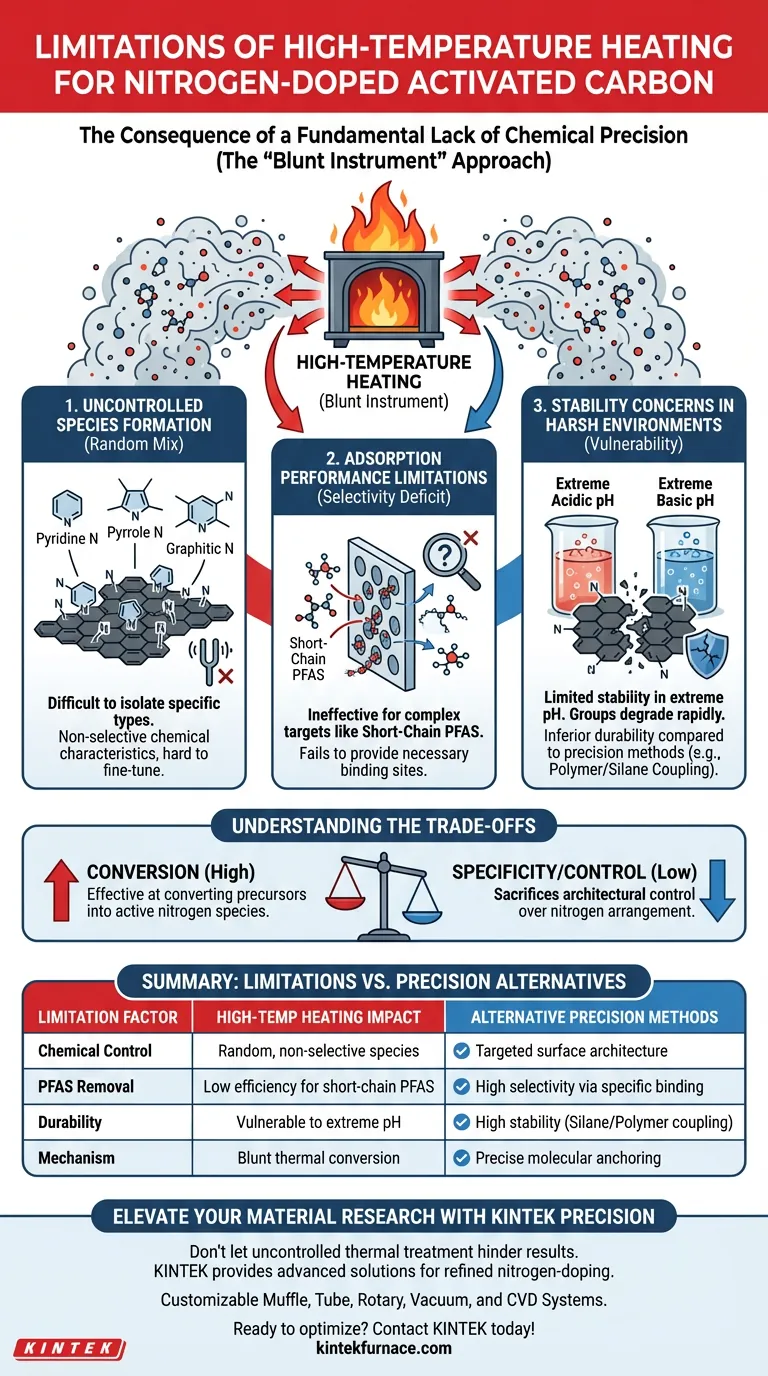
The primary limitation of functional group grafting through high-temperature heating is a fundamental lack of chemical precision. While this method effectively converts nitrogen precursors into active species, it creates a random distribution of functional groups rather than a targeted surface architecture. This lack of control compromises both the selectivity required for specific contaminants and the material's physical stability in harsh environments.
High-temperature heating acts as a "blunt instrument," creating a non-selective mix of nitrogen species that struggles to capture difficult contaminants like short-chain PFAS and fails to maintain stability under extreme pH conditions.
The Consequence of Uncontrolled Species Formation
A Mix of Nitrogen Types
High-temperature heating drives the conversion of precursors into various active nitrogen species.
