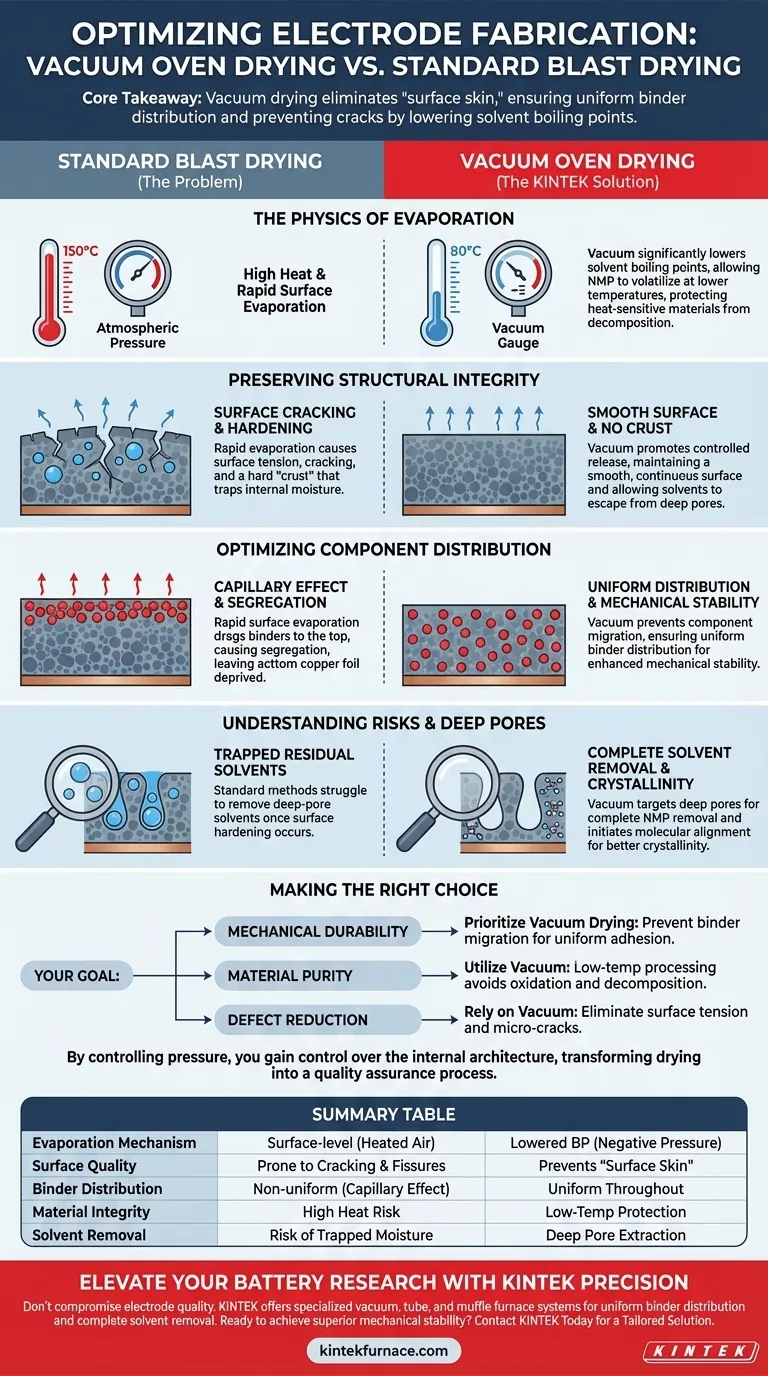
Vacuum drying significantly optimizes electrode fabrication by utilizing negative pressure to lower the boiling point of solvents like NMP. This allows for rapid volatilization at reduced temperatures, ensuring solvents are removed efficiently without subjecting the slurry to excessive heat that could damage the material structure.
Core Takeaway The fundamental advantage of vacuum drying over standard blast drying is the elimination of the "surface skin" effect. By lowering the boiling point, vacuum ovens allow solvents to escape from deep within the slurry pores before the surface hardens, ensuring uniform binder distribution and preventing structural cracking.

The Physics of Low-Temperature Evaporation
Lowering Solvent Boiling Points
By reducing the pressure within the chamber, a vacuum oven significantly lowers the boiling point of solvents. This allows thick solvents like N-Methyl-2-pyrrolidone (NMP) to volatilize rapidly at temperatures much lower than their standard atmospheric boiling points.
