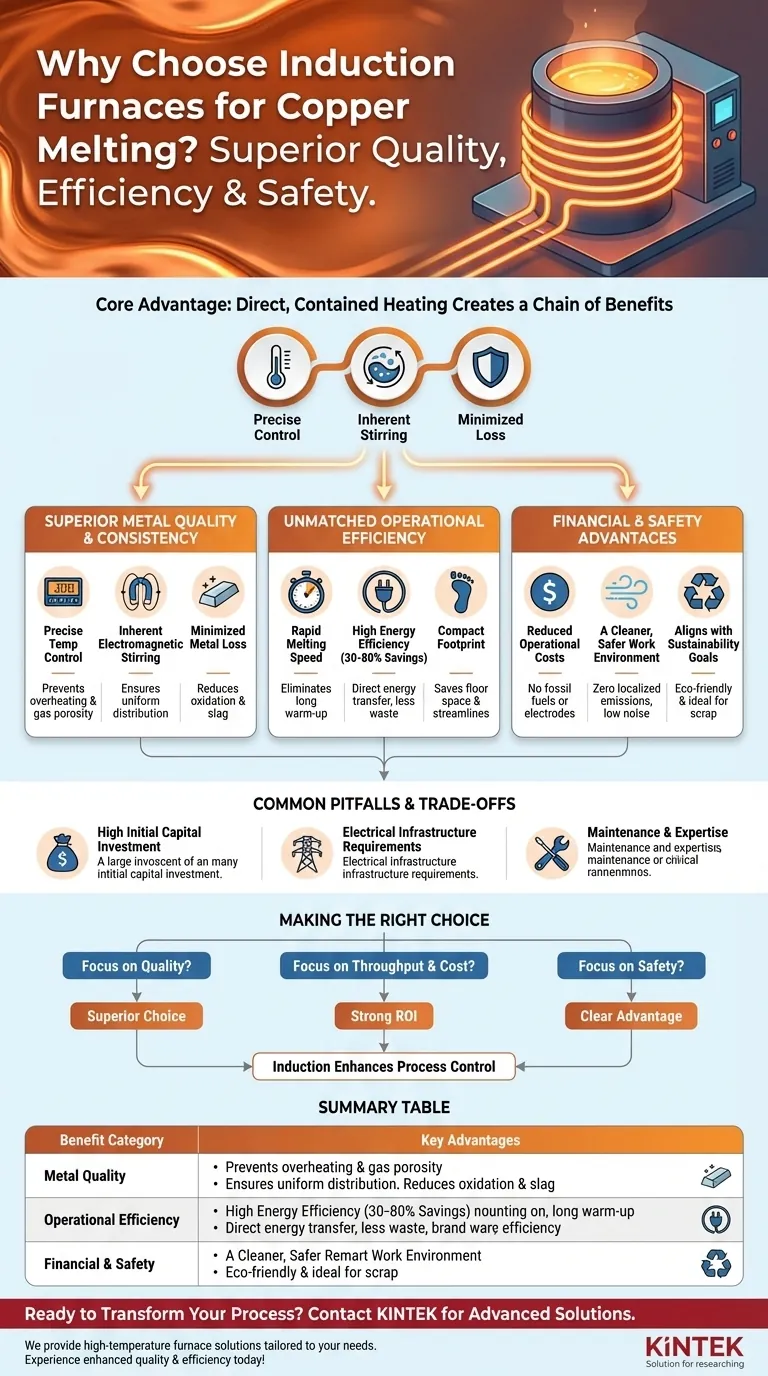
For melting copper, induction furnaces offer a combination of superior metallurgical quality, operational speed, and cost efficiency that traditional fuel-fired methods cannot match. This is achieved through precise electromagnetic heating, which provides tight temperature control, minimizes metal loss to oxidation, and ensures a homogenous final product.
The core advantage of induction melting is not just one feature, but how its principles of direct, contained heating create a chain of benefits—from higher-quality metal and faster production cycles to lower energy bills and a safer, cleaner work environment.
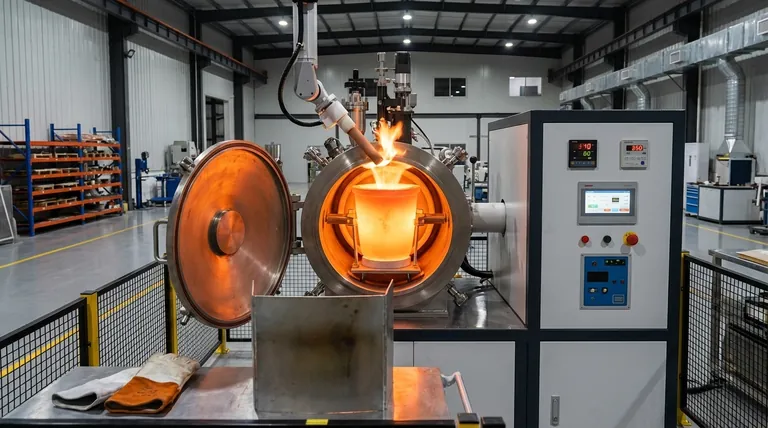

Driving Superior Metal Quality and Consistency
The primary driver for adopting induction technology is its ability to produce better metal. The heating method directly influences the final characteristics of the copper or copper alloy.
