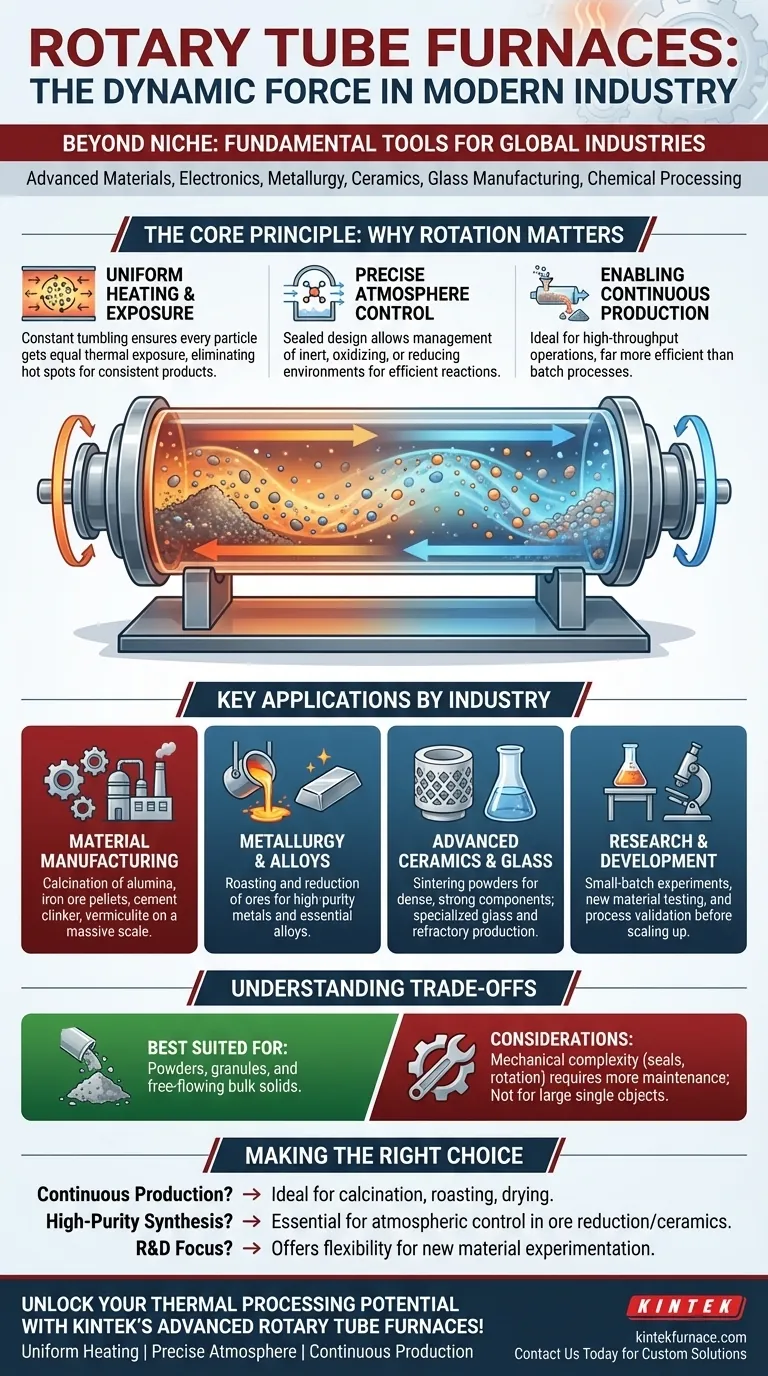
Beyond a few niche applications, rotary tube furnaces are fundamental tools across a broad spectrum of industries, including advanced materials, electronics, metallurgy, ceramics, glass manufacturing, and chemical processing. Their value stems from a unique ability to uniformly heat and continuously process powders, granules, and other loose materials in a tightly controlled environment. This makes them indispensable for both large-scale industrial production and advanced research.
The true significance of a rotary tube furnace isn't just the list of industries it serves, but the specific process it enables. Its ability to continuously tumble and expose every particle of a loose material to a uniform temperature and controlled atmosphere is the core reason for its widespread adoption.

