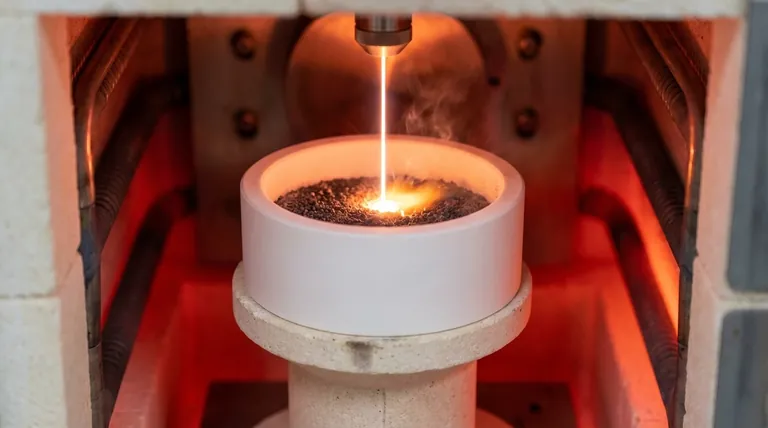
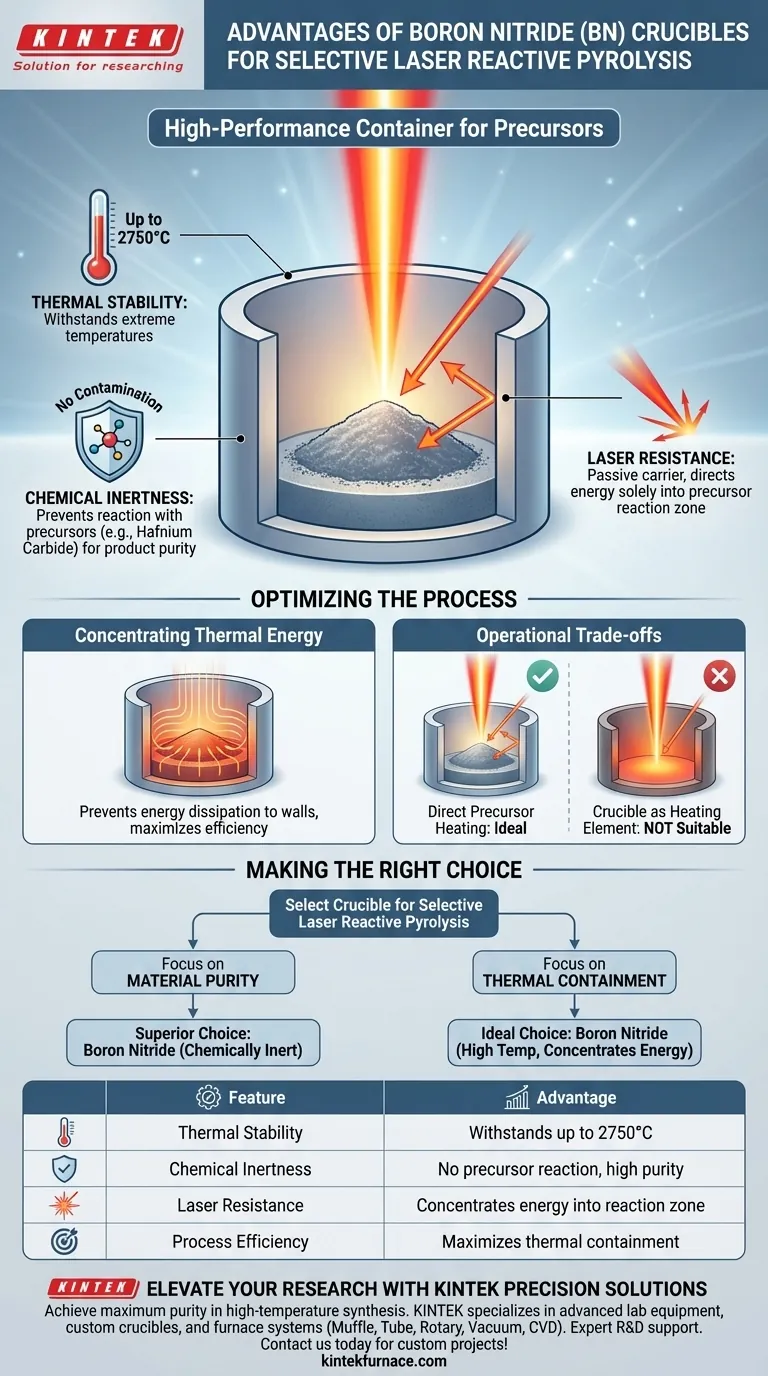
The primary advantages of using a Boron Nitride (BN) crucible lie in its ability to separate the reaction environment from the container itself. It is specifically valued for its exceptional thermal stability and chemical inertness, allowing it to withstand temperatures up to 2750°C. Furthermore, its resistance to laser radiation ensures that the energy is directed entirely into the precursor material rather than the vessel.
