At its core, the continuous movement in a rotary tube furnace ensures every particle of the sample is uniformly exposed to the furnace's heat and atmosphere. This dynamic exposure dramatically improves process efficiency by enhancing gas diffusion and heat transfer, leading to faster results and reduced gas consumption compared to static furnace methods.
The fundamental advantage is transforming a process from static to dynamic. By constantly tumbling the material, you eliminate inconsistencies in temperature and chemical reactions that plague stationary samples, unlocking higher efficiency and scalability.

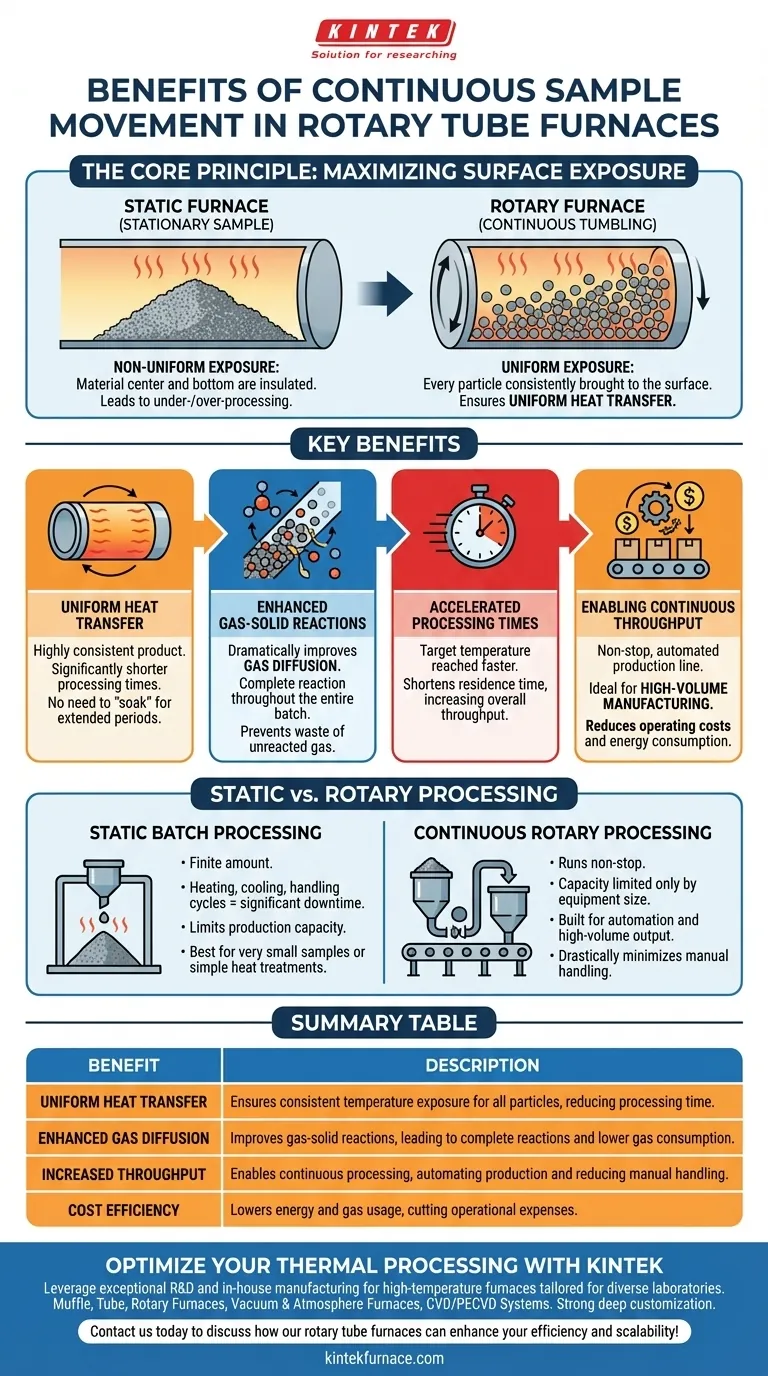
The Core Principle: Maximizing Surface Exposure
The primary benefit of a rotary tube furnace stems from one simple action: rotation. This movement fundamentally changes how a material, particularly a powder or granular solid, interacts with its environment during thermal processing.
