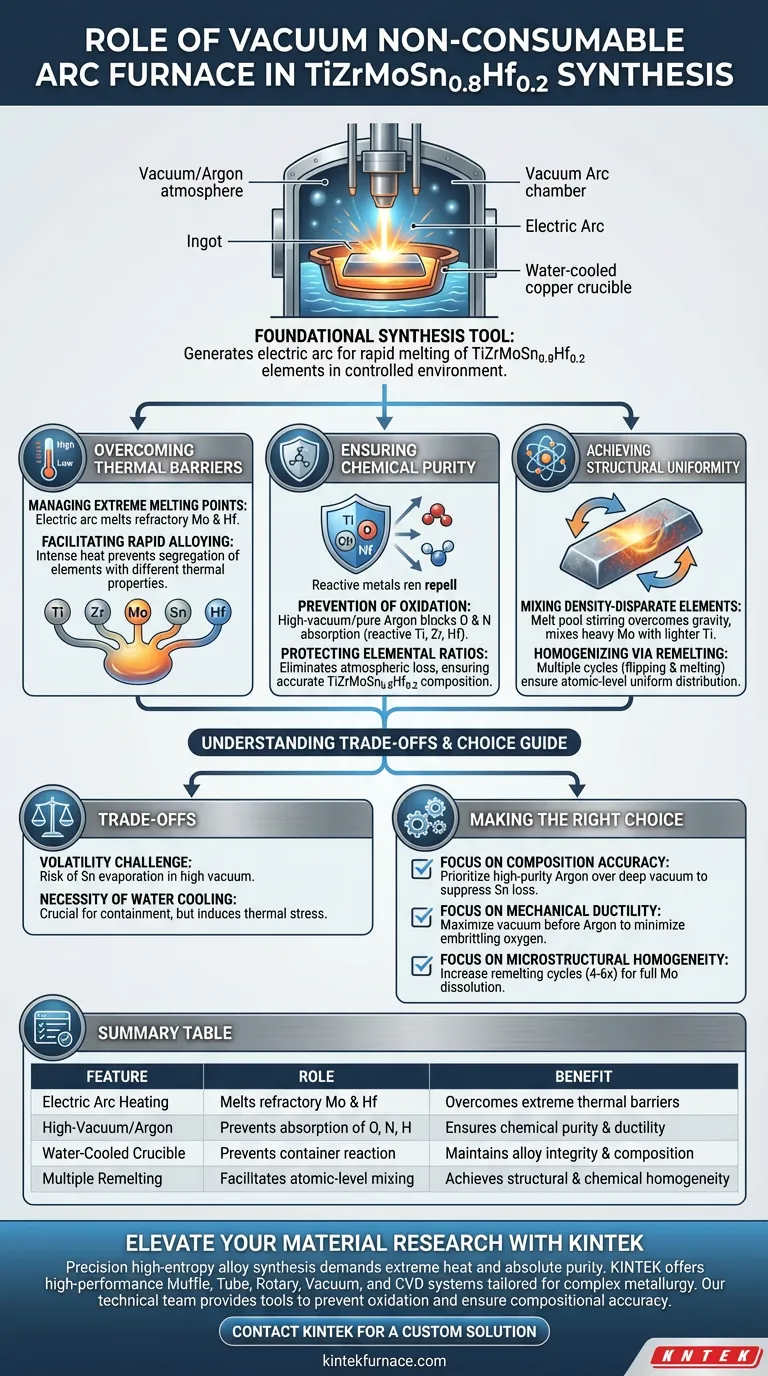
The vacuum non-consumable arc furnace serves as the foundational synthesis tool for preparing TiZrMoSn0.8Hf0.2 high-entropy alloys. Its primary function is to generate an electric arc capable of rapidly melting diverse metallic elements while maintaining a strictly controlled environment to prevent chemical contamination.
Success in fabricating this specific alloy hinges on balancing extreme heat with chemical inertness. The furnace solves the dual challenge of melting elements with vastly different melting points—from Tin to Molybdenum—while shielding the highly reactive matrix from atmospheric contamination.
Overcoming Thermal Barriers
Managing Extreme Melting Points
The TiZrMoSn0.8Hf0.2 alloy contains a complex mix of refractory metals and lower-melting elements.
The furnace utilizes an electric arc to generate the extreme temperatures required to melt components like Molybdenum (Mo) and Hafnium (Hf), which have very high melting points.
Facilitating Rapid Alloying
Standard heating methods often fail to melt refractory metals quickly enough to prevent segregation.
The intense, focused heat of the non-consumable arc allows for rapid melting. This speed is essential for incorporating elements with significantly different thermal properties into a single, cohesive liquid phase.