The resulting surface typically contains a blend of pyridine, pyrrole, and graphitic nitrogen.
The Lack of Tunability
Because these species are generated simultaneously through thermal treatment, it is difficult to isolate or maximize one specific type.
This results in a surface with non-selective chemical characteristics, making it difficult to fine-tune the material for specific adsorption mechanisms.
Limitations in Adsorption Performance
The Selectivity Deficit
The most critical performance drawback is the material's inability to preferentially adsorb specific targets.
Without precise functionalization, the activated carbon lacks the specific adsorption preference needed for complex water treatment scenarios.
Ineffectiveness Against Short-Chain PFAS
This limitation is particularly evident when targeting short-chain PFAS.
These contaminants are notoriously difficult to capture, and the broad, non-specific surface created by high-temperature heating often fails to provide the necessary binding sites for them.
Stability Concerns in Harsh Environments
Vulnerability to pH Extremes
Surfaces modified via high-temperature heating demonstrate limited stability when exposed to extreme chemical conditions.
If the application involves highly acidic or basic (extreme pH) environments, the functional groups may degrade or lose efficacy more rapidly than those created by other methods.
Comparison to Precision Methods
When compared to polymer coating or silane coupling, high-temperature heating yields inferior durability.
Precision methods anchor functional groups more securely, ensuring the material retains its properties over time, whereas thermally grafted surfaces are more susceptible to environmental stress.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Specificity vs. Conversion
While high-temperature heating is effective at converting precursors into active nitrogen species, it sacrifices architectural control.
You gain a nitrogen-doped surface, but you lose the ability to dictate exactly how those nitrogen atoms are arranged to interact with pollutants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Depending on your specific application requirements, the limitations of high-temperature heating may necessitate alternative strategies.
- If your primary focus is general nitrogen doping: High-temperature heating is sufficient to generate a mix of active species like pyridine and pyrrole.
- If your primary focus is targeting short-chain PFAS: You should avoid simple thermal grafting and opt for precise methods like polymer coating or silane coupling to ensure specific adsorption preferences.
- If your primary focus is operational longevity in extreme pH: Choose more robust functionalization techniques like silane coupling to prevent surface degradation.
Select the functionalization method that aligns with the specific contaminant you must capture, rather than defaulting to thermal treatment.
Summary Table:
| Limitation Factor | High-Temperature Heating Impact | Alternative Precision Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Control | Random, non-selective nitrogen species | Targeted surface architecture |
| PFAS Removal | Low efficiency for short-chain PFAS | High selectivity via specific binding |
| Durability | Vulnerable to extreme pH conditions | High stability (Silane/Polymer coupling) |
| Mechanism | Blunt thermal conversion | Precise molecular anchoring |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let the limitations of uncontrolled thermal treatment hinder your laboratory results. KINTEK provides the advanced high-temperature heating solutions and specialized CVD systems needed to refine your nitrogen-doping processes. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to give you the thermal control required for even the most demanding lab applications.
Ready to optimize your carbon functionalization? Contact KINTEK today to find the perfect customizable furnace for your unique research needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Md Manik Mian, Shubo Deng. Recent advances in activated carbon driven PFAS removal: structure-adsorption relationship and new adsorption mechanisms. DOI: 10.1007/s11783-025-1998-3
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is precise preheating in an industrial oven necessary for RAP? Ensure Accurate Characterization & Recycling
- What role does the high-temperature boiling step play in rice husk silica conversion? Boost Your Extraction Yields
- How does a vacuum environment influence the accuracy of thermoelectric performance measurements for TaAs2? Ensure Precision in Your Research
- What is the purpose of performing high-temperature thermal treatment for BSnO thin films? Boost Device Sensitivity
- What are the core process advantages of an infrared image heating furnace? Unlock Rapid 1000°C/min Thermal Control
- Why are c-Si wafers with pyramid structures chosen for MoS2 solar cells? Boost Efficiency with Light Trapping
- How does a rotating substrate holder contribute to the quality of CuGaO2 thin films? Achieve Uniformity in Sputtering
- Why is a cycle of secondary grinding and re-sintering employed in BiCuSeO preparation? Achieve Peak Material Density



















