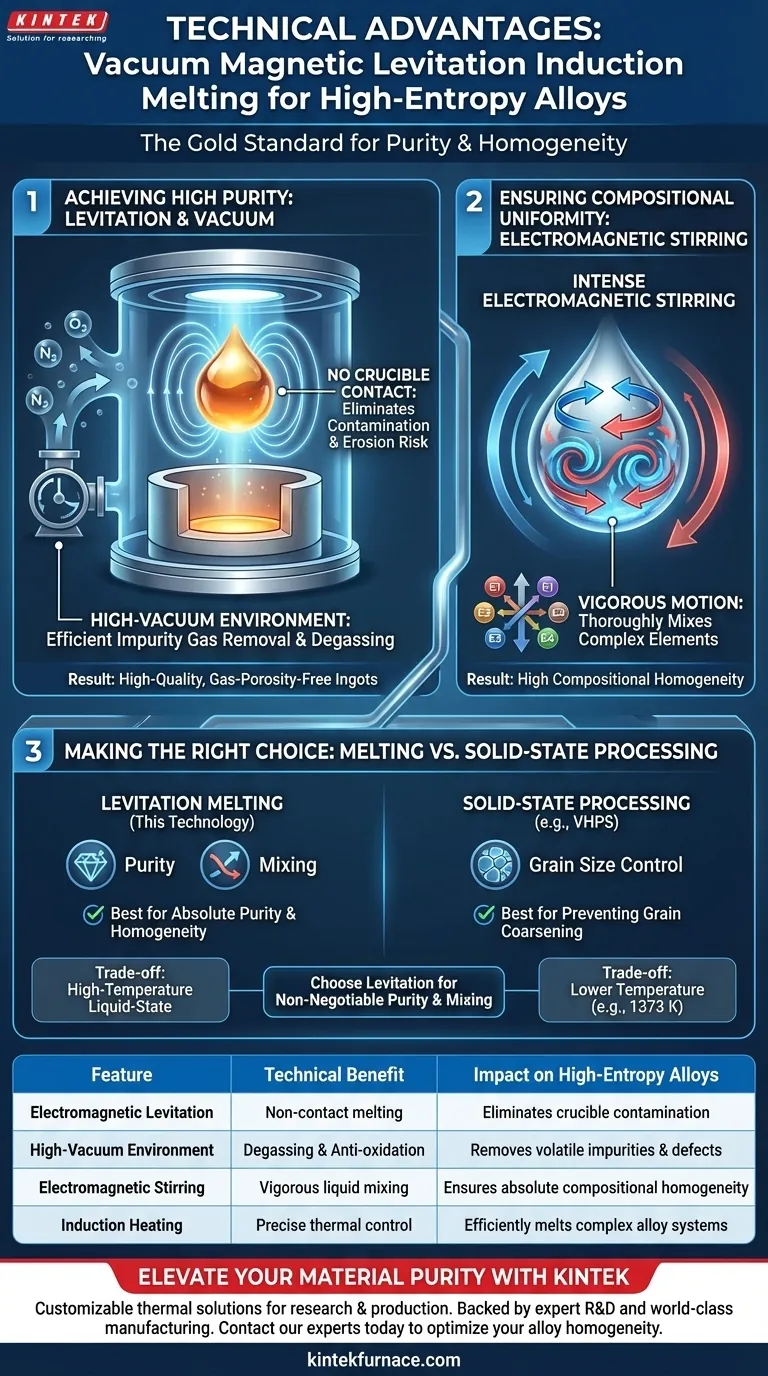
The primary technical advantage of a vacuum magnetic levitation induction melting furnace is the complete elimination of crucible contamination through the use of electromagnetic suspension. This technology enables the production of high-entropy alloys with exceptional purity and compositional uniformity by combining non-contact melting with intense electromagnetic stirring in a high-vacuum environment.
By suspending the molten metal, this method removes the greatest source of impurities—the crucible itself—while simultaneously using electromagnetic forces to aggressively mix complex alloy compositions.
