At its core, a horizontal tube furnace is used for a range of high-temperature material processing applications, including annealing, chemical synthesis, material testing, and heat treatment. Its specific design, featuring a cylindrical chamber, makes it uniquely effective for tasks requiring exceptional temperature uniformity and precise atmospheric control over a linear area.
The primary value of a horizontal tube furnace isn't just its ability to generate high heat. Its true strength lies in creating an extremely uniform and controllable environment, making it the definitive tool for processes where consistency, atmospheric purity, and easy sample access are non-negotiable.

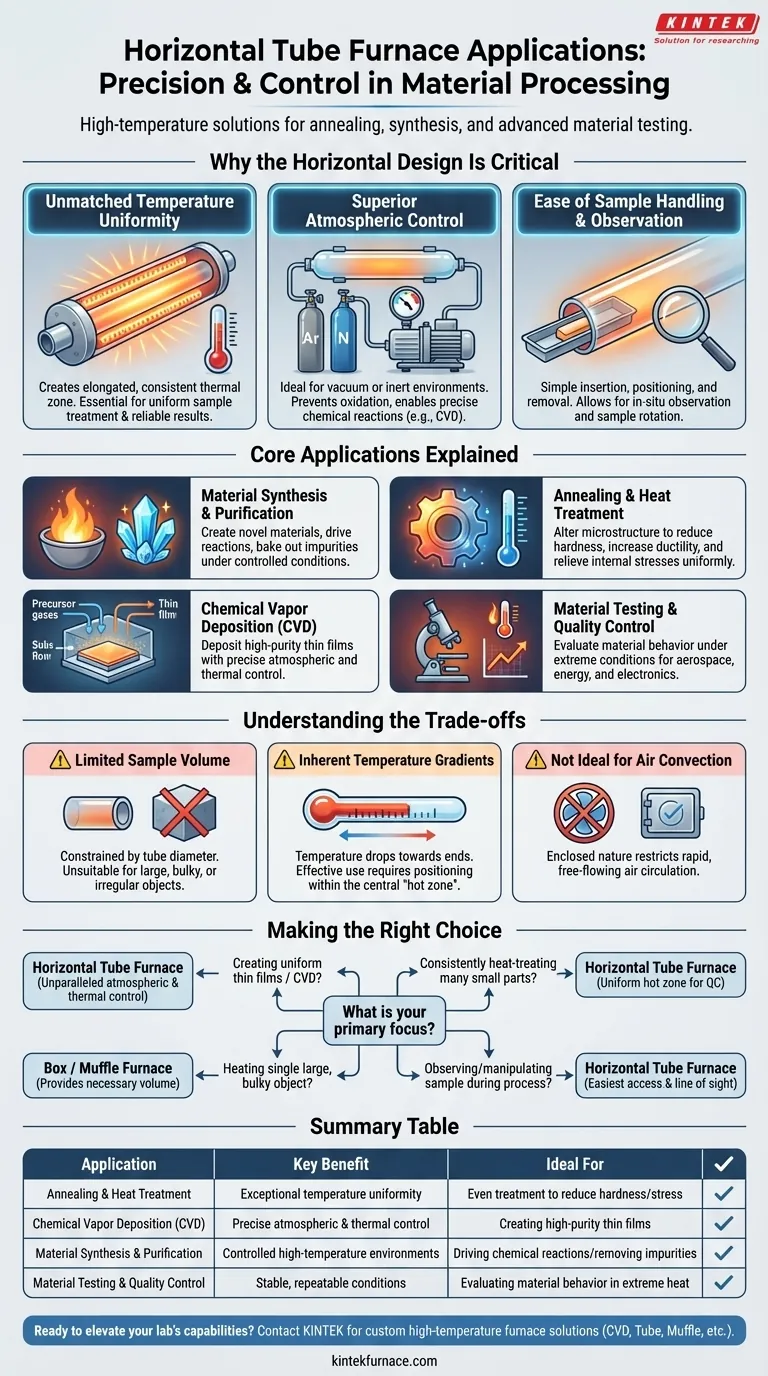
Why the Horizontal Design Is Critical
The specific applications of a horizontal tube furnace are a direct result of its fundamental design advantages. Understanding these principles is key to knowing when to use one.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
A horizontal tube furnace's heating elements surround the process tube, creating an elongated and highly consistent thermal zone. This ensures that the entire length of a sample receives virtually the same thermal treatment.