Precise Temperature Control
An induction system allows for exact temperature management. This precision prevents overheating, which can lead to gas porosity, and ensures the metal is poured at the optimal temperature for the specific casting or application.
Inherent Electromagnetic Stirring
The magnetic field that heats the metal also creates a natural stirring action within the molten bath. This inherent stirring ensures all elements, including alloys, are uniformly distributed, resulting in a perfectly homogenous and consistent final product without mechanical contact.
Minimized Metal Loss
Unlike fuel-fired furnaces, induction melting does not involve products of combustion. This clean environment, combined with rapid melting, significantly reduces oxidation and slag formation, meaning more of your valuable copper ends up in the final product rather than as waste.
Purity in Specialized Applications
For applications requiring the highest purity, vacuum induction furnaces can be used. This process prevents any atmospheric contamination, removes dissolved gases, and ensures the integrity of reactive alloys.
Achieving Unmatched Operational Efficiency
Beyond quality, induction furnaces are engineered for speed and efficiency, directly impacting throughput and operational costs.
Rapid Melting Speed
Induction furnaces transfer energy directly into the metal with extreme speed and efficiency. This eliminates long warm-up periods and allows for much faster melting cycles compared to traditional methods, enabling a more continuous and responsive workflow.
High Energy Efficiency
Modern induction systems can achieve energy savings of 30–80% over older technologies. Heat is generated within the charge material itself, so there is virtually no wasted energy or standby heat loss.
Compact Footprint
The equipment is typically more compact than traditional furnaces, saving valuable floor space. Operations can often be performed directly on the main work floor, streamlining the production process by reducing material handling.
Understanding the Financial and Safety Advantages
The operational model of an induction furnace fundamentally changes cost structures and workplace safety protocols for the better.
Reduced Operational Costs
Induction furnaces eliminate the need for purchasing and handling fossil fuels. They also do not use consumable electrodes, removing another significant operational expense and point of failure.
A Cleaner, Safer Work Environment
These furnaces produce zero localized emissions, meaning no smoke, dust, or harmful fumes are generated at the source. They also operate with very little noise and eliminate the risks associated with handling and storing combustible fuels.
Aligning with Sustainability Goals
The high efficiency and zero-emissions operation make induction melting an environmentally responsible choice that helps companies meet modern sustainability standards. Furthermore, it is ideal for recycling scrap copper efficiently with minimal loss.
Common Pitfalls and Trade-offs
While highly advantageous, adopting induction technology requires careful consideration of its specific requirements.
High Initial Capital Investment
The upfront cost of an induction furnace and its associated power supply is typically higher than that of a simple fuel-fired furnace. This technology should be viewed as a long-term investment where the return is realized through operational savings and improved product quality.
Electrical Infrastructure Requirements
An induction furnace places a significant demand on a facility's electrical system. A thorough assessment is required to ensure your power infrastructure can support the load, and upgrades may be necessary.
Maintenance and Expertise
Though reliable, the high-frequency power supplies and control systems are sophisticated electronic devices. Proper maintenance requires trained technicians who understand the technology, which can represent a different skill set than that needed for traditional furnaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right melting technology depends on your primary business drivers.
- If your primary focus is high-value castings and alloy quality: The precise temperature control and electromagnetic stirring of an induction furnace make it the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is throughput and cost reduction: The rapid melting speeds and exceptional energy efficiency deliver a strong and measurable return on investment.
- If your primary focus is safety and environmental compliance: The fuel-free, zero-emission operation of an induction furnace is a clear and decisive advantage.
Ultimately, choosing an induction furnace is a strategic decision that enhances control over your entire melting process.
Summary Table:
| Benefit Category | Key Advantages |
|---|---|
| Metal Quality | Precise temperature control, electromagnetic stirring, minimized oxidation, high purity |
| Operational Efficiency | Rapid melting, high energy efficiency (30-80% savings), compact footprint |
| Financial & Safety | Reduced operational costs, zero emissions, safer work environment, sustainability |
| Considerations | High initial investment, electrical infrastructure needs, specialized maintenance |
Ready to transform your copper melting process with advanced induction furnace solutions?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Induction Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements.
Experience enhanced metallurgical quality, operational speed, and cost efficiency—contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control



















