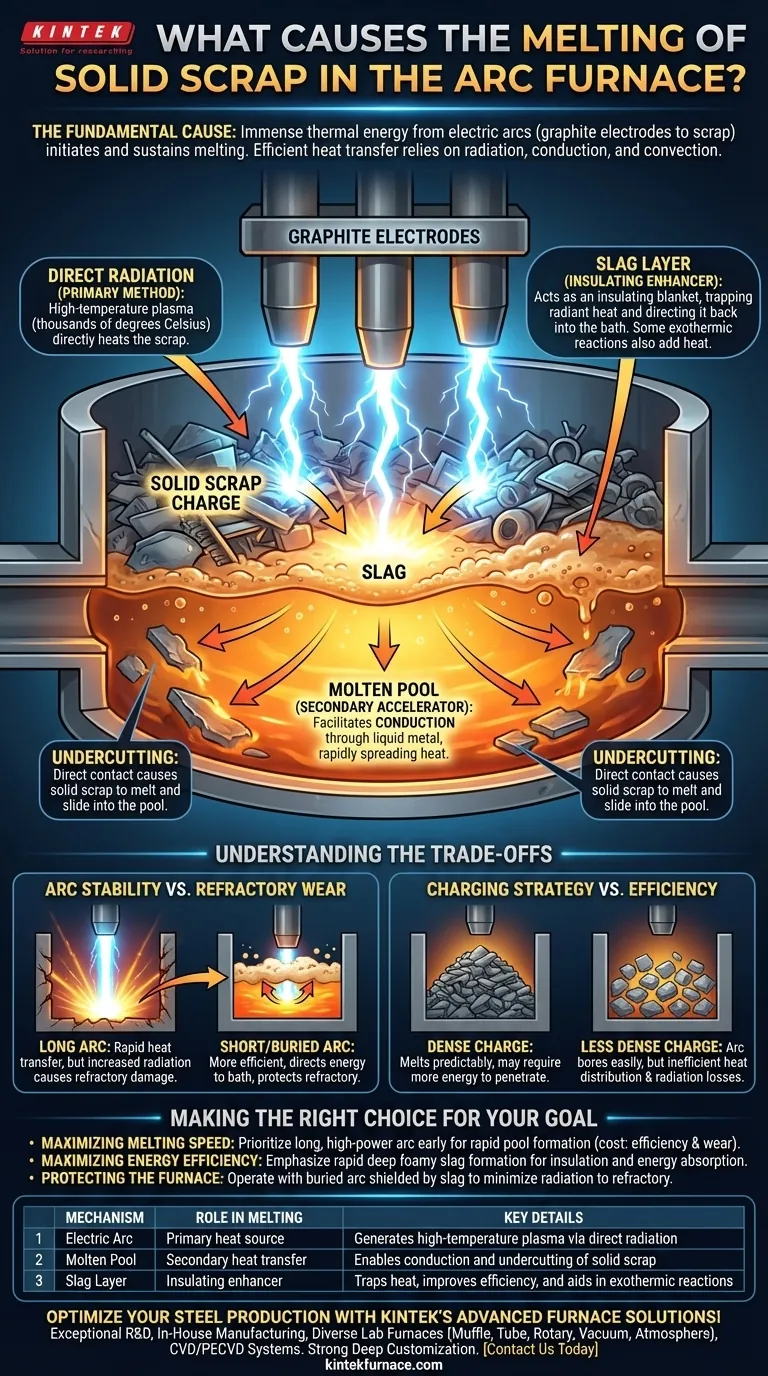
The fundamental cause of melting in an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is the immense thermal energy generated by electric arcs. These arcs, established between the graphite electrodes and the metallic scrap charge, act as the primary heat source that initiates and sustains the melting process.
While the electric arc is the direct catalyst for melting, the truly efficient transfer of heat throughout the furnace relies on a combination of direct radiation, conduction through the molten steel pool, and convection within the slag layer. Understanding these distinct pathways is key to optimizing furnace performance.

