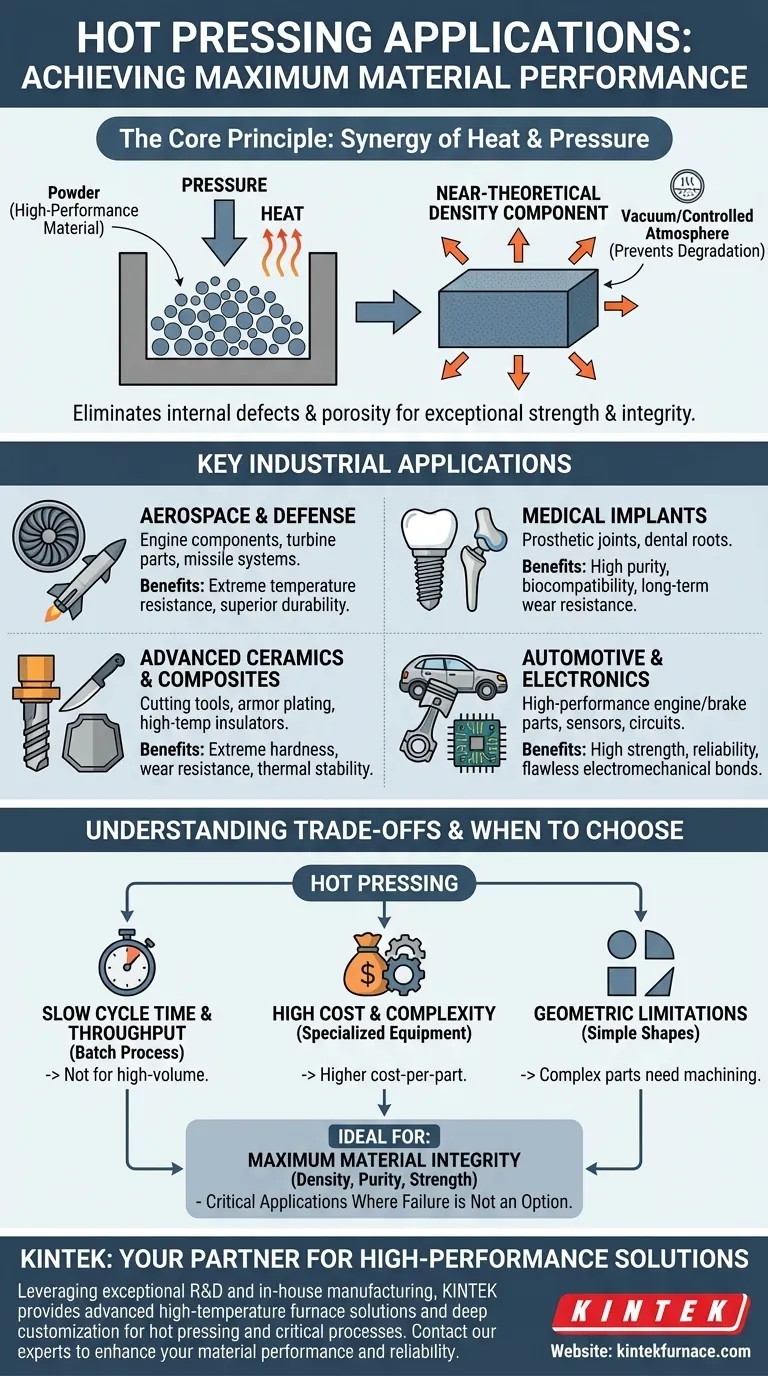
At its most fundamental level, hot pressing is a specialized manufacturing technique used to create exceptionally strong and dense components from high-performance materials. It is the go-to process for critical applications in the aerospace, automotive, medical, electronics, and advanced ceramics industries, where material failure could have catastrophic consequences.
The core purpose of hot pressing is not just to shape a material, but to fundamentally enhance its integrity. It uses a combination of high temperature and intense pressure to eliminate internal defects and produce components with densities approaching their theoretical maximum.

The Core Principle: Why Combine Heat and Pressure?
Hot pressing solves a fundamental materials science challenge: how to consolidate powders into a solid, fully dense part without melting them. The synergy between heat and pressure is what makes this technique so powerful.
