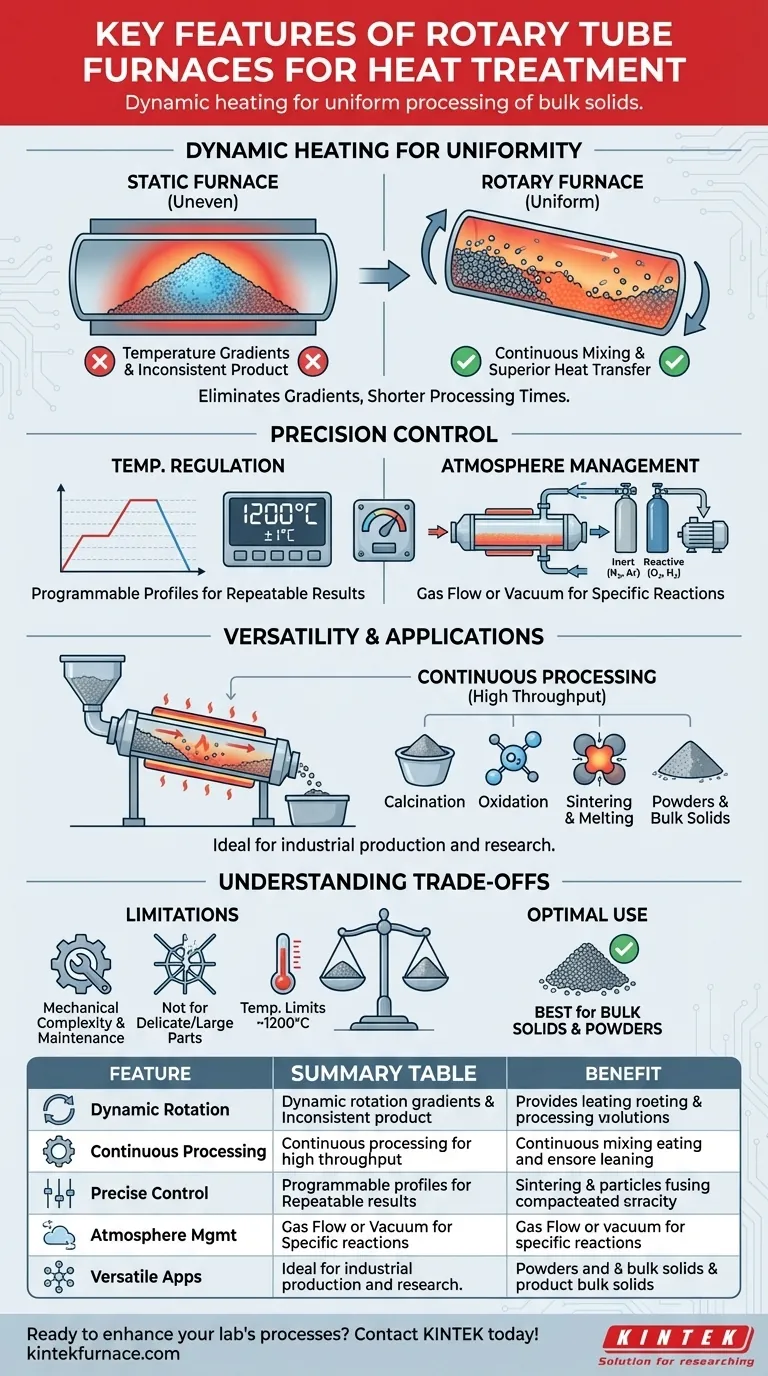
At its core, a rotary tube furnace excels at heat treatment by tumbling materials through a heated, rotating tube. This design ensures every particle is heated uniformly, enables continuous processing for high throughput, and provides precise control over both temperature and atmosphere, making it ideal for processing powders, granules, and other bulk solids.
The fundamental advantage of a rotary tube furnace is its ability to transform the challenge of heating bulk materials from a static, uneven process into a dynamic, highly consistent one. It solves the core problem of temperature gradients that plague traditional furnaces when working with powders and granules.

The Core Principle: Dynamic Heating for Uniformity
The defining feature of a rotary furnace is the rotation itself. Unlike a static box or tube furnace where heat must slowly penetrate a stationary mass, the rotary action actively mixes the material, leading to superior results.
How Rotation Eliminates Temperature Gradients
In a static furnace, the outer layers of a powder or granular material heat up first, effectively insulating the core. This creates a significant temperature difference, or gradient, resulting in an inconsistent final product.
