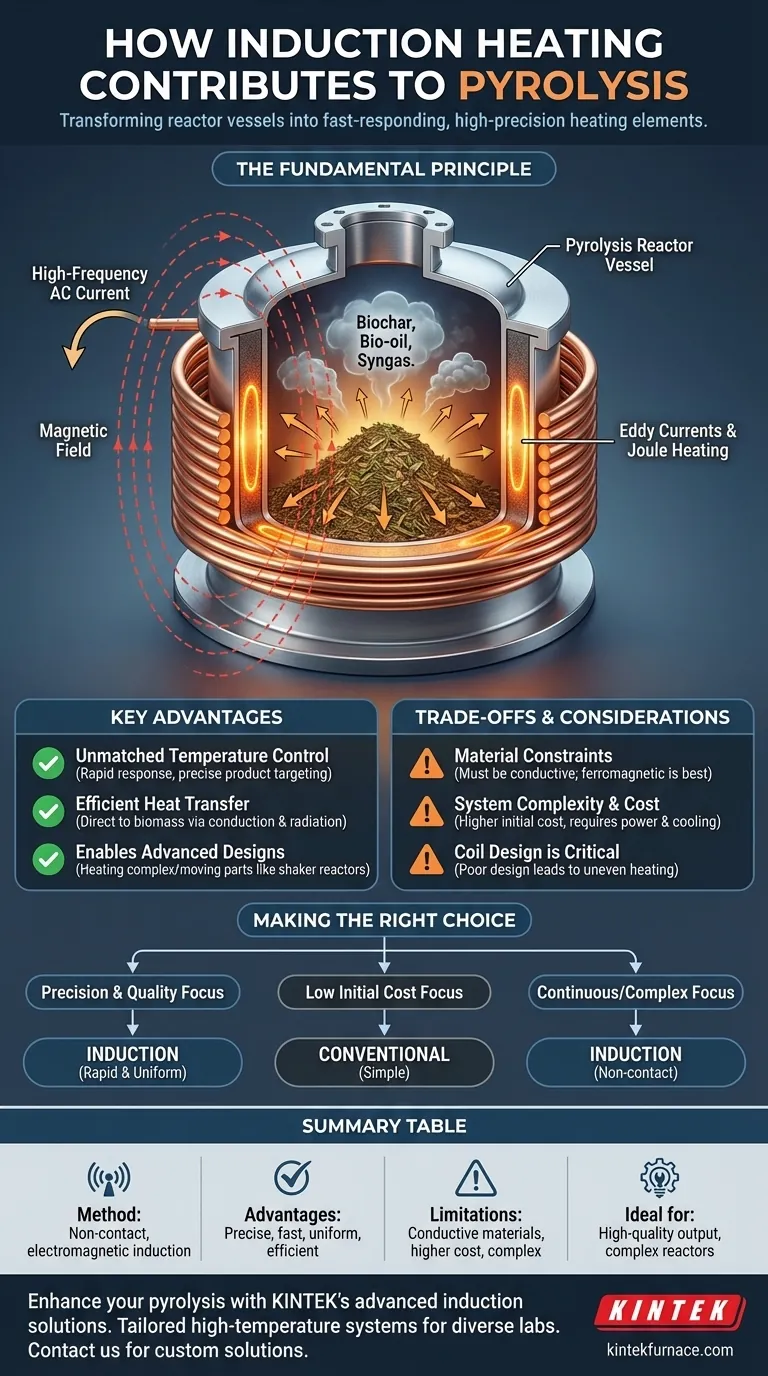
In pyrolysis, induction heating is a non-contact method that uses an electromagnetic field to heat the conductive walls of the reactor. The reactor wall then becomes the heat source, transferring thermal energy to the biomass inside and causing it to decompose. This indirect approach provides rapid, precise, and uniform temperature control, which is critical for managing the outcome of the pyrolysis process.
The core contribution of induction heating to pyrolysis is transforming the reactor vessel itself into a fast-responding, high-precision heating element. This enables superior control over the reaction temperature and improves overall process efficiency compared to traditional external heating.
