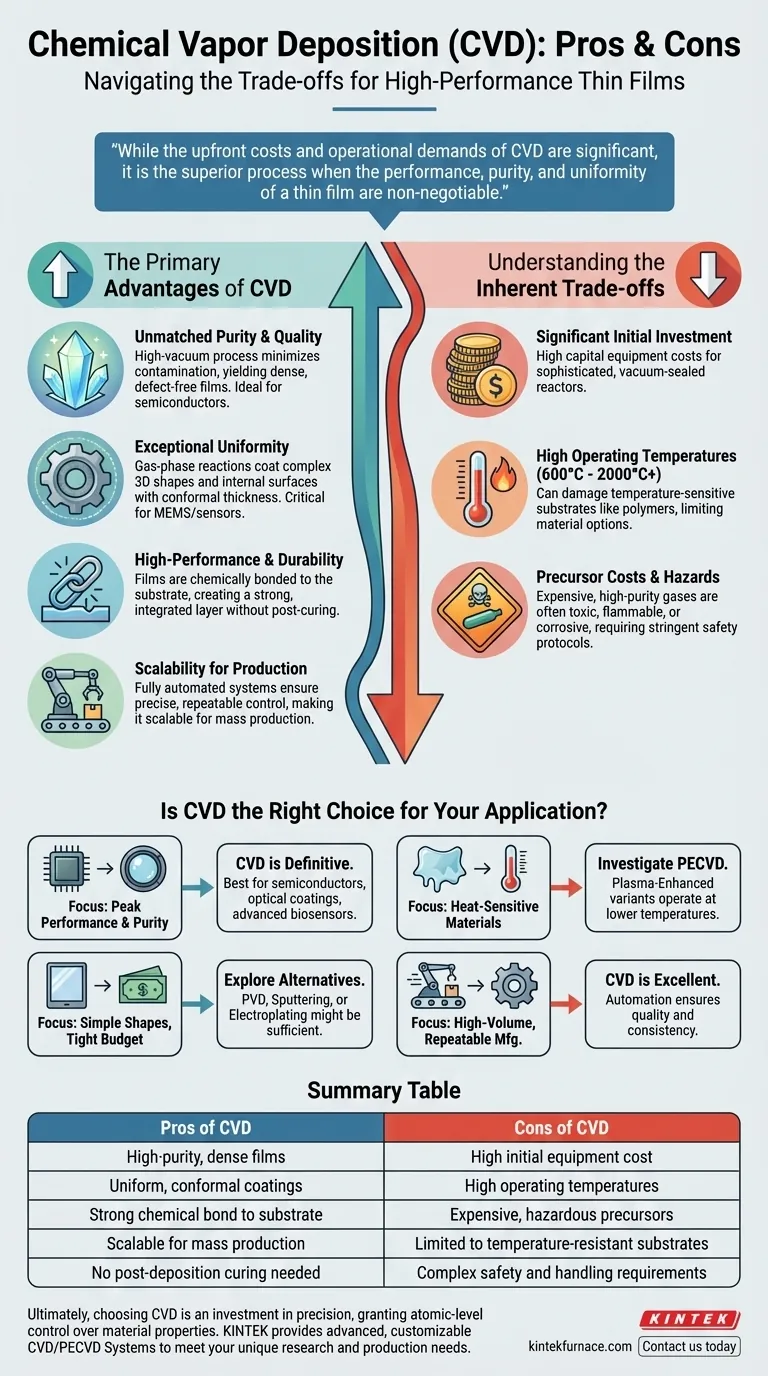
In essence, the primary advantage of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is its ability to produce exceptionally high-purity, uniform, and durable thin films that are chemically bonded to a substrate. However, these benefits come at the cost of high initial equipment investment, expensive and potentially hazardous precursor materials, and high operating temperatures that can limit the types of substrates you can use.
While the upfront costs and operational demands of Chemical Vapor Deposition are significant, it is the superior process when the performance, purity, and uniformity of a thin film are non-negotiable for the final product's success.

