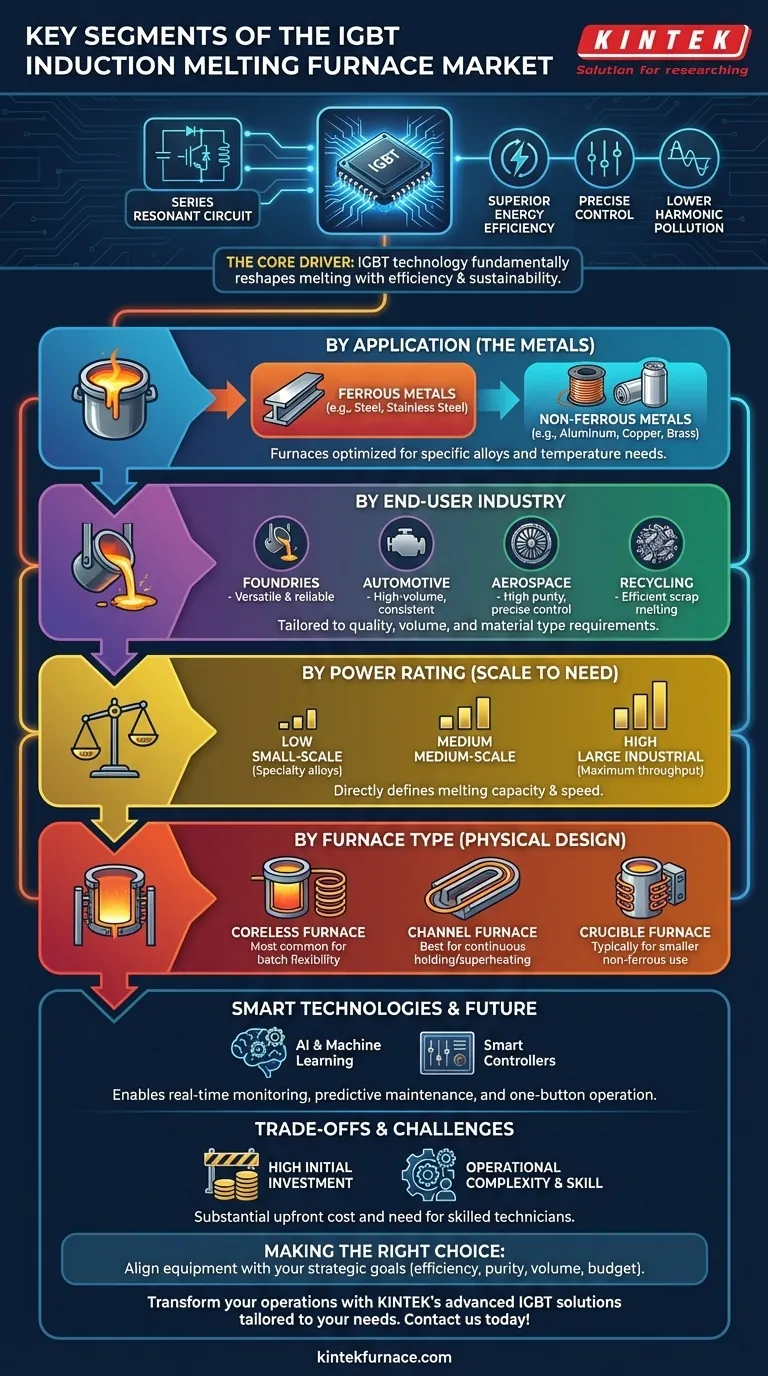
In short, the IGBT induction melting furnace market is segmented by its application (the metals being melted), the end-user industry (like foundry or automotive), its power rating, the specific furnace design, and the level of technology it incorporates. These categories help define a furnace's specific capabilities and its place within the industrial landscape.
The core takeaway is that while these segments define the market's structure, the true driver of change is the IGBT technology itself. Its ability to deliver superior energy efficiency, precise control, and lower environmental impact is fundamentally reshaping how industries approach metal melting.

What Defines an IGBT Induction Furnace?
An IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) induction furnace is a modern evolution of induction melting technology. It uses IGBT modules as high-speed switches in its power supply.
This design creates a series resonant circuit, which is the source of its primary advantages. Unlike older SCR (silicon-controlled rectifier) systems, IGBT furnaces offer excellent startup performance, faster melting speeds, and a consistent power output throughout the entire melting process.
Crucially, this technology produces significantly less harmonic pollution. This means it doesn't disrupt the electrical grid or interfere with other sensitive electronic equipment in the factory, a major operational benefit.
A Breakdown of Key Market Segments
Understanding the market requires looking at it from several angles. Each segment reflects a different aspect of customer need and technical specification.