A rotary furnace solves this by continuously tumbling the material. This action constantly brings cooler particles from the interior to the surface of the pile, exposing them directly to the heat source and ensuring every particle follows a similar thermal path.
Impact on Heat Transfer Efficiency
This constant mixing dramatically increases the rate of heat transfer. Because the material is always in motion, heat is absorbed much more quickly and evenly throughout the entire batch.
This efficiency often leads to significantly shorter processing times compared to static methods, increasing productivity and reducing energy consumption per unit of material.
Precision Control Over the Processing Environment
Modern rotary tube furnaces are not just mechanical mixers; they are sophisticated instruments offering granular control over every aspect of the thermal process.
Advanced Temperature Regulation
These furnaces utilize advanced digital controllers that allow for precise temperature management across the heated zone. Many systems feature programmable controllers that can execute complex thermal profiles.
For instance, a controller might support 30 or more programmable "segments," allowing you to define a precise sequence of heating ramps, holds (soaks), and cooling rates. This ensures processes are not only accurate but also perfectly repeatable.
Atmosphere Management (Gas and Vacuum)
Many heat treatment processes require a controlled atmosphere to prevent unwanted chemical reactions (like oxidation) or to promote desired ones.
Rotary furnaces are often equipped with vacuum-tight seals and ports for gas flow. This allows you to operate in an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen or argon), a reactive one, or under vacuum, providing critical flexibility for advanced materials processing.
Versatility in Application and Process
The combination of dynamic heating and precise control makes rotary tube furnaces highly versatile for both industrial production and research.
Enabling Continuous Processing
A key industrial advantage is the ability to operate continuously. Material can be fed into one end of the tilted tube and slowly travel down to the discharge end as it rotates.
This contrasts with static "batch" furnaces, which must be loaded, run, cooled, and unloaded for each cycle. Continuous processing is essential for high-volume manufacturing where throughput is critical.
Key Thermal Processes
Rotary furnaces are ideal for a range of heat treatments applied to bulk solids:
- Calcination: The thermal decomposition of materials, often to remove water or carbon dioxide, such as converting limestone into lime.
- Oxidation: A controlled chemical reaction involving oxygen, used to modify a material's properties. The furnace ensures a uniform reaction throughout the powder.
- Melting & Sintering: The dynamic mixing is effective for uniformly melting powders or sintering them into a solid mass without overheating the outer layers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, rotary tube furnaces are not the universal solution for all heat treatment needs. Objectivity requires acknowledging their limitations.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating mechanism, including the motor, drive system, and rotary seals, adds a layer of mechanical complexity. These components require more maintenance than a simple static furnace and can be potential points of failure over time.
Material Constraints
The tumbling action that is so beneficial for powders is unsuitable for treating large, single components or delicate structures that could be damaged by the mechanical movement. The furnace is explicitly designed for bulk materials.
Temperature and Tube Limitations
The maximum operating temperature (often around 1200°C) is dictated by the tube material, which can be quartz, ceramic, or a high-temperature metal alloy. Applications requiring higher temperatures may necessitate different furnace designs, such as a graphite furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on your material and your processing goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume processing of powders or granules: The rotary tube furnace is superior due to its continuous operation and unmatched heating uniformity.
- If your primary focus is precise, repeatable chemical reactions (e.g., calcination): This furnace is an excellent choice for its combination of dynamic mixing and tight atmospheric control.
- If your primary focus is heat treating single, large parts or delicate samples: A static box furnace or a standard (non-rotating) tube furnace is the more appropriate tool.
Ultimately, a rotary tube furnace is the definitive tool for achieving thermal consistency and efficiency when processing bulk solids.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Rotation | Tumbles materials in a heated tube | Eliminates temperature gradients for uniform heating |
| Continuous Processing | Allows material feed and discharge during operation | High throughput and efficiency in production |
| Precise Temperature Control | Uses digital controllers with programmable profiles | Accurate, repeatable thermal processes |
| Atmosphere Management | Supports inert gases, reactive atmospheres, or vacuum | Prevents oxidation and enables specific chemical reactions |
| Versatile Applications | Ideal for calcination, oxidation, melting, and sintering | Suitable for powders, granules, and bulk solids |
Ready to enhance your lab's heat treatment processes with precision and efficiency? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're processing powders, granules, or other bulk solids, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your laboratory!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries



















