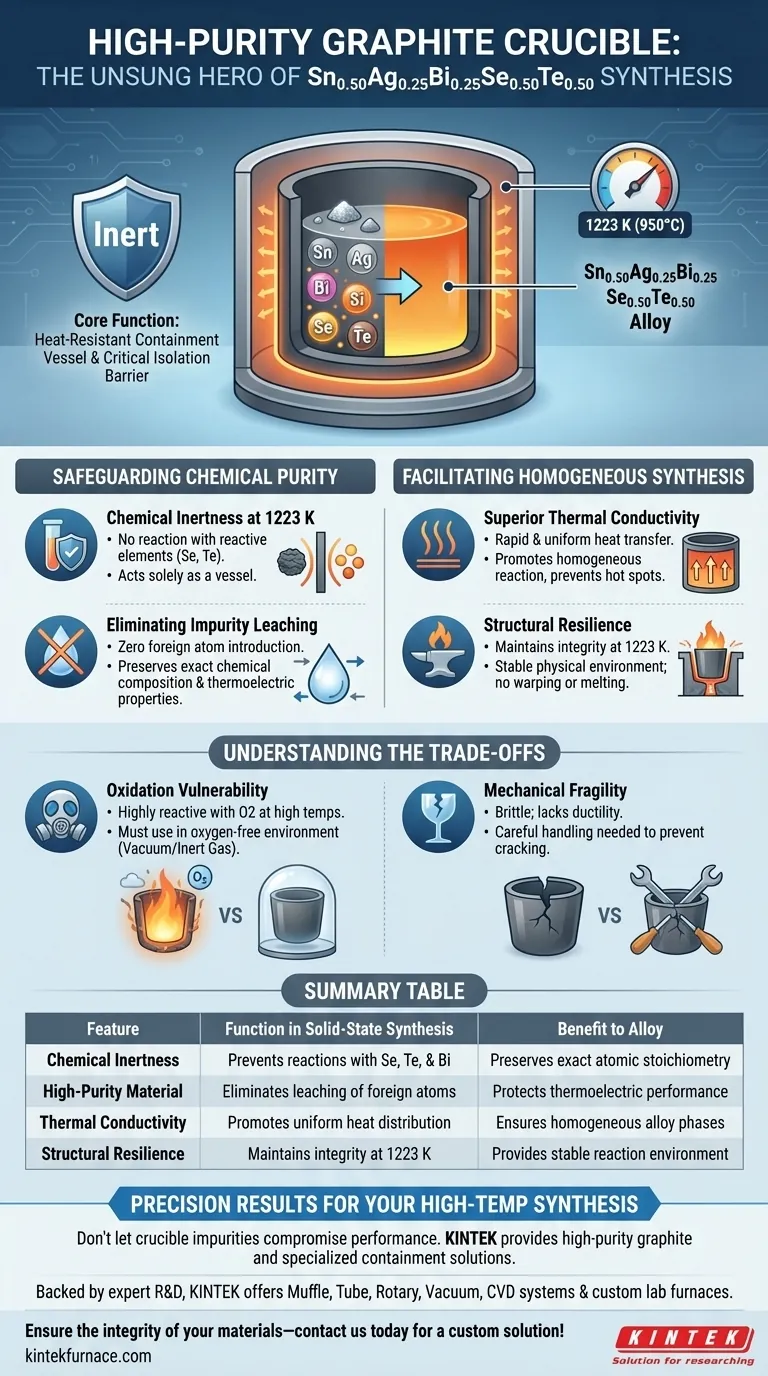
The high-purity graphite crucible serves as an inert, heat-resistant containment vessel during the synthesis of Sn0.50Ag0.25Bi0.25Se0.50Te0.50. It physically holds the raw metallic elements—Tin, Selenium, Bismuth, Tellurium, and Silver—while they undergo a solid-state reaction at 1223 K. Crucially, it prevents the containment material from chemically interacting with the alloy, ensuring the final powder retains the exact chemical composition required for optimal performance.
The crucible acts as a critical isolation barrier, utilizing graphite’s superior thermal stability to maintain the atomic stoichiometry of the semiconductor alloy. Its refusal to react with the raw elements prevents impurity introduction, which is essential for preserving the material’s thermoelectric properties.

Safeguarding Chemical Purity
Chemical Inertness at 1223 K
The synthesis of this complex alloy requires an environment reaching 1223 K. At these temperatures, many standard containment materials would soften or react chemically with the molten elements.