The Primary Advantages of CVD
To understand if CVD is right for you, it's necessary to look beyond a simple list of pros and cons and examine the specific outcomes the process delivers. It is a method of choice for many high-performance applications for several key reasons.
Unmatched Purity and Quality
Because CVD takes place in a high-vacuum chamber, contamination from the atmosphere is minimized. The process uses highly pure precursor gases to deposit material molecule-by-molecule, resulting in a dense and defect-free film with superior quality.
This level of control is why CVD is a foundational process in the semiconductor industry, where even minuscule impurities can ruin a microchip.
Exceptional Uniformity Across Surfaces
Unlike line-of-sight deposition methods (like sputtering), CVD involves gas-phase reactions. The precursor gases flow around the substrate, allowing the chemical reaction to occur evenly across all exposed areas, including complex 3D shapes and internal surfaces.
This creates a highly conformal coating of uniform thickness, which is critical for components like sensors and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS).
High-Performance and Durability
The "C" in CVD stands for chemical, meaning the film is not just painted on; it is chemically bonded to the substrate surface. This creates an incredibly strong and durable layer that becomes an integral part of the component.
The resulting films are deposited in their final, stable state and do not require a separate curing process, streamlining production.
Scalability for High-Volume Production
Modern CVD systems are fully automated, allowing for precise and repeatable control over temperature, pressure, and gas flow.
Once a process recipe is perfected, it can be executed repeatedly with minimal variation, making CVD highly scalable for the mass production of high-performance components used in consumer electronics, automotive sensors, and smart devices.
Understanding the Inherent Trade-offs
The high performance of CVD is the result of a complex and resource-intensive process. Acknowledging these trade-offs is critical for making an informed decision.
Significant Initial Investment
CVD reactors are sophisticated machines that must maintain high vacuum, handle precise gas mixtures, and operate at extreme temperatures. This complexity translates directly into high capital equipment costs.
For small-scale projects or applications where "good enough" is acceptable, the initial investment for an industrial CVD system can be prohibitive.
High Operating Temperatures
Traditional CVD processes often require substrate temperatures ranging from 600°C to over 2000°C for the necessary chemical reactions to occur.
This heat can damage or warp temperature-sensitive substrates like polymers or certain low-melting-point metals, severely limiting the materials you can coat.
Precursor Material Costs and Hazards
The specialized, high-purity gases used as precursors in CVD are often expensive. Their costs can be a significant factor in the overall price per part.
Furthermore, many of these precursors are toxic, flammable, or corrosive. This necessitates stringent safety protocols, specialized handling equipment, and robust exhaust management systems, adding to both operational complexity and cost.
Is CVD the Right Choice for Your Application?
The decision to use CVD hinges entirely on your specific technical requirements and business goals. Use these points as a guide.
- If your primary focus is peak performance and material purity: CVD is the definitive choice for creating the high-quality films required for semiconductors, optical coatings, and advanced biosensors.
- If your primary focus is coating simple shapes on a tight budget: The high cost and complexity of CVD may be overkill; you should explore alternatives like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), sputtering, or electroplating.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials: Traditional high-temperature CVD is unsuitable. You must investigate lower-temperature variants like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) to avoid damaging your substrate.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, repeatable manufacturing: Once the process is established, CVD's automation makes it excellent for scalable production where quality and consistency cannot be compromised.
Ultimately, choosing CVD is an investment in precision, granting you atomic-level control over your material's properties where it matters most.
Summary Table:
| Pros of CVD | Cons of CVD |
|---|---|
| High-purity, dense films | High initial equipment cost |
| Uniform, conformal coatings | High operating temperatures |
| Strong chemical bond to substrate | Expensive, hazardous precursors |
| Scalable for mass production | Limited to temperature-resistant substrates |
| No post-deposition curing needed | Complex safety and handling requirements |
Need a high-performance CVD solution tailored to your unique requirements? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including our specialized CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we can precisely meet your experimental and production needs, whether you're working with semiconductors, MEMS, or optical coatings. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your thin film deposition process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the main components of a PECVD system? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma enhanced CVD work? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection



