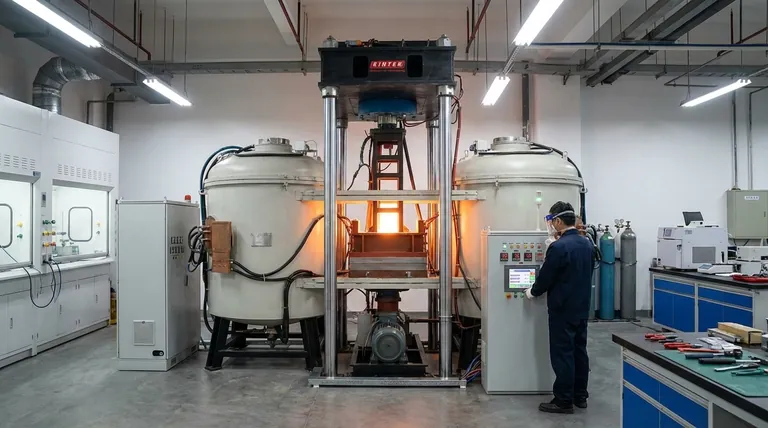

The Fundamental Principle: How Induction Heats the Reactor
Induction heating is fundamentally different from conventional heating methods that apply heat from an external source. The heat is generated directly within the material of the reactor.
Creating the Magnetic Field
The process begins with a high-frequency alternating current (AC) being passed through a copper coil. This coil is positioned around the pyrolysis reactor but does not touch it. The AC flowing through the coil generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field.
Inducing Electrical Currents
When the conductive metal walls of the reactor are placed within this magnetic field, the field induces small, circular electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
Generating Heat from Within
The reactor's metal has natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents. This resistance causes the energy from the currents to be converted into heat through a process called Joule heating. For reactors made of ferromagnetic materials like steel, additional heat is generated by magnetic hysteresis losses, further increasing efficiency.
Key Advantages in a Pyrolysis Context
Using induction provides several distinct advantages for controlling the thermal decomposition of materials like biomass.
Unmatched Temperature Control
The heat generation is nearly instantaneous and stops the moment the magnetic field is turned off. This gives operators extremely fast response times and precise control over the reaction temperature, which is crucial for targeting specific products like biochar, bio-oil, or syngas.
Efficient Heat Transfer
Because the reactor wall is the heat source, energy is transferred directly to the biomass via conduction and radiation. This is far more efficient than conventional furnaces, which must first heat the air or a large thermal mass around the reactor, leading to significant energy loss.
Enabling Advanced Reactor Designs
The non-contact nature of induction allows for heating reactors with complex or moving parts, such as the shaker reactors mentioned in process literature. It is difficult or impossible to attach conventional heating elements to such systems, making induction a key enabling technology.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. It comes with specific requirements and limitations that must be considered.
Material Constraints
The primary limitation is that the part of the reactor being heated must be electrically conductive. Performance is significantly enhanced with ferromagnetic materials. This constrains the choice of construction materials compared to other heating methods.
System Complexity and Cost
An induction heating system consists of a power supply, a cooling system, and a carefully designed induction coil. This setup can have a higher initial capital cost and be more complex to implement than simple resistance heaters or a gas-fired furnace.
Coil Design is Critical
The geometry of the induction coil is paramount to performance. A poorly designed coil can lead to uneven heating or "hot spots" on the reactor surface, which can negatively impact the uniformity of the pyrolysis process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right heating method depends entirely on your project's specific goals, constraints, and scale.
- If your primary focus is process precision and high-quality output: Induction is an excellent choice due to its rapid response and uniform temperature control.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial cost for a simple batch process: A conventional electric furnace or direct resistance heating may be a more practical solution.
- If your primary focus is a continuous process with a complex or moving reactor: Induction's non-contact heating capability makes it a superior and often necessary technology.
By understanding these core principles and trade-offs, you can determine if induction heating is the right tool to achieve your specific pyrolysis objectives.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Contribution to Pyrolysis |
|---|---|
| Heating Method | Non-contact, indirect heating via electromagnetic induction |
| Key Advantages | Precise temperature control, rapid response, uniform heating, high efficiency |
| Ideal Applications | Processes requiring high-quality output, complex reactor designs, continuous systems |
| Limitations | Requires conductive reactor materials, higher initial cost, complex setup |
Ready to enhance your pyrolysis process with advanced induction heating solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature furnace systems. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can improve your efficiency and output quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station CVD Machine
People Also Ask
- How does the use of vacuum in hot-pressing affect the material processing? Achieve Denser, Purer, and Stronger Materials
- What are the overall benefits of using hot pressing in manufacturing? Achieve Superior Performance and Precision
- What are the main applications of vacuum hot pressing? Create Dense, Pure Materials for Demanding Industries
- What are the advantages of ceramic/metal composites produced using a vacuum press? Achieve Superior Strength and Durability
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density



















