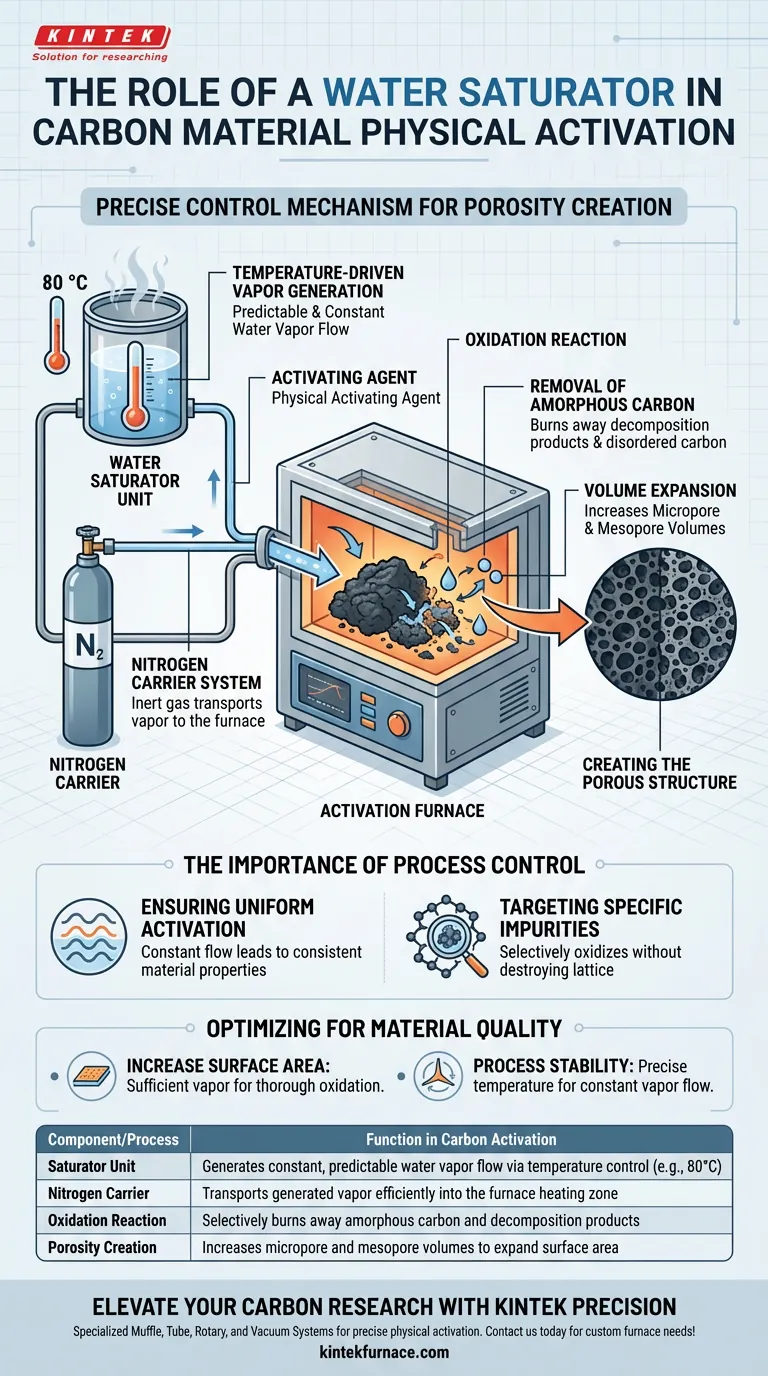
The water saturator acts as a precise control mechanism for introducing the necessary chemical agent into the physical activation process. It generates a continuous flow of water vapor by maintaining water at a specific temperature (such as 80 °C), which is then transported into the activation furnace using nitrogen as a carrier gas.
The saturator converts the activation process from a passive heating event into an active chemical transformation. By delivering a steady stream of water vapor, it enables the targeted oxidation required to hollow out the carbon structure and create high-value porosity.

The Mechanics of Delivery
Temperature-Driven Vapor Generation
The fundamental role of the saturator is to create the activating agent itself. By strictly controlling the water temperature (for example, at 80 °C), the device generates a predictable and constant flow of water vapor.
The Nitrogen Carrier System
The water vapor cannot effectively reach the carbon material on its own. The system utilizes nitrogen as a carrier gas. This inert gas sweeps the generated vapor from the saturator and delivers it efficiently into the heart of the activation furnace.
Creating the Porous Structure
The Activating Agent
Once introduced to the furnace, the water vapor serves as the primary physical activating agent. It is the active ingredient responsible for changing the internal landscape of the carbon material.
Removal of Amorphous Carbon
The vapor penetrates the carbon structure to perform a specific function: oxidation. It reacts with and burns away unwanted decomposition products and disordered, amorphous carbon that clogs the material.
Volume Expansion
The removal of this amorphous material creates voids where solid matter once stood. This process significantly increases the micropore and mesopore volumes, transforming dense carbon into a highly porous structure.
The Importance of Process Control
Ensuring Uniform Activation
The saturator's ability to maintain a constant flow is critical to the process. Without steady vapor generation, the oxidation process would be uneven, leading to inconsistent material properties.
Targeting Specific Impurities
The process is selective by design. The saturator provides the precise environment needed to oxidize decomposition products without destroying the structural integrity of the entire carbon lattice.
Optimizing for Material Quality
To achieve the best results in carbon activation, consider the following based on the saturator's function:
- If your primary focus is increasing surface area: Ensure the saturator delivers sufficient vapor to thoroughly oxidize amorphous carbon, as this directly creates micropores and mesopores.
- If your primary focus is process stability: Prioritize the precise temperature control of the saturator to maintain a constant, unvarying flow of the activating agent via the nitrogen carrier.
The water saturator is not just a humidifier; it is the engine of porosity that unlocks the performance potential of carbon materials.
Summary Table:
| Component/Process | Function in Carbon Activation |
|---|---|
| Saturator Unit | Generates constant, predictable water vapor flow via temperature control (e.g., 80°C) |
| Nitrogen Carrier | Transports generated vapor efficiently into the furnace heating zone |
| Oxidation Reaction | Selectively burns away amorphous carbon and decomposition products |
| Porosity Creation | Increases micropore and mesopore volumes to expand surface area |
Elevate Your Carbon Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let inconsistent vapor delivery compromise your material performance. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum systems designed for precise physical activation. Whether you need a standard setup or a customized high-temperature furnace for unique carbon processing, our engineering team provides the stability and control your lab requires.
Ready to optimize your activation process? Contact us today to discuss your custom furnace needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Reuse of Polymeric Resin for Production of Activated Hydrochar Applied in Removal of Bisphenol A and Diclofenac Synthetic Aqueous Solution. DOI: 10.3390/coatings15010027
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the necessity of configuring non-contact infrared pyrometers for temperature monitoring? Ensure Sintering Precision
- Why is a carrier gas flow control system necessary for thermal sludge treatment? Ensure Precision & Protect Equipment
- Why is a platinum-gold alloy crucible utilized during the glass melting process? Achieve Unmatched Purity
- What are the advantages of using a Boron Nitride crucible? Maximize Purity and Efficiency in Laser Pyrolysis
- Why use a covered crucible for g-C3N4 calcination? Enhance Surface Area via Self-Exfoliation
- Why is the integration of a K-type thermocouple and a data logger necessary for Vanadis 60 steel? Unlock Precision.
- What is the function of a water-cooled copper crucible? Master High-Purity Alloy Synthesis with KINTEK
- What functions do carbon black and carbon fiber felt serve as insulation? Maximize Efficiency in 3000°C Furnaces



