The Journey from Solid to Liquid: Heat Transfer in an EAF
The process of melting a solid scrap charge is not a single event but a sequence of coordinated heat transfer mechanisms. The electric arc is the starting point, but other elements quickly become critical to the efficiency of the operation.
The Primary Driver: The Electric Arc
The arc itself is a discharge of high-current electricity across a gap, creating a plasma column with temperatures reaching thousands of degrees Celsius. This intense energy is transferred to the scrap through several methods.
The primary method is direct radiation. The arc radiates enormous amounts of thermal energy in all directions, directly heating the scrap it "sees." This is most effective on the scrap located immediately below and around the electrodes.
As the scrap directly under the arc begins to melt, it forms a pool of liquid metal. The arc then makes contact with this liquid pool, ensuring a stable and continuous electrical circuit.
The Secondary Accelerator: The Molten Pool
Once a liquid pool of metal is established, it becomes a crucial secondary medium for heat transfer. It plays two significant roles in melting the remaining solid scrap.
First, it facilitates conduction. The liquid metal, superheated by the arc, is an excellent thermal conductor. Heat rapidly spreads from the arc impingement zone throughout the molten bath.
Second, the hot liquid metal directly contacts the surrounding solid scrap. This direct contact allows for rapid heat transfer, causing the solid scrap to melt and slide down into the growing pool, a process often referred to as "undercutting."
The Insulating Enhancer: The Slag Layer
As melting progresses, fluxes like lime and dolomite are added, which combine with oxides and impurities to form a liquid slag layer that floats on top of the molten steel.
This slag layer serves as an insulating blanket. It traps the radiant heat from the arc, preventing it from escaping to the furnace walls and roof, and directs it back down into the molten bath. This dramatically improves the furnace's thermal efficiency.
Furthermore, chemical reactions within the slag can be exothermic (releasing heat), providing an additional, albeit smaller, source of thermal energy to the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Optimizing the melting process involves balancing competing factors. A focus on speed can sometimes compromise efficiency or final product quality.
Arc Stability vs. Refractory Wear
A long, powerful arc can transfer heat very rapidly over a wide area. However, this increased radiation can also cause significant damage to the furnace's refractory-lined walls and roof, leading to higher maintenance costs and downtime.
Conversely, a short, "buried" arc that is shielded by a foamy slag is much more efficient. It directs its energy primarily into the bath, protecting the refractory. Achieving and maintaining this ideal foamy slag condition requires careful control of carbon and oxygen injection.
Charging Strategy vs. Efficiency
The way scrap is loaded (or "charged") into the furnace also presents a trade-off. A dense charge melts more predictably but may require more energy to penetrate. A less dense charge allows the arc to bore through more easily but can lead to inefficient heat distribution and higher radiation losses to the walls.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The operational focus of an EAF dictates how these heat transfer mechanisms are managed.
- If your primary focus is maximizing melting speed: Prioritize a long, high-power arc early in the process to rapidly form a liquid pool, even at the cost of some initial thermal efficiency and refractory wear.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency: Emphasize the rapid formation of a deep, foamy slag layer to insulate the bath and ensure the majority of the arc's energy is absorbed by the charge, not lost to the surroundings.
- If your primary focus is protecting the furnace: Operate with a buried arc shielded by slag as much as possible, minimizing direct radiation to the refractory walls and roof.
Ultimately, mastering the melting process is about controlling the flow of energy from the arc to the solid scrap through the most effective pathways available.
Summary Table:
| Mechanism | Role in Melting | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Arc | Primary heat source | Generates high-temperature plasma via direct radiation |
| Molten Pool | Secondary heat transfer | Enables conduction and undercutting of solid scrap |
| Slag Layer | Insulating enhancer | Traps heat, improves efficiency, and aids in exothermic reactions |
Optimize your steel production with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance efficiency and performance in your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency



