Protecting Heat-Sensitive Materials
This low-temperature capability is critical for handling heat-sensitive chemical substances. It allows for thorough drying without reaching temperatures that would cause the active materials to decompose or oxidize, preserving the chemical integrity of the electrode.
Preserving Structural Integrity
Preventing Surface Cracking
Standard blast drying often causes rapid evaporation at the surface layer. This creates surface tension that can lead to cracking or fissures in the electrode coating. Vacuum drying promotes a more controlled release of volatiles, maintaining a smooth, continuous surface.
Eliminating Surface Hardening
In atmospheric conditions, rapid drying can form a hard "crust" on the slurry surface while the interior remains wet. This phenomenon, known as surface hardening, traps internal moisture and solvents inside the sample. Vacuum environments prevent this crust formation, allowing solvents to escape freely from deep within the material.
Optimizing Component Distribution
Halting the Capillary Effect
A critical advantage of vacuum drying is the prevention of the capillary effect, where rapid surface evaporation drags liquid and dissolved components toward the outer surface. This migration leads to component segregation, where binders or additives pool at the top rather than staying uniformly distributed.
Ensuring Mechanical Stability
By preventing component migration, the vacuum process ensures a uniform distribution of the binder between the active material and the copper foil current collector. This directly correlates to enhanced mechanical stability, ensuring the electrode does not delaminate during battery assembly or operation.
Understanding the Risks of Standard Drying
The Danger of Residual Solvents
Standard drying methods struggle to remove solvents trapped in deep pores once surface hardening occurs. Vacuum drying specifically targets these deep pores, ensuring the complete removal of residual NMP, which is vital for proper electrochemical performance.
Impact on Crystallinity
Proper solvent removal is not just about cleanliness; it affects the material's internal structure. The vacuum process initiates the molecular alignment of organic components, providing a critical foundation for enhancing the material's crystallinity in subsequent processing stages.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the performance of your electrode slurries, align your drying strategy with your specific quality metrics:
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability: Prioritize vacuum drying to prevent binder migration (segregation), ensuring the active material adheres uniformly to the current collector.
- If your primary focus is material purity: Utilize the vacuum's low-temperature capabilities to ensure complete NMP removal without triggering oxidation or thermal decomposition.
- If your primary focus is defect reduction: Rely on vacuum processing to eliminate the surface tension and hardening that cause micro-cracks in the electrode layer.
By controlling pressure, you gain control over the internal architecture of your electrode, transforming a simple drying step into a critical quality assurance process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Drying | Standard Blast Drying |
|---|---|---|
| Evaporation Mechanism | Lowered boiling point via negative pressure | Surface-level evaporation via heated air |
| Surface Quality | Prevents "surface skin" and cracking | Prone to surface hardening and fissures |
| Binder Distribution | Uniform throughout the slurry | Non-uniform due to capillary effect migration |
| Material Integrity | Low-temperature processing protects structure | High heat risk for sensitive components |
| Solvent Removal | Deep pore extraction of residual NMP | Risk of trapped internal moisture/solvents |
Elevate Your Battery Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let surface defects or binder segregation compromise your electrode quality. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized vacuum, tube, and muffle furnace systems designed to optimize your drying processes. Whether you need a standard solution or a customized system for unique material needs, our high-temperature lab furnaces ensure uniform binder distribution and complete solvent removal.
Ready to achieve superior mechanical stability in your electrodes?
Contact KINTEK Today for a Tailored Solution
Visual Guide
References
- Hong Shang, Bing Sun. Activated Carbon from Spartina alterniflora and Its N-Doped Material for Li-Ion Battery Anode. DOI: 10.3390/nano15090658
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering and Brazing Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a vacuum pyrolysis furnace in lunar ceramic 3D printing? High-Precision Debinding Solutions
- What maintenance advantages do multiple-chamber vacuum furnaces offer? Boost Uptime and Extend Lifespan
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary during the SPS of CoCrFeMnNi alloy powders? Ensure Purity and Density
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum sintering furnace for MgO? Unlock Density and Optical Clarity
- What are some everyday products manufactured using vacuum furnaces? Discover the Hidden Tech in Your Tools and Devices
- Why is repeated flipping and remelting required in vacuum arc furnaces? Achieving Uniform Refractory Alloy Ingots
- What is the purpose of using a vacuum oven in two-step magnesium sintering? Ensure Pore Integrity & Prevent Oxidation
- Why is a vacuum drying oven essential for LLTO solid electrolytes? Ensure High-Purity Battery Material Processing



