Overcoming Static Limitations
In a static or stationary furnace, a sample sits motionless. This means the material on the bottom and in the center of the pile is insulated, receiving heat and atmospheric gases far less effectively than the material on the surface.
This leads to non-uniform processing, where parts of your sample may be under-processed while others are over-processed.
Ensuring Uniform Heat Transfer
Continuous rotation tumbles the material, ensuring that every particle is consistently brought to the surface. This action guarantees that the entire sample batch receives direct, uniform heat transfer.
The result is a highly consistent product and significantly shorter processing times, as you no longer need to "soak" the material for extended periods to heat its core.
Enhancing Gas-Solid Reactions
For processes involving reactive gases—such as calcination, reduction, or synthesis—rotation is critical. It constantly exposes new material surfaces to the process gas.
This active mixing dramatically improves gas diffusion into the solid particles, ensuring a complete reaction throughout the entire batch and preventing the waste of unreacted gas.
Translating Uniformity into Process Efficiency
Achieving uniform exposure is not just an academic goal; it produces tangible benefits in cost, speed, and scale. These advantages make rotary tube furnaces a superior choice for many industrial and research applications.
Accelerating Processing Times
Because heat transfer is so efficient, the target temperature is reached throughout the material much faster. This directly shortens the required residence time in the furnace, increasing overall throughput.
Reducing Operating Costs
Improved gas diffusion means less gas is needed to complete a reaction, lowering consumption costs. Faster processing cycles also reduce energy consumption per batch, further cutting operational expenses.
Enabling Continuous Throughput
The rotary motion is what makes a continuous process possible. Material can be fed into one end of the tilted tube and, as it tumbles, it travels to the other end for collection.
This transforms the operation from a series of discrete, manual batches into a non-stop, automated production line, ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Rotary vs. Static Furnaces
Choosing between a rotary and a static furnace depends entirely on your process goals. While rotation offers clear advantages, understanding the operational differences is key.
The Inefficiency of Static Batch Processing
A static batch process requires loading a finite amount of material, running the heating cycle, cooling the entire furnace, and then manually unloading the sample.
This cycle of heating, cooling, and handling introduces significant downtime and limits production capacity.
The Scalability of Continuous Rotary Processing
A continuous rotary process runs non-stop. Material is fed from a large hopper and collected in another, with capacity limited only by the size of this peripheral equipment.
This method is built for automation and high-volume output, drastically minimizing manual handling and maximizing uptime.
When a Static Furnace Is Sufficient
For very small sample sizes, simple heat treatments (annealing) that don't involve reactive gases, or applications where perfect uniformity is not the primary goal, a simpler static tube furnace can be a perfectly adequate and more economical choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision depends on the specific demands of your material and your production goals. Use these guidelines to make an informed choice.
- If your primary focus is sample uniformity and reaction efficiency: The continuous movement of a rotary furnace is unmatched for ensuring consistent heat and gas exposure.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, automated production: A continuous rotary system is the clear choice for its scalability and reduced manual intervention.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment or small-scale R&D: A static tube furnace may provide the necessary functionality at a lower initial cost.
By understanding how continuous movement solves the core problems of uniformity and efficiency, you can select the right tool to achieve your processing objectives.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Uniform Heat Transfer | Ensures consistent temperature exposure for all particles, reducing processing time. |
| Enhanced Gas Diffusion | Improves gas-solid reactions, leading to complete reactions and lower gas consumption. |
| Increased Throughput | Enables continuous processing, automating production and reducing manual handling. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lowers energy and gas usage, cutting operational expenses. |
Ready to optimize your thermal processing with advanced furnace solutions? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide high-temperature furnaces tailored for diverse laboratories. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our rotary tube furnaces can enhance your efficiency and scalability!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- How do rotary tube furnaces support real-time monitoring and continuous processing? Boost Efficiency with Continuous Flow & Live Observation
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput



