The Core Principle: Why Rotation Matters
Understanding why these furnaces are so versatile begins with their fundamental design. Unlike a static furnace, the entire process chamber rotates, which provides several critical advantages.
Uniform Heating and Material Exposure
The constant tumbling motion ensures that the material—be it a powder, pellet, or granule—is mixed thoroughly as it travels through the furnace.
This dynamic movement prevents hot spots and guarantees that every particle is exposed to the same thermal conditions, resulting in a highly consistent and uniform final product.
Precise Atmosphere Control
The sealed tube design allows for the precise management of the internal atmosphere. Processes can be conducted in inert, oxidizing, or reducing environments.
Rotation ensures that the process gas interacts with the entire surface area of the material, leading to efficient and complete chemical reactions like oxidation or reduction.
Enabling Continuous Production
Rotary furnaces are ideal for continuous throughput operations where raw material is fed into one end and a finished product is discharged from the other.
This design is far more efficient for large-scale manufacturing than batch furnaces, which must be loaded, heated, cooled, and unloaded in distinct cycles.
Key Applications by Industry
The unique processing capabilities of rotary tube furnaces make them essential for specific tasks across many sectors.
Material Manufacturing
These furnaces are workhorses for producing key industrial commodities. The process of calcination—heating a solid to a high temperature to cause a phase transition or thermal decomposition—is a common application.
Examples include producing alumina, iron ore pellets, vermiculite, and cement clinker on a massive scale.
Metallurgy and Alloy Production
In metallurgy, rotary furnaces are critical for refining ores and creating high-purity metals and alloys.
They facilitate crucial processes like roasting (heating in the presence of air) and reduction (removing oxygen), which are essential steps in extracting metals from their ores.
Advanced Ceramics and Glass
For advanced ceramics, the uniform heating provided by a rotary furnace is used for sintering powders. This process creates dense, strong, and homogenous ceramic components.
They are also used in specialized glass manufacturing and in the production of refractory materials designed to withstand extreme heat.
Research and Development
In university labs, research institutes, and corporate R&D departments, smaller lab-scale rotary furnaces offer unparalleled flexibility.
Their adaptability allows researchers to experiment with new materials, test novel chemical processes in small batches, and validate production parameters before scaling up to industrial levels.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, rotary tube furnaces are not a universal solution. Their advantages are tied to specific use cases, and understanding their limitations is key to proper application.
Best Suited for Loose Materials
Their core strength is processing powders, granules, and other free-flowing bulk solids. They are not designed for heating large, single objects, liquids, or materials that could clump or stick to the tube walls.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotation mechanism, including the drive motor, gears, and especially the seals at either end of the tube, adds mechanical complexity. These components require more maintenance than a simple, static tube or box furnace.
Throughput vs. Batch Size
While excellent for continuous flow, their effective volume at any given moment can be smaller than that of a large batch furnace. For applications requiring a single, very large object or batch to be heated simultaneously, a different furnace type may be more suitable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal processing equipment depends entirely on your objective. The decision to use a rotary tube furnace should be driven by the nature of your material and desired process.
- If your primary focus is continuous industrial production: A rotary tube furnace is the ideal choice for calcination, roasting, or drying of powders and pellets.
- If your primary focus is high-purity material synthesis: The precise atmospheric and thermal control of a rotary furnace is essential for processes like ore reduction or creating advanced ceramic powders.
- If your primary focus is research and development: A flexible, lab-scale rotary furnace provides the control and adaptability needed for experimenting with new material compositions and processes.
Ultimately, understanding the principle of dynamic material exposure is the key to leveraging the full potential of a rotary tube furnace in any application.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications |
|---|---|
| Material Manufacturing | Calcination (e.g., alumina, cement clinker) |
| Metallurgy | Roasting and reduction of ores |
| Advanced Ceramics and Glass | Sintering powders for dense components |
| Chemical Processing | Controlled atmosphere reactions |
| Research and Development | Small-batch experiments and process validation |
Unlock the full potential of your thermal processing with KINTEK's advanced rotary tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for uniform heating, precise atmosphere control, and continuous production. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your efficiency and results in materials, metallurgy, ceramics, and beyond!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing
- What are the key features of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Control



















