At its core, induction heating is a staple of modern industry, primarily used in metallurgy for melting and heat-treating metals, in advanced manufacturing for processes like welding and semiconductor fabrication, and even in commercial kitchens for cooking. Its applications span from massive foundries melting tons of steel to delicate procedures requiring microscopic precision.
Induction heating is not just another way to generate heat; it is a method for generating heat with extreme precision, speed, and efficiency. Its common applications all capitalize on its unique ability to heat only a targeted, electrically conductive material without physical contact, making it a superior choice for processes that demand control and consistency.

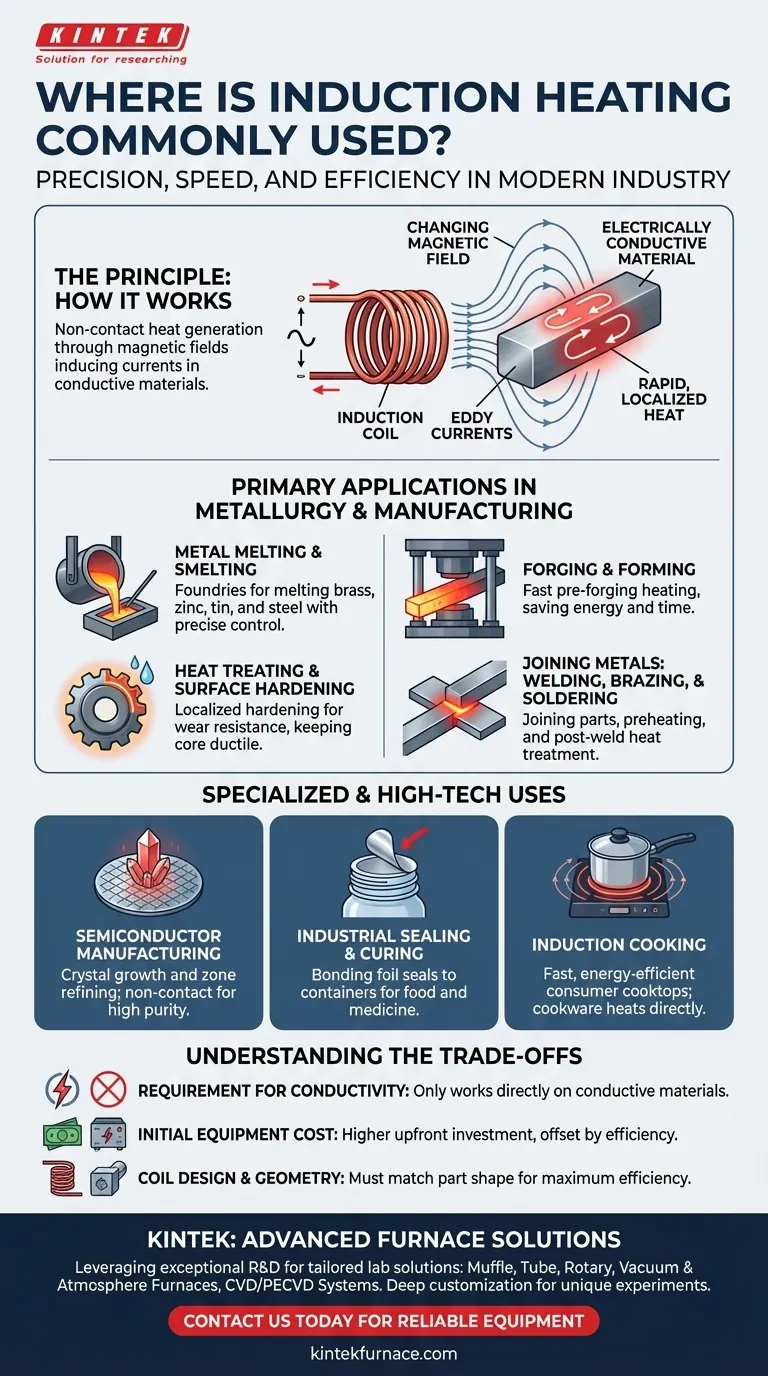
The Principle That Drives Its Use
To understand where induction heating is used, you must first understand how it works. The entire technology is based on two simple elements.
A Changing Magnetic Field
An induction heater uses a coil through which a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed. This creates a rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within and around the coil.