By Application: The Metals Being Melted
The primary function of a furnace is to melt metal, making this a critical segment. Furnaces are optimized for different materials, which are broadly categorized as ferrous metals (like carbon steel, cast steel, and stainless steel) and non-ferrous metals (like copper, aluminum, and brass).
The specific alloy and its required melting temperature and purity directly influence the choice of furnace. For instance, the constant power output of an IGBT furnace is particularly efficient for melting stainless steel, copper, and aluminum.
By End-User Industry: Where the Furnaces are Deployed
Different industries have unique requirements for quality, volume, and material type. Key end-user segments include:
- Foundries: The backbone of metal casting, requiring versatile and reliable furnaces.
- Automotive: Needs high-volume, consistent production for engine and chassis components.
- Aerospace: Demands the highest purity and precise alloy compositions, making advanced control critical.
- Recycling: Focuses on efficiently melting and refining scrap metal, where energy efficiency is paramount.
By Power Rating: Matching Scale to Need
Power rating, typically classified as low, medium, or high, corresponds directly to the furnace's melting capacity and speed.
A small-scale specialty alloy producer would use a low-power furnace for small batches, while a large industrial foundry would require a high-power system for maximum throughput.
By Furnace Type: The Core Physical Design
While the power supply is key, the physical structure of the furnace also defines its use. The main types are:
- Coreless Furnace: The most common type for IGBT systems, offering excellent flexibility for melting different alloys in batches.
- Channel Furnace: Better suited for holding and superheating large volumes of a single molten metal continuously.
- Crucible Furnace: Typically used for smaller, non-ferrous applications.
The Technology Driving the Market
The segmentation itself is being shaped by technological advancement. The move from traditional systems to IGBT is a response to clear operational demands.
The Core Advantage of IGBT
The primary driver for IGBT adoption is efficiency. By maintaining a constant, high power factor throughout the melt, these furnaces use less energy and melt metal faster than older technologies.
This efficiency, combined with low harmonic distortion, directly addresses the global push for sustainability. Industries are increasingly measured by their carbon footprint, and energy-efficient systems are a direct path to compliance and cost savings.
The Rise of Smart Technologies
The most advanced segment of the market integrates smart technologies. This includes smart controllers for one-button operation and precise temperature management.
Furthermore, the integration of AI and machine learning enables real-time monitoring and predictive maintenance. This minimizes downtime and optimizes the entire melting process, representing the future of the industry.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Despite the clear benefits, adopting advanced IGBT technology involves significant considerations that can be barriers for some operators.
High Initial Investment
The primary challenge is the high initial cost of advanced IGBT furnace systems compared to more traditional options. While the long-term energy savings often provide a strong return on investment, the upfront capital expenditure can be substantial.
Operational Complexity and Skill
These are sophisticated systems. They require skilled technicians for proper operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting. The technological complexity means that a well-trained workforce is essential to realize the full benefits of the equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy efficiency and sustainability: Prioritize an advanced IGBT system, potentially with a water circulation system that uses heat exchangers to reclaim energy.
- If your primary focus is melting diverse, high-purity alloys (e.g., for aerospace): A coreless IGBT furnace with a smart controller for precise process management is the ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production of a single metal: A channel furnace may be more suitable, but investigate IGBT power supplies for their efficiency benefits.
- If your primary focus is managing a tight budget: Carefully weigh the high initial investment of an IGBT furnace against its lower long-term operating costs from energy savings and reduced maintenance.
Understanding these market dynamics empowers you to select a melting solution that is not just a piece of equipment, but a strategic asset aligned with your long-term goals.
Summary Table:
| Segment | Key Categories | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Ferrous Metals (Steel, Stainless Steel), Non-Ferrous Metals (Aluminum, Copper, Brass) | Determines the furnace's material compatibility and temperature requirements. |
| End-User Industry | Foundries, Automotive, Aerospace, Recycling | Reflects the specific production, volume, and quality needs of different sectors. |
| Power Rating | Low, Medium, High | Defines the furnace's melting capacity, speed, and suitability for operation scale. |
| Furnace Type | Coreless, Channel, Crucible | Indicates the physical design, influencing flexibility, batch vs. continuous use, and metal type. |
| Technology Level | Standard, Smart Controllers, AI Integration | Shows the degree of automation, control precision, and predictive capabilities. |
Ready to transform your metal melting operations with precision and efficiency?
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced IGBT induction furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Whether you're in foundry, automotive, aerospace, or recycling, our expertise in high-temperature furnace technology—including deep customization—ensures you get a system that maximizes energy savings, improves control, and reduces environmental impact.
Contact us today to discuss how our strategic melting solutions can become your long-term competitive advantage.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency



















