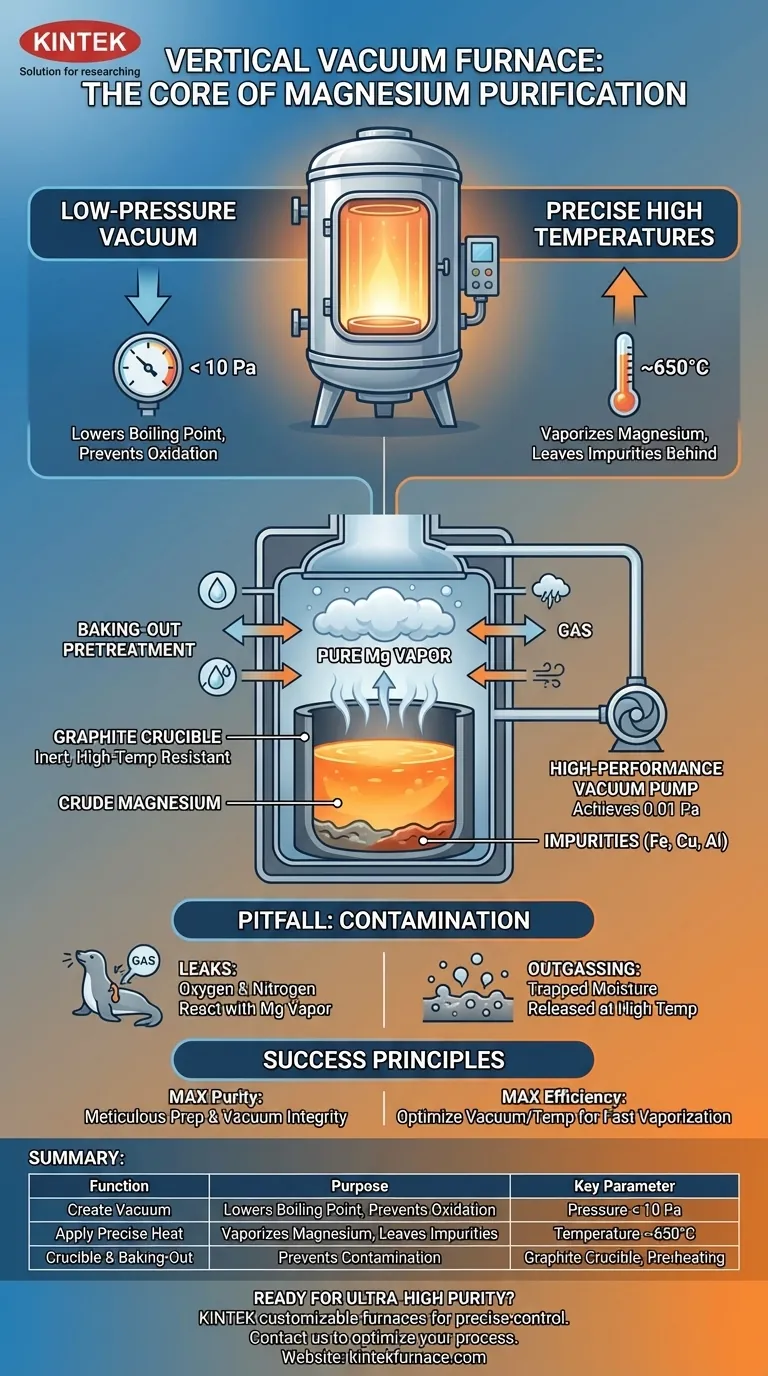
At its core, a vertical vacuum furnace functions as a precision instrument that establishes two critical physical conditions for purifying crude magnesium. It simultaneously creates a low-pressure vacuum and applies precise, high temperatures, which forces the magnesium to vaporize and physically separate from less volatile metallic impurities.
The furnace doesn't just heat the metal; it fundamentally alters the physical laws governing it. By creating a vacuum, it lowers magnesium's boiling point, allowing for a controlled, selective evaporation that leaves heavier contaminants behind.

The Two Pillars of Vacuum Distillation
The entire purification process hinges on the furnace's ability to manipulate two key environmental variables: pressure and temperature. These two factors work in tandem to achieve a clean separation that would be impossible under normal atmospheric conditions.
