecting a vacuum pump and introducing specific gases if needed.
Creating the Vacuum or Controlled Atmosphere
Before heating begins, a vacuum pump is used to evacuate all air and moisture from the sealed tube. This step is critical because it removes oxygen and other reactive gases that could contaminate or oxidize the sample at high temperatures.
Once a vacuum is established, the process can run in that state. Alternatively, the tube can be backfilled with a specific controlled atmosphere, such as an inert gas like Argon to prevent any reaction, or a reactive gas for processes like carburizing or nitriding.
How Heating is Achieved and Controlled
With the environment secured, the furnace's second primary function—precise heating—can begin. The design is optimized for thermal accuracy and uniformity.
External Heating Elements
Heating elements, often made of materials like Kanthal, SiC, or MoSi2 depending on the temperature range, are positioned around the outside of the process tube.
This external heating method transfers thermal energy through the tube wall to the sample inside. It protects the elements from any off-gassing or reactions happening within the tube, extending their lifespan.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
The cylindrical geometry of the tube and the placement of the heating elements are designed to create a uniform hot zone in the center of the furnace. This ensures that the entire sample experiences the same temperature, which is critical for consistent material processing, annealing, or crystal growth.
Precise Temperature Control
Modern vacuum tube furnaces are governed by sophisticated programmable controllers. These allow operators to define precise heating and cooling rates, set specific temperature "soak" times, and automate complex thermal cycles with high repeatability. Safety features like over-temperature protection are standard.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Tube vs. Box Furnace
Choosing the right furnace requires understanding its specific strengths and limitations, especially when compared to a more general-purpose box furnace.
Tube Furnace: Precision and Atmosphere
The strength of a tube furnace is its unparalleled control over the processing atmosphere. It is the ideal tool for processing sensitive materials, small samples, powders, or thin films where preventing oxidation is non-negotiable.
Box Furnace: Capacity and Simplicity
A box furnace, by contrast, features a large, accessible chamber for heating bigger or irregularly shaped objects. While some models can use a controlled atmosphere, they are generally less effective at achieving the high-purity vacuum or sealed environment of a tube furnace.
Key Limitations to Consider
The primary limitation of a tube furnace is its limited sample volume dictated by the tube's diameter. Furthermore, the most uniform temperature is in the center of the tube, with potential temperature drop-offs near the cooler ends.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal determines whether the unique capabilities of a vacuum tube furnace are necessary for your work.
- If your primary focus is material purity and preventing oxidation: The vacuum capability is the most critical feature, making a tube furnace the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing materials in a specific gas environment: The sealed-tube design with gas inlet ports is essential for your process.
- If your primary focus is general heat treatment of larger parts where atmosphere is not critical: A simpler and larger-capacity box furnace is likely the more practical solution.
Understanding these principles allows you to use the furnace not merely as a heater, but as a precise tool for manipulating a material's environment.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Heats materials in a vacuum-sealed tube to prevent oxidation and ensure purity. |
| Key Components | Sealed tube (quartz/alumina), flanges, vacuum pump, heating elements, programmable controller. |
| Heating Method | External heating elements for uniform temperature and protection from reactions. |
| Atmosphere Control | Vacuum or inert/reactive gases for precise environmental control. |
| Best For | Sensitive materials, small samples, powders, thin films requiring high purity. |
| Limitations | Limited sample volume, temperature gradients near tube ends. |
Unlock Precision in Your Lab with KINTEK's Advanced Vacuum Tube Furnaces
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're processing sensitive materials, conducting high-purity syntheses, or need tailored thermal solutions, our expertise ensures optimal performance and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss how our vacuum tube furnaces can enhance your material processing and achieve superior results in your research or production!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety



















