In short, vacuum smelting was the essential breakthrough that enabled the creation of modern, high-performance superalloys. By removing atmospheric gases during melting, it allowed metallurgists to design and produce alloys with higher strength, greater purity, and the ability to withstand extreme temperatures—properties that were previously unattainable.
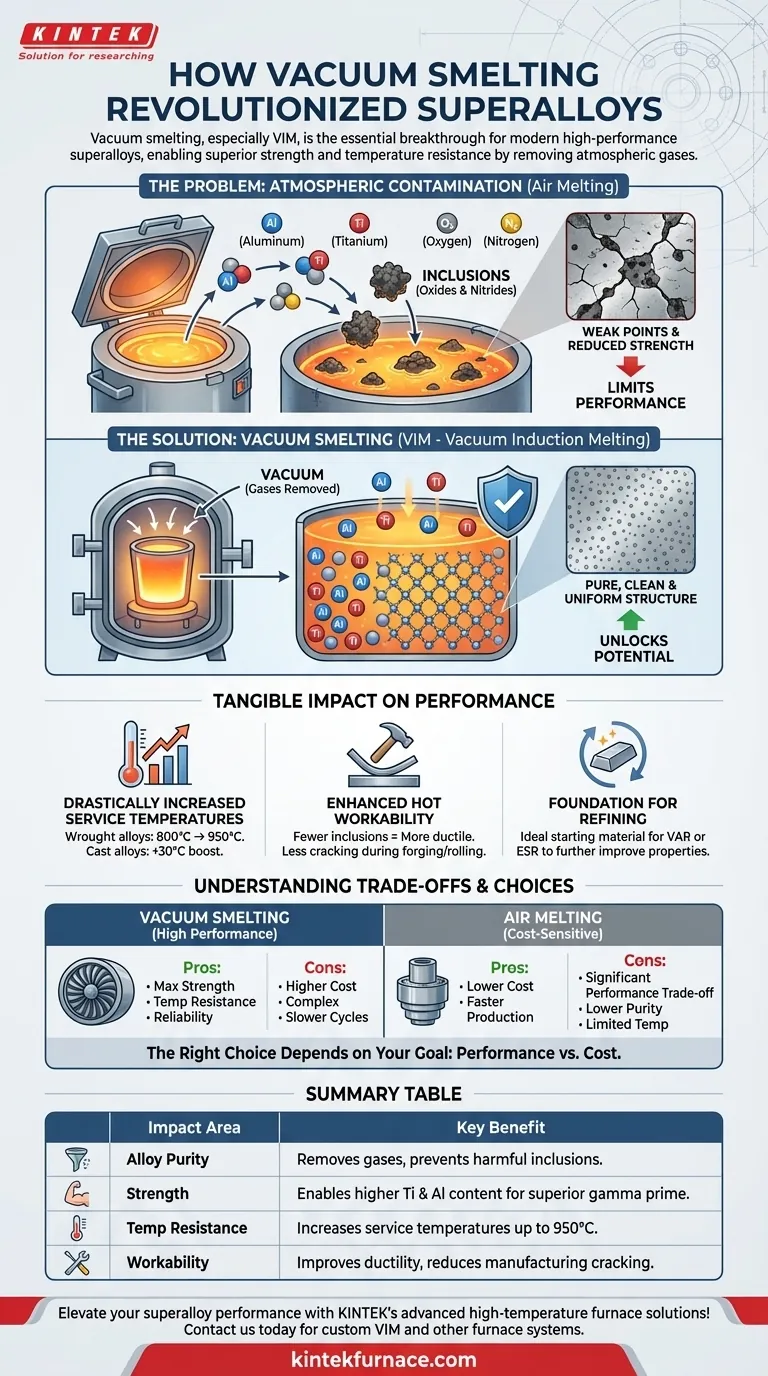
The core challenge in superalloy design is that the most critical strengthening elements, like titanium and aluminum, are highly reactive with oxygen and nitrogen in the air. Vacuum smelting solves this by creating a protected environment, preventing contamination and unlocking the full potential of the alloy's chemistry.