High-purity graphite possesses exceptional chemical stability. It remains inert even when in direct contact with reactive elements like Selenium and Tellurium, ensuring the crucible acts solely as a vessel, not a participant in the reaction.
Eliminating Impurity Leaching
The primary goal of this synthesis is to create a high-performance semiconductor alloy. The introduction of even trace foreign atoms can drastically alter the material's electronic and thermal properties.
By using high-purity graphite, you eliminate the risk of the vessel leaching contaminants into the mix. This guarantees that the final Sn0.50Ag0.25Bi0.25Se0.50Te0.50 powder maintains the precise purity levels necessary for its intended thermoelectric application.
Facilitating Homogeneous Synthesis
Superior Thermal Conductivity
Beyond simple containment, the graphite crucible plays an active role in thermal management. Graphite offers high thermal conductivity compared to ceramic alternatives.
This property facilitates rapid and uniform heat transfer from the furnace to the raw materials inside. A uniform temperature distribution helps promote a homogeneous reaction across the entire mixture, preventing localized hot spots that could lead to inconsistent alloy phases.
Structural Resilience
The solid-state reaction process involves significant thermal stress. The crucible must maintain its structural integrity without warping or degrading.
Graphite’s resistance to high temperatures ensures it does not melt or soften at 1223 K. This provides a stable physical environment for the solid-state reaction to occur safely and predictably.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Oxidation Vulnerability
While graphite is chemically stable against the metallic raw materials, it is highly reactive with oxygen at high temperatures.
If the reaction environment is not strictly controlled (e.g., vacuum or inert gas atmosphere), the crucible will oxidize and degrade rapidly. This restricts the use of graphite crucibles to oxygen-free synthesis environments.
Mechanical Fragility
Despite its thermal resilience, graphite is mechanically brittle. It lacks the ductility of metal crucibles and can fracture under physical impact or extreme, rapid thermal shock.
Careful handling is required during loading and unloading to prevent cracking, which could lead to a catastrophic leak of the molten alloy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The selection of a crucible is not just about holding material; it is about defining the quality of your reaction.
- If your primary focus is preserving thermoelectric performance: Rely on high-purity graphite to prevent foreign impurities from altering the semiconductor's electronic properties.
- If your primary focus is reaction homogeneity: Leverage graphite’s high thermal conductivity to ensure the complex 5-element mix reacts evenly throughout the volume.
Ultimately, the high-purity graphite crucible is the invisible guardian of your alloy's stoichiometry, ensuring the material you design is the material you actually produce.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Solid-State Synthesis | Benefit to Alloy |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents reactions with Se, Te, and Bi | Preserves exact atomic stoichiometry |
| High-Purity Material | Eliminates leaching of foreign atoms | Protects thermoelectric performance |
| Thermal Conductivity | Promotes uniform heat distribution | Ensures homogeneous alloy phases |
| Structural Resilience | Maintains integrity at 1223 K | Provides stable reaction environment |
Precision Results for Your High-Temp Synthesis
Don't let crucible impurities compromise your semiconductor performance. KINTEK provides high-purity graphite and specialized containment solutions designed for the most demanding solid-state reactions.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, alongside customizable lab high-temp furnaces tailored to your unique research needs.
Ensure the integrity of your materials—contact us today for a custom solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Zhenyu Tan, Degang Zhao. Enhanced Thermoelectric Properties in Cubic Sn0.50Ag0.25Bi0.25Se0.50Te0.50 via MWCNTs Incorporation. DOI: 10.3390/cryst15040365
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the general ambient temperature limit for water circulating vacuum pumps? Ensure Peak Performance and Avoid Damage
- What should be evaluated when assessing supplier reliability for alumina ceramic furnace tubes? Ensure Consistent Performance and Support
- Why are evaporators and condensers required for zirconium tetrachloride purification? Mastering Nuclear-Grade Standards
- What is the primary function of the transparent quartz tube in the Floating-Zone technique? Optical & Atmospheric Control
- Why is a Pt5%Au crucible required for S53P4 bioactive glass? Ensure Purity at 1400°C
- What role does a water saturator play in the physical activation of carbon materials? Unlock High-Performance Porosity
- What role does a precision drying oven play in the pre-treatment of Bi-Fe oxide powders? Safeguard Your Nano-Morphology
- What is the function of molybdenum fixtures in high-temperature heat treatment? Ensure Perfect Diffusion Integrity
