Achieving Near-Theoretical Density
Heat makes the individual particles of a material more pliable. Simultaneously, the application of immense, uniform pressure forces these softened particles together, squeezing out the microscopic voids (porosity) between them. This results in a final product with exceptional density and strength.
Preventing Material Degradation
Many advanced materials, especially metals, are highly reactive to oxygen at high temperatures. Hot pressing is typically conducted in a vacuum or a controlled inert gas atmosphere. This environment prevents oxidation and other chemical reactions that would otherwise contaminate the material and compromise its final properties.
Enabling Difficult-to-Sinter Materials
Some advanced ceramics and composites do not bond well with heat alone (a process called conventional sintering). The addition of pressure provides the necessary mechanical energy to force consolidation, creating strong, defect-free components from materials that are otherwise impossible to process effectively.
Key Industrial Applications
The unique capabilities of hot pressing make it indispensable for manufacturing parts where performance and reliability are paramount.
Aerospace and Defense
Components in aircraft engines, turbines, and missiles must withstand extreme temperatures and mechanical stress. Hot pressing is used to create parts from high-strength alloys and ceramic composites that offer superior durability and heat resistance, ensuring operational safety and longevity.
Advanced Ceramics and Composites
For applications requiring extreme hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability, hot pressing is essential. It produces defect-free ceramic components for items like industrial cutting tools, armor plating, and high-temperature insulators, where even a microscopic internal flaw could lead to failure.
Medical Implants
The human body is an aggressive environment, and implants like prosthetic joints and dental roots must be strong, pure, and biocompatible. Hot pressing in a vacuum creates fully dense components free of contaminants, ensuring they integrate safely and withstand decades of mechanical wear.
Automotive and Electronics
In high-performance automotive systems, hot pressing is used for engine, brake, and suspension components that require high strength and reliability. In electronics, the process creates permanent, flawless electromechanical bonds essential for high-power circuits and sensors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, hot pressing is a specialized technique with specific limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for making an informed manufacturing decision.
Cycle Time and Throughput
Hot pressing is a relatively slow, batch-based process. The time required to heat the die, apply pressure, hold, and cool down in a controlled atmosphere limits throughput. It is not suitable for high-volume, low-cost parts.
Cost and Complexity
The equipment required—including vacuum furnaces, hydraulic presses, and specialized tooling—is expensive to purchase and operate. This contributes to a higher cost-per-part compared to methods like conventional casting or sintering.
Geometric Limitations
The process is best suited for producing relatively simple geometries, such as discs, blocks, or cylinders, that can be easily pressed in a die. Complex shapes often require extensive and costly post-process machining, which can negate some of the material benefits.
When to Choose Hot Pressing
Your choice of manufacturing process should be driven by the final application's requirements.
- If your primary focus is maximum material performance: Hot pressing is the optimal choice for achieving the highest possible density, purity, and strength in advanced materials.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost production: You should explore faster alternatives like conventional sintering or metal injection molding.
- If your primary focus is creating highly complex shapes: Additive manufacturing (3D printing) or investment casting may be more suitable and cost-effective.
Ultimately, hot pressing is the definitive solution for applications where material integrity is the single most important factor.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Key Material Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace & Defense | Engine components, turbine parts, missile systems | Extreme temperature resistance, superior durability |
| Medical Implants | Prosthetic joints, dental roots | High purity, biocompatibility, long-term wear resistance |
| Advanced Ceramics | Cutting tools, armor plating, high-temperature insulators | Extreme hardness, wear resistance, thermal stability |
| Automotive & Electronics | High-performance engine/brake parts, sensors, circuits | High strength, reliability, flawless electromechanical bonds |
Need to manufacture components with maximum density and strength?
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements for hot pressing and other critical processes.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your material performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials can be densified using a vacuum press and what are their applications? Unlock High-Performance Material Densification
- What are the overall benefits of using hot pressing in manufacturing? Achieve Superior Performance and Precision
- Which process parameters must be optimized for specific materials in a vacuum hot press furnace? Achieve Optimal Density and Microstructure
- What is a vacuum hot press furnace? Unlock Superior Material Performance
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity



