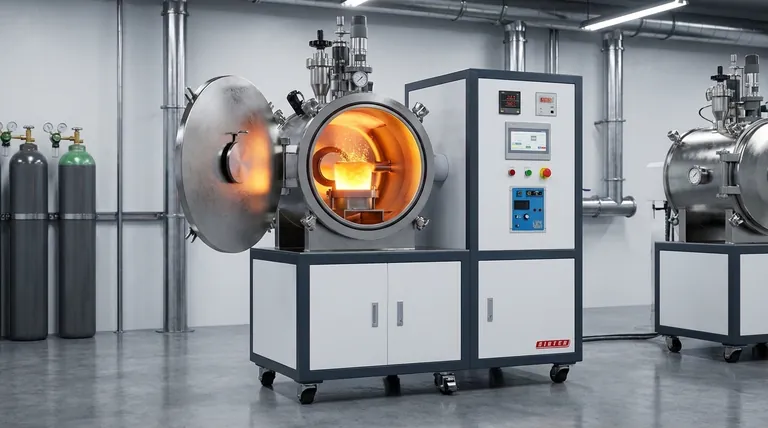

The Core Problem: Atmospheric Contamination
Before the widespread adoption of vacuum processing, superalloy development faced a fundamental limit. The very act of melting the metals in air was degrading their potential performance.
The Critical Role of Reactive Elements
Superalloys derive their incredible high-temperature strength from the precise formation of internal microstructures, primarily the gamma prime (γ') phase. This phase is formed by specific alloying elements, most notably aluminum (Al) and titanium (Ti).
The more Al and Ti you can successfully add to the nickel-based alloy, the stronger and more temperature-resistant it becomes.
The Formation of Harmful Inclusions
When melted in the presence of air, these highly reactive elements (Al, Ti) instantly bond with oxygen and nitrogen. This forms non-metallic inclusions like oxides and nitrides.
These tiny, brittle particles get trapped in the final metal. They act as microscopic weak points, reducing ductility, initiating cracks, and severely limiting the material's fatigue life and overall strength.
How Vacuum Smelting Provides the Solution
Vacuum smelting, particularly Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM), directly addresses the contamination problem. By placing the entire melting process inside a vacuum chamber, it fundamentally changes what is possible.
Preventing Oxidation and Nitridation
The most direct benefit of the vacuum is the removal of reactive gases. With virtually no oxygen or nitrogen present, the aluminum and titanium remain free to perform their intended function: strengthening the alloy.
Enabling Higher Alloy Content
Because the reactive elements are protected from contamination, metallurgists can confidently add them in much higher concentrations. This directly leads to a greater volume of the strengthening gamma prime phase, pushing the boundaries of material performance.
Improving Material Purity and Cleanliness
The vacuum environment also helps to remove other dissolved gases from the molten metal, resulting in a "cleaner" and more uniform final product. This inherent purity significantly improves the alloy's properties.
The Tangible Impact on Superalloy Performance
The shift to vacuum processing was not an incremental improvement; it was a revolutionary step that redefined the capabilities of superalloys.
Drastically Increased Service Temperatures
The ability to create cleaner, more highly-alloyed materials had a direct impact on how hot they could operate. For wrought (deformed) superalloys, vacuum processing raised maximum service temperatures from around 800°C to 950°C.
Even for advanced cast superalloys, the move to vacuum techniques provided an additional performance boost of approximately 30°C.
Enhanced Hot Workability
A cleaner alloy with fewer brittle inclusions is more ductile and forgiving during manufacturing. This enhanced hot workability means the material is less likely to crack during forging, rolling, or other shaping processes, leading to better yields and more reliable components.
A Foundation for Further Refining
VIM is often the critical first step in a multi-stage process for the most demanding applications. The high-purity ingots produced by VIM serve as the ideal starting material for secondary refining processes like Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) or Electroslag Remelting (ESR), which further improve the material's structure and properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its benefits are undeniable, vacuum processing is a more demanding manufacturing route.
Increased Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more expensive to build, operate, and maintain than air-melt furnaces. The process requires complex vacuum systems and precise controls, adding to the overall cost of the final material.
Slower Production Cycles
Each melting cycle requires time to pump the chamber down to the required vacuum level. This makes the process inherently slower than continuous or batch melting in air, impacting throughput and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the impact of vacuum smelting helps in specifying the right material for a given application.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance and reliability (e.g., jet engine turbine blades, power generation): Vacuum-processed superalloys are non-negotiable. The protection they offer is the only way to achieve the required strength and temperature resistance.
- If your primary focus is a less demanding, cost-sensitive application: An air-melted alloy might be considered, but you must accept the significant trade-off in performance, purity, and temperature capability.
Ultimately, vacuum smelting transformed superalloys from high-performance materials into the extreme-environment solutions that power our modern world.
Summary Table:
| Impact Area | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Alloy Purity | Removes gases and prevents harmful inclusions for cleaner materials |
| Strength | Enables higher titanium and aluminum content for superior gamma prime phase |
| Temperature Resistance | Increases service temperatures up to 950°C for extreme environments |
| Workability | Improves ductility and reduces cracking during manufacturing processes |
Elevate your superalloy performance with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with custom Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise solutions for your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve breakthrough results in material development. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can benefit your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors



















