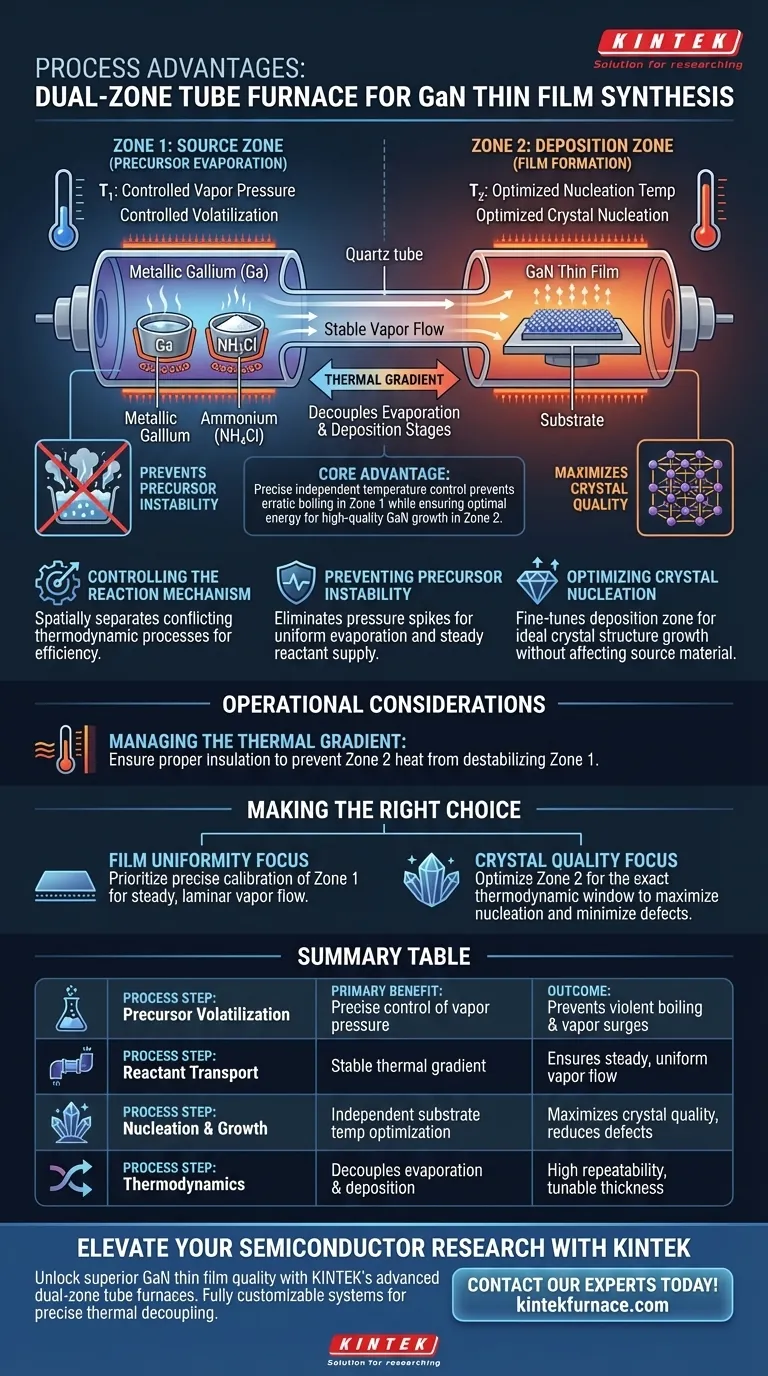
The specific process advantage of a dual-zone tube furnace lies in its ability to decouple the precursor evaporation stage from the film formation stage. By utilizing independent heating zones, you can precisely control the volatilization rate of source materials—specifically metallic gallium and ammonium chloride—while simultaneously maintaining a completely different, optimal temperature at the substrate for high-quality film deposition.
A dual-zone configuration solves the thermodynamic conflict between source material stability and crystal growth. It creates a controlled thermal gradient that prevents erratic boiling of precursors while ensuring the substrate remains at the precise energy level required for Gallium Nitride (GaN) nucleation.

Controlling the Reaction Mechanism
To achieve high-quality GaN thin films, you must manage two distinct thermodynamic processes that often require conflicting temperatures. A dual-zone furnace addresses this by spatially separating these processes.