By resisting laser radiation and remaining chemically inert at extreme temperatures, Boron Nitride ensures that thermal energy is concentrated solely on the precursor material. This prevents container degradation and guarantees that the synthesized product remains free of contaminants.

Thermal and Chemical Integrity
Withstanding Extreme Temperatures
The Selective Laser Reactive Pyrolysis process generates intense heat. Boron Nitride crucibles offer exceptional stability, capable of withstanding temperatures as high as 2750°C. This allows researchers to push experiments to thermal extremes without the risk of the container melting or failing.
Ensuring Chemical Inertness
In high-temperature synthesis, the purity of the final product is paramount. Boron Nitride is highly chemically inert, meaning it does not react with precursors or synthesized products, such as Hafnium Carbide. This neutrality prevents the crucible from contaminating the reaction, ensuring the chemical integrity of your results.
Optimizing the Laser Process
Resistance to Laser Radiation
Unlike some materials that might absorb laser energy and heat up inadvertently, Boron Nitride is highly resistant to laser radiation. It acts as a passive carrier rather than an active participant in the energy transfer.
Concentrating Thermal Energy
Because the crucible resists the laser, the thermal energy does not dissipate into the container walls. Instead, the energy is effectively concentrated within the precursor reaction zone. This makes Boron Nitride an ideal carrier material for maximizing the efficiency of high-temperature pyrolysis.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
Thermal Coupling Limitations
While the laser resistance of Boron Nitride is an advantage for direct precursor heating, it can be a limitation if your process relies on the crucible itself to generate heat.
If your experimental design requires the container to absorb laser energy and transfer it to the sample via conduction, Boron Nitride is not suitable. It is designed to isolate the reaction zone, not to act as a heating element.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When selecting a crucible material for Selective Laser Reactive Pyrolysis, consider your specific experimental priorities:
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Boron Nitride is the superior choice because its chemical inertness prevents reaction with precursors like Hafnium Carbide.
- If your primary focus is Thermal Containment: Boron Nitride is ideal because it withstands up to 2750°C while concentrating laser energy directly into the reaction zone.
Boron Nitride provides the isolation and stability required to turn high-energy inputs into pure, high-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Advantage for Laser Pyrolysis |
|---|---|
| Thermal Stability | Withstands extreme temperatures up to 2750°C |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents contamination; no reaction with precursors |
| Laser Resistance | Concentrates energy into the reaction zone instead of the vessel |
| Process Efficiency | Maximizes thermal containment for high-quality material synthesis |
Elevate Your Research with KINTEK Precision Solutions
Are you looking to achieve maximum purity in your high-temperature synthesis? KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment designed for the most demanding applications. Whether you need specialized crucibles or fully customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, our expert R&D and manufacturing teams are here to support your unique research goals.
Experience the KINTEK difference:
- Superior thermal containment for extreme environments.
- Customizable furnace solutions tailored to your lab's needs.
- Expert technical support to optimize your material processing.
Ready to enhance your lab's efficiency? Contact us today to discuss your custom project requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Shalini Rajpoot, Chengying Xu. Synthesis of hafnium carbide (HfC) via one‐step selective laser reaction pyrolysis from liquid polymer precursor. DOI: 10.1111/jace.20650
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- How does a batch type controlled atmosphere furnace operate? Master Precision Heat Treatment for Superior Materials
- What are the applications of inert atmosphere furnaces? Essential for Metal Processing, Electronics, and Additive Manufacturing


