Ensuring Chemical Purity
Prevention of Oxidation
Titanium (Ti), Zirconium (Zr), and Hafnium (Hf) are highly reactive "getter" metals that avidly absorb oxygen and nitrogen.
The furnace operates in a high-vacuum environment or under high-purity argon gas. This isolation effectively blocks oxidation and gas absorption, which prevents the material from becoming brittle or forming unwanted ceramic phases.
Protecting Elemental Ratios
Precise chemical composition is critical for high-entropy alloys to function as intended.
By eliminating atmospheric interference, the vacuum environment ensures the accuracy of the designed elemental ratios. It prevents reactive elements from burning off as oxides, ensuring the final ingot matches the intended TiZrMoSn0.8Hf0.2 formula.
Achieving Structural Uniformity
Mixing Density-Disparate Elements
The alloy components vary significantly in density (e.g., Molybdenum is much denser than Titanium).
The furnace facilitates melt pool stirring. This dynamic movement within the liquid metal helps overcome gravity-induced segregation, ensuring heavy and light elements mix thoroughly.
Homogenizing via Remelting
A single melt is rarely sufficient for complex high-entropy alloys.
The equipment is designed to support multiple re-melting cycles. By flipping and melting the ingot repeatedly, the furnace ensures an atomic-level uniform distribution of elements, eliminating localized concentrations of specific metals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Volatility Challenge
While the furnace excels at high heat, the vacuum environment introduces a risk for volatile elements.
Tin (Sn) has a relatively low melting point and high vapor pressure compared to Molybdenum. If the vacuum is too high or the melt time too long, there is a risk of evaporating the Tin, altering the final stoichiometry.
The Necessity of Water Cooling
To contain temperatures that melt Molybdenum, the furnace itself requires aggressive cooling.
The use of a water-cooled copper crucible is non-negotiable. While this ensures the purity of the alloy by preventing reaction with the container, it also creates a steep thermal gradient that can induce rapid solidification stresses in the ingot.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When configuring your melting process for TiZrMoSn0.8Hf0.2, prioritize your parameters based on your specific requirements:
- If your primary focus is Compositional Accuracy: Prioritize high-purity argon backfilling over deep vacuum during the melt to suppress the evaporation of Tin (Sn).
- If your primary focus is Mechanical Ductility: Maximize the vacuum level prior to introducing Argon to ensure the absolute minimum oxygen content, as interstitial oxygen causes embrittlement in Ti/Zr/Hf systems.
- If your primary focus is Microstructural Homogeneity: Increase the number of remelting cycles (typically 4-6 times) to ensure the refractory Molybdenum is fully dissolved into the matrix.
The vacuum non-consumable arc furnace is not just a heater; it is a precision reactor designed to force chemically diverse and thermally resistant elements into a unified, high-purity lattice.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role in TiZrMoSn0.8Hf0.2 Synthesis | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Arc Heating | Melts refractory metals like Mo and Hf | Overcomes extreme thermal barriers |
| High-Vacuum/Argon | Prevents absorption of O, N, and H | Ensures high chemical purity and ductility |
| Water-Cooled Crucible | Prevents reaction with container | Maintains alloy integrity and composition |
| Multiple Remelting | Facilitates atomic-level mixing | Achieves structural and chemical homogeneity |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision in high-entropy alloy synthesis demands equipment that can withstand extreme heat while ensuring absolute purity. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, including customizable lab high-temp furnaces tailored for complex metallurgy.
Whether you are melting refractory metals or developing next-generation HEAs, our technical team provides the specialized tools you need to prevent oxidation and ensure compositional accuracy.
Ready to optimize your alloying process? Contact KINTEK today for a custom solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Yanfei Xu, Guangsheng Zeng. Effect of annealing treatment on microstructure, wear resistance and corrosion properties of TiZrMoSn0.8Hf0.2 high-entropy alloy for biomedical applications. DOI: 10.1088/2053-1591/ae0fdd
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- Why is a graphite crucible used for melting Ti50Ni47Fe3? Optimize Heat & Efficiency in Vacuum Induction
- How does the induction furnace work? Master Contactless, High-Purity Metal Melting
- How is heat generated in induction heating? Discover Efficient Non-Contact Heating Methods
- What components make up a Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace? Discover the Key Systems for Pure Metal Melting
- How do IGBT modules contribute to cost savings in melting machines? Boost Efficiency and Slash Operational Costs
- Where is induction heating commonly used? Discover Its Key Industrial and Commercial Applications
- What are the benefits of using induction furnaces for copper melting? Boost Quality, Efficiency & Safety
- What is the role of a vacuum induction furnace in MRDO preparation? Enabling Rare Earth Magnet Recycling



