Achieving High Purity Through Levitation
Elimination of Crucible Contact
The defining feature of this technology is the utilization of electromagnetic force to suspend the molten metal.
Because the liquid metal never makes direct contact with the crucible walls, there is zero risk of the crucible material eroding and contaminating the melt. This is critical for high-entropy alloys (HEAs) that may contain reactive elements that typically attack standard crucible linings.
Efficient Removal of Impurity Gases
The furnace operates within a high-vacuum environment, which serves a dual purpose beyond simple isolation.
The vacuum actively promotes the removal of volatile impurity gases from the melt. By lowering the oxygen partial pressure, the system prevents oxidation and degasses the material, resulting in high-quality ingots free from gas porosity.
Ensuring Compositional Uniformity
Intense Electromagnetic Stirring
High-entropy alloys consist of multiple principal elements, making segregation a significant technical challenge during production.
The same electromagnetic field that levitates the metal also induces intense stirring within the molten droplet. This continuous, vigorous motion ensures that all constituent elements are thoroughly mixed, resulting in an alloy with high compositional homogeneity throughout the ingot.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Melting vs. Solid-State Processing
While vacuum magnetic levitation is superior for purity and mixing, it is fundamentally a high-temperature liquid-state process.
In contrast, methods like Vacuum Hot Pressing Sintering (VHPS) operate at lower, solid-state temperatures (e.g., 1373 K). While levitation melting ensures mixing, the high temperatures involved may not offer the same inhibition of grain growth found in lower-temperature sintering techniques.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this furnace aligns with your production needs, consider your specific targets for the alloy's microstructure and purity.
- If your primary focus is absolute purity and homogeneity: Use vacuum magnetic levitation to prevent crucible contamination and ensure complex elements are fully mixed.
- If your primary focus is grain size control: Consider that while levitation offers purity, solid-state methods like VHPS may be better suited for preventing grain coarsening during formation.
This technology represents the gold standard for producing complex alloys where chemical purity and homogeneity are non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Technical Benefit | Impact on High-Entropy Alloys |
|---|---|---|
| Electromagnetic Levitation | Non-contact melting | Eliminates crucible contamination and reactive element erosion |
| High-Vacuum Environment | Degassing & anti-oxidation | Removes volatile impurities and prevents oxygen-induced defects |
| Electromagnetic Stirring | Vigorous liquid mixing | Ensures absolute compositional homogeneity across multiple elements |
| Induction Heating | Precise thermal control | Efficiently melts complex alloy systems with high melting points |
Elevate Your Material Purity with KINTEK
Precision in high-entropy alloy production demands equipment that eliminates contamination at the source. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides advanced Vacuum Magnetic Levitation systems alongside our full suite of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and CVD furnaces. Whether you require absolute purity through non-contact melting or specialized grain size control, our laboratory high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research and production needs.
Ready to optimize your alloy homogeneity? Contact our experts today to find the perfect thermal solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- Mateusz Włoczewski, Dariusz M. Jarząbek. AlCoCrFeNiTi0.2 High-Entropy Alloy Under Plasma Nitriding: Complex Microstructure Transformation, Mechanical and Tribological Enhancement. DOI: 10.1007/s11661-025-07752-1
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using an IGBT induction melting machine? Boost Efficiency & Quality
- What is vacuum melting technology and how does it work? Unlock Pure, High-Performance Metals
- How does induction heating improve quality control in manufacturing? Achieve Unprecedented Repeatability & Reduce Defects
- What role does a vacuum non-consumable arc furnace play in high-entropy alloys? Master Complex Alloy Synthesis
- How does induction heating contribute to pyrolysis? Unlock Precision and Efficiency in Biomass Processing
- What causes the melting of the solid scrap in the arc furnace? Unlock Efficient Steel Production
- What is the necessity of a water cooling unit for high-power induction heating systems? Protect Your Equipment Now
- What are the key segments of the IGBT induction melting furnace market? A Guide to Modern Metal Melting



