An Electrically Conductive Material
When an electrically conductive workpiece (like a piece of metal) is placed into this field, the magnetic field induces small, circular electric currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents.
The Result: Rapid, Localized Heat
The metal's natural resistance to the flow of these eddy currents generates intense and immediate heat. The heat is generated inside the workpiece itself, not from an external flame or heating element.
Primary Applications in Metallurgy and Manufacturing
The vast majority of induction heating applications are in industrial settings where metal must be heated or melted with speed and precision.
Metal Melting and Smelting
In foundries, induction furnaces are a workhorse for melting non-ferrous metals like brass, zinc, and tin, as well as for melting and refining steel. The process is clean and allows for precise control over the metallurgy of the final alloy.
Heat Treating and Surface Hardening
Induction is ideal for heat treatment processes like quenching and tempering steel bars. Because the heat can be localized to a very specific area, it is widely used for surface hardening. This creates a wear-resistant outer layer on a part, like a gear tooth, while keeping the core ductile and tough.
Forging and Forming
Before a piece of metal can be forged or pressed into a new shape, it must be heated to a malleable temperature. Induction is used for this pre-forging heating because it is incredibly fast, heating only the workpiece and not the entire furnace, saving energy and time.
Joining Metals: Welding, Brazing, and Soldering
Induction is used to join metal parts together through brazing and soldering. It can also be used to preheat a section of metal before welding or to provide a post-weld heat treatment to relieve stress in the joint, improving its strength and longevity.
Specialized and High-Tech Uses
The precision of induction heating makes it suitable for highly specialized tasks beyond heavy industry.
Semiconductor Manufacturing
In the pristine environment of semiconductor fabrication, induction is used for crystal growth and zone refining. Because it is a non-contact method, it introduces no contaminants, which is critical for producing high-purity silicon crystals.
Industrial Sealing and Curing
You have likely seen the results of induction sealing. It is the technology used to bond the foil safety seals to the tops of plastic bottles and containers for food and medicine. A metal foil layer in the cap is heated by induction, melting a polymer that seals it to the container lip.
Induction Cooking
On a consumer level, induction cooktops use the same principle. The magnetic field from the cooktop induces eddy currents directly in the pot or pan, heating the cookware itself. This is why the cooking surface remains cool to the touch and the process is so fast and energy-efficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, induction heating is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Requirement for Conductivity
Induction heating works directly only on materials that are electrically conductive, like metals. Non-conductive materials like plastics or ceramics cannot be heated directly, though they can be heated indirectly by placing them in a conductive graphite crucible.
Initial Equipment Cost
The upfront investment for an induction heating system, including the power supply and custom coils, can be higher than for a conventional gas-fired or resistance furnace. This cost is often offset over time by higher energy efficiency and increased throughput.
Coil Design and Geometry
The induction coil must be designed to match the geometry of the part being heated for maximum efficiency. This can present a challenge for highly complex parts or for shops that process a wide variety of part shapes in low volumes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting induction heating depends entirely on the requirements of your specific task.
- If your primary focus is bulk heating or melting: Induction offers unmatched speed and energy efficiency for processes like forging and foundry work.
- If your primary focus is precision surface treatment: Its localized heating is ideal for hardening specific areas of a part or brazing joints without distorting the entire workpiece.
- If your primary focus is a high-purity, clean process: The non-contact nature of induction heating makes it essential for semiconductor manufacturing and medical applications where contamination is unacceptable.
By understanding its principles, you can leverage induction heating as a precise, fast, and highly efficient tool for a vast range of industrial challenges.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Uses |
|---|---|
| Metallurgy | Metal melting, heat treating, forging |
| Manufacturing | Welding, brazing, semiconductor fabrication |
| Commercial | Induction cooking, industrial sealing |
Need advanced high-temperature furnace solutions for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with tailored solutions. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your processes with our reliable and efficient equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main applications of vacuum hot pressing? Create Dense, Pure Materials for Demanding Industries
- What are the applications of hot pressing? Achieve Maximum Material Performance
- How does the use of vacuum in hot-pressing affect the material processing? Achieve Denser, Purer, and Stronger Materials
- What are the advantages of ceramic/metal composites produced using a vacuum press? Achieve Superior Strength and Durability
- What other types of furnaces are related to hot pressing? Explore Key Thermal Processing Technologies



