This uniformity is critical for research and quality control, where slight temperature variations could invalidate results or create defects in a material.
Superior Atmospheric Control
The sealed tube design is ideal for modifying the processing environment. It can be easily evacuated to create a vacuum or filled with inert gases like argon or nitrogen to prevent oxidation and unwanted reactions.
This capability is essential for processing sensitive materials and for enabling specific chemical reactions, such as those required for Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Ease of Sample Handling and Observation
The horizontal orientation provides the simplest method for inserting, positioning, and removing samples, which are typically held in "sample boats."
This straightforward access is invaluable for experiments that require observation during the heating process or involve frequent sample changes. Some systems even allow for sample rotation to further improve uniformity.
Core Applications Explained
The design principles of a horizontal tube furnace make it the standard for several critical scientific and industrial processes.
Material Synthesis and Purification
These furnaces are used to synthesize novel materials or purify existing ones. High heat can be used to drive chemical reactions or to bake out volatile impurities from a sample under a vacuum or inert gas flow.
Annealing and Heat Treatment
Annealing involves heating a material to alter its microstructure, often to reduce hardness, increase ductility, and relieve internal stresses. The exceptional temperature uniformity of a tube furnace ensures the entire part is treated evenly, preventing weak spots.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is a process where precursor gases react within the hot zone to deposit a high-purity thin film onto a substrate. A horizontal tube furnace provides the two most critical conditions for this process: a stable, uniform temperature and precise control of the reactive gas atmosphere.
Material Testing and Quality Control
Engineers and scientists use these furnaces to test how materials behave under extreme heat and in specific atmospheres. This is vital for qualifying components for high-performance applications in aerospace, energy, and electronics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, the horizontal tube furnace is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is just as important as knowing its strengths.
Limited Sample Volume
The primary constraint is the diameter of the process tube. While ideal for small components, wires, powders, or wafers, a tube furnace is unsuitable for heating large, bulky, or irregularly shaped objects. For those tasks, a box furnace is a more appropriate choice.
Inherent Temperature Gradients
Although a furnace has a uniform "hot zone" in its center, the temperature will naturally drop off toward the ends of the tube. Effective use requires careful positioning of the sample within this optimal zone to ensure it receives the intended thermal exposure.
Not Ideal for Air Convection
The enclosed nature of the tube, perfect for controlled atmospheres, makes it unsuitable for processes that require rapid or free-flowing air circulation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing tool depends entirely on your objective. Use these guidelines to make a clear decision.
- If your primary focus is creating uniform thin films or coatings: A horizontal tube furnace is the industry standard due to its unparalleled atmospheric and thermal control.
- If your primary focus is consistently heat-treating many small, identical parts: The long, uniform hot zone ensures that every sample receives the same treatment, making it ideal for quality control.
- If your primary focus is heating a single large, bulky, or irregularly shaped object: A box or muffle furnace provides the necessary volume and is a far more practical choice.
- If your primary focus is observing or manipulating a sample during processing: The horizontal layout offers the easiest access and best line of sight for in-situ experimental work.
Understanding these core capabilities allows you to select not just a piece of equipment, but the right process for achieving reliable and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing and Heat Treatment | Exceptional temperature uniformity | Even treatment of materials to reduce hardness and stress |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Precise atmospheric and thermal control | Creating high-purity thin films on substrates |
| Material Synthesis and Purification | Controlled high-temperature environments | Driving chemical reactions or removing impurities |
| Material Testing and Quality Control | Stable, repeatable conditions | Evaluating material behavior in extreme heat and atmospheres |
Ready to elevate your lab's capabilities with a custom high-temperature furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs for applications in material synthesis, annealing, CVD, and quality control. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can enhance your research and industrial processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















