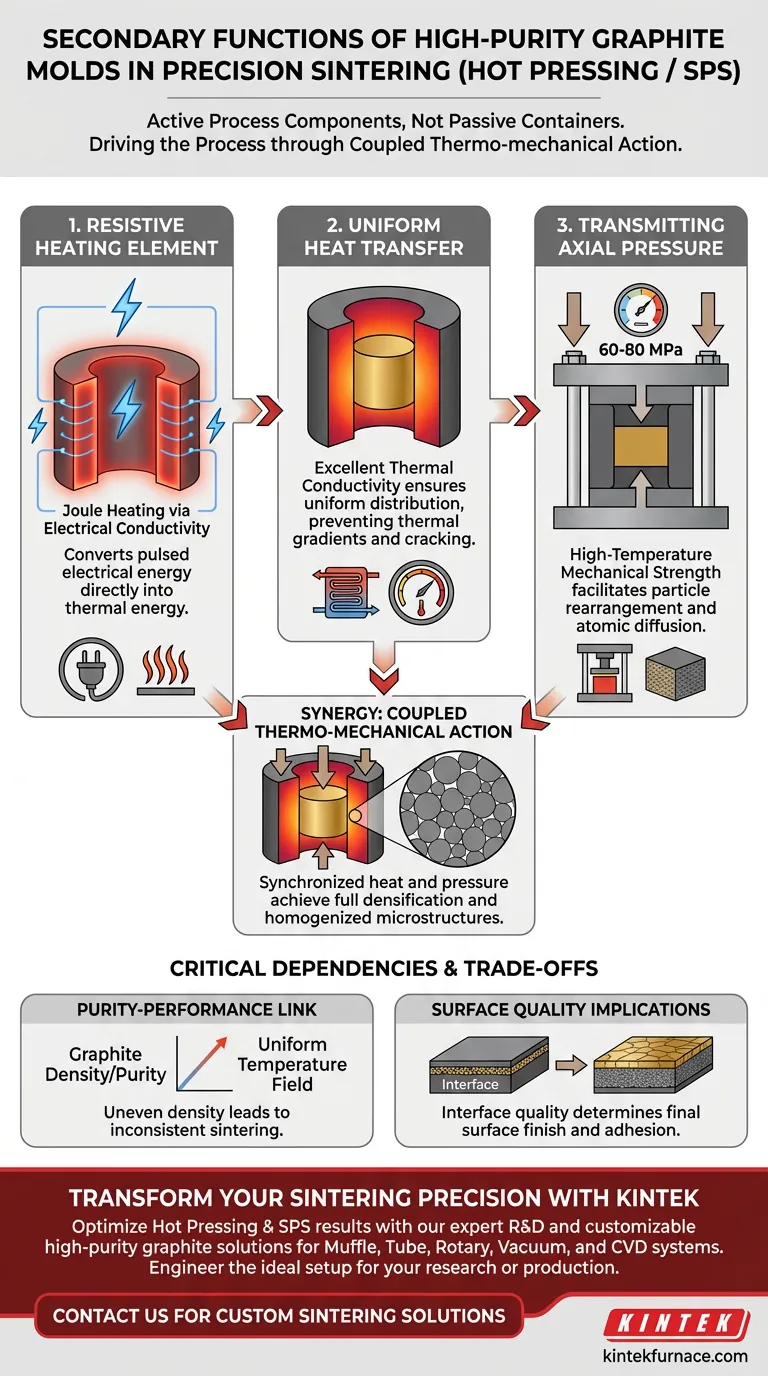
High-purity graphite molds function as active process components, not merely passive containers. In precision sintering environments like Hot Pressing or Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), their critical secondary functions include acting as resistive heating elements, efficient heat transfer media, and robust transmitters of mechanical pressure.
Core Takeaway While the primary role of the mold is to define the sample's shape, its secondary functions drive the sintering process itself. The mold’s ability to convert electrical current into heat while simultaneously transmitting high axial pressure allows for the synchronized coupling of thermal and mechanical forces, which is essential for achieving uniform microstructures.

The Active Thermal Role
In advanced sintering, the mold is an integral part of the heating system. It does not simply sit inside a furnace; often, it is the furnace.
Acting as a Resistive Heating Element
In processes like SPS, the mold serves as a direct conductor of electrical current. Due to its high electrical conductivity, the graphite efficiently converts pulsed electrical energy into thermal energy via Joule heating.