Creating a Low-Pressure Environment
The first and most critical function is the removal of air and other gases to create a vacuum, often below 10 Pa.
This low-pressure environment achieves two essential goals. First, it dramatically lowers the boiling point of magnesium, allowing it to turn into a vapor at a much more manageable and energy-efficient temperature (e.g., 650°C).
Second, by evacuating reactive gases like oxygen and nitrogen, the vacuum prevents the hot magnesium vapor from oxidizing or nitriding, which would otherwise contaminate the final product and reduce yield.
Applying Precise Thermal Control
While the vacuum enables the process, the furnace's heating system provides the control.
The system heats the crude magnesium in its crucible to a specific temperature where the magnesium actively vaporizes but other common impurities—such as iron, copper, and aluminum—do not.
Because these impurities have much higher boiling points, they remain behind in the molten state as the pure magnesium vapor rises to be collected and condensed elsewhere in the system.
Anatomy of a High-Purity System
The furnace chamber itself is the platform, but achieving high purity depends on several interconnected components and procedures that ensure the integrity of the process.
The Role of the Graphite Crucible
The crude magnesium is not placed directly into the furnace but is contained within a graphite crucible.
This material is chosen for its excellent high-temperature resistance and chemical stability. It is inert, meaning it will not react with the molten magnesium, thus preventing any secondary contamination from the container itself.
The 'Baking-Out' Pretreatment
Before the distillation process begins, the entire furnace system undergoes a "baking-out" procedure.
This involves heating the empty furnace chamber and its components under vacuum to drive off any adsorbed moisture, residual gases, or other volatile impurities from the internal surfaces. This crucial step prevents these contaminants from being released at high temperatures and mixing with the pure magnesium vapor.
The Necessity of a High-Performance Vacuum Pump
The heart of the low-pressure system is the vacuum pump. A high-performance pump is essential for quickly and effectively reducing the internal pressure to the target level, often as low as 0.01 Pa or 10⁻² mmHg.
A powerful and reliable pump system ensures the magnesium's boiling point remains low and that the environment stays free of reactive gases throughout the entire distillation cycle.
Understanding the Primary Pitfall: Contamination
The effectiveness of vacuum distillation is entirely dependent on maintaining an ultra-clean, tightly controlled environment. The greatest risk to the process is not equipment failure in the traditional sense, but contamination.
The Intolerance for Leaks
Even a minuscule leak in the vacuum chamber can introduce oxygen or nitrogen, which will immediately react with the hot magnesium vapor. This compromises the purity of the final product and reduces the overall process yield.
The Threat of Outgassing
If the furnace interior and crucible are not properly cleaned and "baked-out" before the process, trapped moisture and surface contaminants will be released at high temperatures. This phenomenon, known as outgassing, introduces impurities directly into the vacuum, defeating the purpose of the purification.
Key Principles for Successful Magnesium Purification
To effectively leverage a vertical vacuum furnace, you must focus on controlling the environment to achieve your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximizing purity: Meticulous preparation is non-negotiable; this includes a thorough 'baking-out' procedure and ensuring the highest possible vacuum integrity to prevent any contamination.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: The key is to optimize the relationship between the vacuum level and temperature to achieve the fastest possible vaporization rate without accidentally vaporizing any impurities.
Ultimately, the vertical vacuum furnace enables the transformation of a raw material into a high-value product by precisely controlling the laws of physics.
Summary Table:
| Function | Purpose | Key Parameter |
|---|---|---|
| Create Vacuum | Lowers boiling point, prevents oxidation | Pressure < 10 Pa |
| Apply Precise Heat | Vaporizes magnesium, leaves impurities | Temperature ~650°C |
| Crucible & Baking-Out | Prevents contamination from container/surfaces | Graphite crucible, pre-heating cycle |
Ready to Achieve Ultra-High Purity in Your Metal Processing?
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, CVD systems, and other lab high-temp furnaces, all customizable for unique needs. Our vertical vacuum furnaces are engineered for the precise control and contamination-free environment required for successful vacuum distillation.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK furnace can optimize your purification process, maximize yield, and ensure the highest product quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency



















