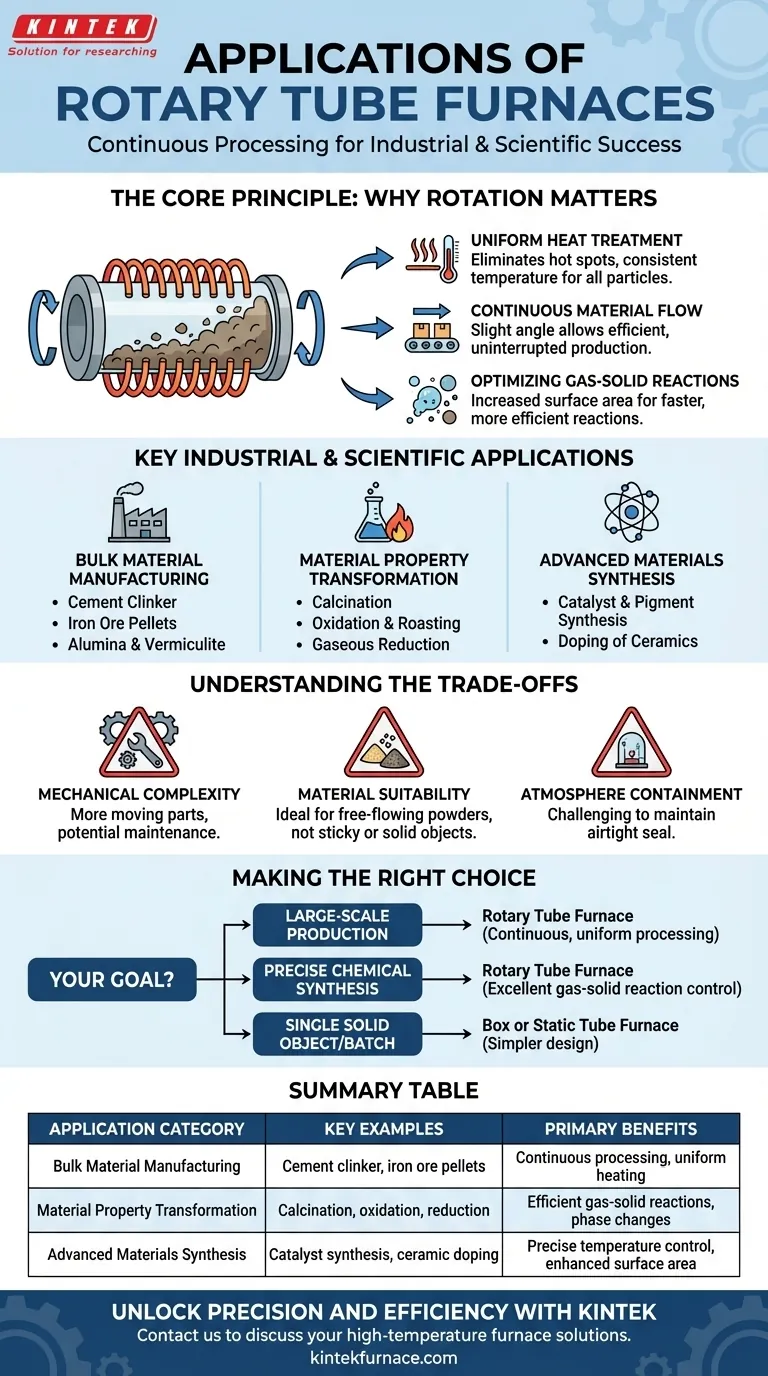
From industrial manufacturing to advanced research, rotary tube furnaces are employed for a specific set of high-temperature tasks that require the continuous processing of loose materials. Their applications range from producing essential industrial commodities like cement clinker and iron ore pellets to executing precise chemical processes such as oxidation, calcination, and catalyst synthesis.
The core challenge in many thermal processes is achieving uniform heat treatment and atmospheric reaction throughout a bulk powder or granular material. Rotary tube furnaces solve this by continuously tumbling the material, ensuring every particle is evenly exposed to heat and the process atmosphere, making them indispensable for continuous, high-throughput applications.
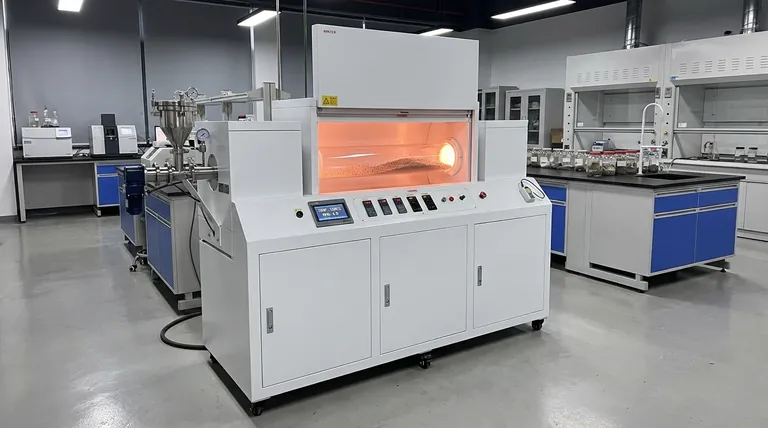

The Core Principle: Why Rotation Matters
The defining feature of a rotary tube furnace is its ability to mix materials while heating them. This simple mechanical action provides several fundamental advantages over static furnace designs.