Ensuring Uniform Heat Transfer
Once heat is generated, the mold acts as a thermal regulation medium. Its excellent thermal conductivity ensures that heat is transferred uniformly from the mold walls to the sample core. This uniform distribution is critical for preventing thermal gradients that could lead to cracking or uneven sintering in the final product.
Mechanical Integrity Under Stress
Beyond thermal management, the mold must act as a mechanical tool, actively compressing the material while it is heated.
Transmitting Axial Pressure
The mold is responsible for transmitting significant unidirectional mechanical pressure to the sample. High-purity graphite maintains exceptional mechanical strength even at very high temperatures, allowing it to withstand pressures (often between 60–80 MPa) that would deform other materials.
Facilitating Microstructural Homogenization
The combination of pressure transmission and heat application creates a "coupled thermo-mechanical action." This dual force promotes atomic diffusion and particle rearrangement. The result is a fully densified material with a homogenized microstructure, superior to what could be achieved by heat alone.
Critical Dependencies and Trade-offs
While graphite molds are versatile, their performance is strictly tied to material quality. Understanding these dependencies is key to process control.
The Purity-Performance Link
The effectiveness of the mold as a heating element is directly dependent on the purity and density of the graphite. Variations in graphite density can lead to an uneven temperature field, resulting in inconsistent sintering.
Surface Quality Implications
The interface between the mold and the sample dictates the final surface finish. While the mold applies pressure, the quality of the graphite surface (often managed with interface layers like graphite paper) determines whether the final composite has a clean, high-quality surface or suffers from adhesion issues.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of your sintering process, you must match the mold properties to your specific processing targets.
- If your primary focus is Microstructural Uniformity: Prioritize graphite with high density and homogeneity to ensure a perfectly uniform temperature field during the heating phase.
- If your primary focus is High-Density Compaction: Select graphite grades rated for maximum high-temperature mechanical strength to safely transmit higher axial pressures without deformation.
Success in precision sintering relies on treating the graphite mold as a dynamic energy-transfer tool rather than a static vessel.
Summary Table:
| Secondary Function | Mechanism | Impact on Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Resistive Heating | Joule heating via electrical conductivity | Converts electrical energy into thermal energy directly. |
| Heat Transfer | High thermal conductivity | Ensures uniform temperature distribution and prevents cracking. |
| Pressure Transmission | High-temperature mechanical strength | Facilitates particle rearrangement and atomic diffusion. |
| Thermo-mechanical Coupling | Synchronized heat and pressure | Achieves full densification and homogenized microstructures. |
Transform Your Sintering Precision with KINTEK
Are you looking to optimize your Hot Pressing or Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) results? At KINTEK, we understand that your mold is an active component in your success. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-purity graphite solutions tailored for Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems.
Our customizable high-temp lab furnaces and precision molds are designed to withstand extreme axial pressures while maintaining perfect thermal gradients. Whether you are aiming for microstructural uniformity or high-density compaction, our experts are ready to engineer the ideal setup for your unique research or production needs.
Ready to elevate your material science? Contact us today to discuss your custom sintering solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Zhanjiang Pei, Yanling Yu. The Enhancing Effect of Biochar Derived from Biogas Residues on the Anaerobic Digestion Process of Pig Manure Water. DOI: 10.3390/fermentation10120644
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What process challenges are addressed by vacuum filtration equipment during the construction of CsPbBr3@CA-SiO2 films?
- How does a laboratory blast drying oven facilitate the treatment of Au/ZnO/In2O3 precursor precipitates? Key Benefits
- What are the key properties of alumina ceramic furnace tubes? Discover Their High-Temp and Chemical Resistance
- What properties make quartz tubes ideal for heat treatment processes? Unlock High-Temperature Purity and Stability
- What is the function of graphite stirring rods in aluminum casting? Achieve Perfect Alloy Homogenization
- What are the advantages of using high-purity quartz tubes as reaction vessels? Unlock Active Flux Synthesis
- Why are alumina liners and quartz boats selected as consumables for sintering lunar soil simulant? Key Material Roles
- What is the importance of using spot-welded K-type thermocouples in DP steel heat treatment? Master Thermal Precision



