Decoupling Volatilization from Deposition
In a single-zone system, the source material and the substrate are often exposed to similar thermal conditions. This is inefficient for GaN synthesis.
A dual-zone system allows you to set a lower temperature for the source zone to control the vapor pressure of the precursors. Simultaneously, you can set a higher temperature in the deposition zone to facilitate the chemical reaction on the substrate.
Preventing Precursor Instability
A critical challenge in GaN synthesis is the behavior of ammonium chloride. If exposed to excessive heat too quickly, this precursor tends to undergo violent boiling.
Violent boiling results in erratic surges of vapor, leading to uneven film thickness and poor structural quality.
By programming the first heating zone specifically for the precursors, you ensure a controlled, uniform evaporation. This eliminates pressure spikes and ensures a steady supply of reactant gas to the substrate.
Optimizing Crystal Nucleation
Once the stable vapor reaches the substrate, the focus shifts to crystallization. The deposition zone requires a specific thermodynamic environment to encourage nucleation—the initial step of crystal growth.
If the substrate is too cool, the reaction may not occur; if it is too hot, the film may re-evaporate or degrade.
Independent control allows you to fine-tune this zone exclusively for the crystal structure of the GaN film, without worrying about how that heat affects the source material upstream.
Operational Considerations
While the dual-zone furnace offers superior control, it introduces variables that must be managed to ensure success.
Managing the Thermal Gradient
The benefit of this system relies entirely on the temperature gradient between the two zones.
You must ensure that the transition between the source zone and the deposition zone is managed correctly. If the zones are too close or the insulation is poor, heat from the deposition zone can bleed into the source zone, destabilizing the precursor evaporation rate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a dual-zone configuration is largely driven by the specific quality requirements of your thin film.
- If your primary focus is Film Uniformity: Prioritize the precise calibration of the first zone to prevent ammonium chloride boiling, ensuring a steady, laminar flow of vapor.
- If your primary focus is Crystal Quality: Focus your optimization on the second zone to find the exact thermodynamic window that maximizes GaN nucleation and minimizes defects.
By leveraging independent temperature zones, you transform a chaotic chemical reaction into a tunable, repeatable manufacturing process.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Primary Benefit of Dual-Zone Control | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Precursor Volatilization | Precise control of ammonium chloride vapor pressure | Prevents violent boiling and vapor surges |
| Reactant Transport | Stable thermal gradient maintenance | Ensures steady, uniform vapor flow to substrate |
| Nucleation & Growth | Independent substrate temperature optimization | Maximizes crystal quality and reduces film defects |
| Thermodynamics | Decouples evaporation and deposition stages | High repeatability and tunable film thickness |
Elevate Your Semiconductor Research with KINTEK
Unlock superior GaN thin film quality with KINTEK’s advanced dual-zone tube furnaces. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific research or production requirements. Our dual-zone technology provides the precise thermal decoupling necessary to eliminate precursor instability and maximize crystal nucleation.
Ready to transform your GaN synthesis into a repeatable, high-yield process?
Contact our technical experts today to discuss your unique needs and explore our customizable high-temperature solutions.
Visual Guide
References
- Olzat Toktarbaiuly, Г. Сугурбекова. ENHANCEMENT OF POWER CONVERSION EFFICIENCY OF DYE-SENSITIZED SOLAR CELLS VIA INCORPORATION OF GAN SEMICONDUCTOR MATERIAL SYNTHESIZED IN HOT-WALL CHEMICAL VAPOR DEPOSITION FURNACE. DOI: 10.31489/2024no4/131-139
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Magnesium Extraction and Purification Condensing Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes a vertical tube furnace easy to operate? Discover Intuitive Automation for Precision Heating
- What are the common applications of a horizontal tube furnace? Unlock Precision in High-Temperature Processing
- What safety precautions should be followed when operating a multi zone tube furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Lab Operations
- What materials and processes is an atmosphere tube furnace suitable for? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment Solutions
- How is solid-gas phase conversion achieved in a tube furnace? Master Fe-CoP/CW Catalyst Phosphatization
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace contribute to the pre-carbonization of biomass? Optimize Carbon Yield Today
- What are the common applications of tube furnaces in laboratories? Discover Versatile High-Temperature Solutions
- What are the key features and advantages of tube furnaces? Precision Control for High-Temp Materials Processing



