Ensuring Uniform Heat Treatment
In a stationary furnace, materials at the top of a pile can become overheated while those at the bottom remain too cool. The tumbling action of a rotary furnace constantly circulates the material, eliminating hot spots and ensuring every particle experiences a consistent temperature profile.
Enabling Continuous Material Flow
Most rotary tube furnaces are designed on a slight angle. This allows raw material to be continuously fed into the higher end and for the processed product to be steadily discharged from the lower end, creating an efficient, uninterrupted production line ideal for industrial scales.
Optimizing Gas-Solid Reactions
Processes like oxidation (adding oxygen), reduction (removing oxygen), or calcination often require a specific gas atmosphere to react with the solid material. The constant mixing dramatically increases the surface area exposed to the process gas, leading to faster, more complete, and more efficient chemical reactions.
Key Industrial and Scientific Applications
The unique capabilities of rotary tube furnaces make them a preferred solution across several sectors, from heavy industry to materials science.
Bulk Material Manufacturing
This is the most common application, focused on high-volume production.
- Cement Clinker: A crucial intermediate component in the manufacturing of Portland cement.
- Iron Ore Pellets: Preparing iron ore for use in a blast furnace.
- Alumina & Vermiculite: Processing raw minerals into usable industrial forms.
Material Property Transformation
These applications use heat and controlled atmospheres to fundamentally change a material's chemical or physical structure.
- Calcination: A high-temperature process that induces phase transformations or removes volatile fractions, such as when converting oil shale or preparing catalyst supports.
- Oxidation & Roasting: Used extensively in metallurgy to convert ores into their oxides, making them easier to process further.
- Gaseous Reduction: The reverse of oxidation, used to reduce metal oxides back to their metallic form using a reducing gas.
Advanced Materials Synthesis
In laboratory and specialized production settings, precision is key. These furnaces are used for:
- Catalyst & Pigment Synthesis: Creating materials with specific surface properties and chemical compositions that depend on precise temperature control.
- Doping of Ceramics: Introducing small amounts of other elements, like rare earth metals, into a ceramic's crystal structure to alter its properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, rotary tube furnaces are not a universal solution. Their specialized design comes with specific limitations.
Mechanical Complexity
The motor, drive system, and rotating seals add mechanical complexity compared to a simple static box or tube furnace. This introduces additional maintenance requirements and potential points of failure.
Material Suitability
These furnaces are designed for free-flowing powders, granules, and pellets. They are not suitable for materials that are sticky, that could melt and agglomerate into a large mass, or for single, solid objects.
Atmosphere Containment
Maintaining a perfectly airtight seal at the ends of a rotating tube can be more challenging than with a static tube. For processes requiring extremely pure or highly controlled atmospheres, this is a critical design consideration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a rotary tube furnace depends entirely on your material's form and your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is large-scale production of bulk materials: A rotary tube furnace is ideal due to its capacity for continuous, uniform processing of powders and pellets.
- If your primary focus is precise chemical synthesis: A rotary furnace offers excellent control over gas-solid reactions, making it superior for applications requiring constant material agitation.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating a single solid object or a static powder batch: A rotary furnace is unsuitable; a simpler box or static tube furnace is the correct tool.
Ultimately, the unique advantage of a rotary tube furnace lies in its ability to combine high-temperature treatment with continuous material agitation, a capability essential for a specific but critical set of industrial and scientific processes.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Examples | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Bulk Material Manufacturing | Cement clinker, iron ore pellets | Continuous processing, uniform heating |
| Material Property Transformation | Calcination, oxidation, reduction | Efficient gas-solid reactions, phase changes |
| Advanced Materials Synthesis | Catalyst synthesis, ceramic doping | Precise temperature control, enhanced surface area |
Unlock Precision and Efficiency in Your Thermal Processes with KINTEK
Are you working with powders, granules, or pellets and need uniform heat treatment for applications like calcination, oxidation, or catalyst synthesis? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your experimental and production requirements, whether for industrial manufacturing or advanced research.
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities? Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can drive your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are the common applications of a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating for Powders and Granules
- What are the main advantages of rotary tube furnaces? Achieve Superior Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries



















